Applications of Parallel Processing in AI Circuits
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Deep Learning and Neural Networks
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to dive into the application of parallel processing in deep learning, particularly how it affects neural networks. Why do you think such a hefty computational task is necessary?

Is it because neural networks need to handle large amounts of data?

Exactly! Deep neural networks require efficient handling of vast datasets for training, involving many computations. So, what kind of hardware do you think is best for this?

Are GPUs used for that purpose?

Yes! GPUs excel at parallel processing, allowing operations on thousands of data points at once, which is essential for tasks like matrix multiplications. Remember the acronym 'GPU' — **G**raphics **P**rocessing **U**nit.

So, does that mean using GPUs can speed up the model training process significantly?

Absolutely! Parallel processing with GPUs makes learning faster. Quick recap: GPUs aid in handling large datasets for deep learning effectively.
Large-Scale Data Processing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s shift our focus to large-scale data processing. What do you think are some challenges AI systems face with huge datasets?

I think managing and processing all that data can be complex and slow.

You’re spot on! That's where parallel processing comes to the rescue. Would anyone have an idea how data is managed in parallel settings?

I believe data can be split into smaller parts and processed simultaneously?

Correct! This method allows AI circuits to efficiently manage large datasets. A key concept here is 'distributed computing.' Can anyone explain what that entails?

It's where the dataset is spread across multiple machines, each handling a piece, right?

Exactly! Distributing datasets is crucial to handle large volumes efficiently. Remember, breaking down complex datasets is key. Great job, everyone!
Real-Time Inference
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s discuss real-time inference. Why do you think low-latency decision-making is critical in AI?

In applications like robotics or self-driving cars, quick decisions are essential to respond to the environment.

Excellent point! Parallel processing enhances these capabilities. Can someone explain how edge AI fits into this picture?

Edge AI runs models on local devices instead of sending data to the cloud for processing.

Great observation! This reduces latency by performing inference closer to the data source. As a takeaway: fast processing leads to efficient real-time applications.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Parallel processing is vital for modern AI systems, providing the necessary computational power to train models, process large datasets, and enable quick decision-making. The section highlights applications, particularly in deep learning, image processing, and real-time inference, emphasizing hardware optimizations such as GPUs and distributed computing.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
Parallel Processing plays a foundational role in enhancing the efficiency and performance of AI systems, especially where significant computational resources are required, such as in deep learning. This section highlights three major applications of parallel processing:
- Deep Learning and Neural Networks: Neural networks, especially deep neural networks (DNNs), rely on intensive computation for training, involving vast datasets, matrix operations, and backpropagation. Parallel processing significantly speeds up these tasks, allowing faster model training and inference. GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) are a prime example of hardware optimized for this purpose, enabling simultaneous operations across thousands of data points.
- Large-Scale Data Processing: AI applications often require the analysis of extensive datasets (e.g., videos and images). Parallel processing architectures efficiently divide these large datasets into smaller subsets for simultaneous processing. Distributed computing allows AI systems to utilize multiple machines, each processing parts of a large dataset, facilitating the handling of data that is too extensive to manage within a single system.
- Real-Time Inference: Applications like autonomous vehicles and robotics necessitate low-latency inference and rapid decision-making. Parallel processing aids this by enhancing computational speeds. Edge AI leverages local devices (smartphones, drones, IoT devices) to conduct inference, minimizing latency by reducing reliance on cloud services.
This section articulately underscores how parallel processing serves as a backbone for key AI applications, transforming immense computational tasks into manageable and efficient processes.
Youtube Videos
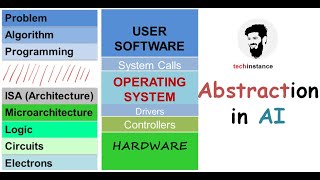

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Deep Learning and Neural Networks
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Neural networks, particularly deep neural networks (DNNs), require significant computational resources for training. Training involves iterating over large datasets, adjusting weights in the network through backpropagation, and performing operations like matrix multiplications. Parallel processing accelerates these tasks, enabling faster model training and more efficient inference.
● GPUs for Parallelism: GPUs are optimized for parallel processing and are widely used in AI applications to perform operations on thousands of data points simultaneously. They are particularly effective for training deep learning models, where each operation in the model (such as multiplying matrices) can be done in parallel.
Detailed Explanation
Deep learning models, especially deep neural networks, need a lot of calculations to learn from data. Training these models means running through large sets of data multiple times and constantly updating the model's parameters. With parallel processing, tasks like adjusting model weights and performing matrix operations can be done much faster. This is achieved using powerful GPUs (Graphics Processing Units), which can handle many calculations at once. Just like an assembly line makes car manufacturing faster by dividing tasks among many workers, parallel processing speeds up the training of AI models.
Examples & Analogies
Think of training a neural network like learning to ride a bicycle. If you're alone, you can only practice one bike at a time. But if you had many bikes and friends to practice with, you could all learn at the same time and faster. Similarly, GPUs allow multiple operations to happen simultaneously, making the training of AI models much quicker.
Large-Scale Data Processing
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
AI systems often require processing large datasets, such as image or video data. Parallel processing architectures enable AI circuits to handle these large-scale datasets efficiently by dividing the data into smaller chunks and processing them simultaneously.
● Distributed Computing: Large-scale AI systems may distribute the dataset across multiple machines in a cluster, where each machine processes a portion of the data. This enables the system to handle datasets that would be too large to fit on a single machine.
Detailed Explanation
AI applications often need to analyze vast amounts of data, like high-resolution images or long videos. Processing all this data on one machine can be slow or even impossible if the dataset is too large. However, parallel processing allows the dataset to be split into smaller pieces, which can be processed at the same time on different machines. This strategy, known as distributed computing, helps manage large datasets efficiently, similar to how a group can finish a big project quicker than just one person working alone.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to clean a huge house all by yourself. It would take a long time! But, if you invited a few friends over and assigned each person a room to clean at the same time, the whole house would be clean much faster. In the same way, distributed computing allows multiple computers to work on a big dataset together.
Real-Time Inference
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In real-time AI applications, such as autonomous vehicles, robotics, and video streaming, low-latency inference is critical. Parallel processing enables faster computation and quicker decision-making, which is essential for real-time operations.
● Edge AI: With edge AI, parallel processing can be used to run AI models directly on devices like smartphones, drones, and IoT devices. These devices perform inference on the data locally, reducing the need for time-consuming communication with the cloud and ensuring faster response times.
Detailed Explanation
In applications where immediate responses are needed, like self-driving cars or real-time video analysis, it’s vital that the system processes data quickly. Parallel processing allows these systems to make decisions faster by computing multiple tasks at once. Edge AI brings this capability closer to the user by deploying AI models on local devices instead of relying on a distant server, thus reducing latency and ensuring quicker responses.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a police officer in a fast-paced situation who needs to make split-second decisions. If they rely on a radio to get updates from a distance, it might take too long. However, if they have an onboard computer that processes data in real-time, they can react much faster. Similarly, edge AI allows devices to analyze data instantly, leading to quicker reactions in critical situations.
Key Concepts
-
Parallel Processing: Critical for AI applications due to the simultaneous execution of multiple computations.
-
Deep Learning: Requires substantial computational power for training models effectively.
-
GPUs: Hardware that excels in parallel processing, particularly useful in AI applications.
-
Distributed Computing: Allows for efficient processing of large datasets by utilizing multiple machines.
-
Real-Time Inference: Essential for applications requiring quick decision-making.
Examples & Applications
Training a deep learning model on image data using GPUs to speed up matrix multiplications.
Distributing a video dataset across a cloud cluster for simultaneous processing of frames.
Using edge computing in autonomous vehicles to make real-time decisions based on sensor data.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Parallel processing, tasks in a race, simultaneous computing, set a fast pace.
Stories
Imagine a chef in a kitchen preparing a feast. Instead of making one dish at a time, he delegates tasks to his sous chefs, each working simultaneously. This efficiency transforms the kitchen into a hub of productivity, much like parallel processing optimizes tasks in AI.
Memory Tools
Remember the acronym 'D-G-R' for Deep learning, GPUs, and Real-time inference as the key aspects of parallel processing in AI.
Acronyms
Use the acronym 'DLA' - Deep learning, Large-scale data processing, and Real-time inference to recall the main applications in AI.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Parallel Processing
The simultaneous execution of multiple computations to enhance performance and efficiency.
- Deep Learning
A subset of machine learning involving neural networks with many layers, used for complex data processing.
- GPU
Graphics Processing Unit, a type of hardware optimized for parallel processing, especially in graphics and neural network operations.
- Distributed Computing
A method of computing where a task is divided across multiple systems or machines for processing.
- RealTime Inference
The capability of a system to provide immediate processing and decision-making based on input data.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
