Principles of Parallel Processing Architectures
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Single Instruction, Multiple Data (SIMD)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to learn about SIMD, which stands for Single Instruction, Multiple Data. This means that one instruction is applied to multiple data points at the same time. Can anyone think of where this might be useful?

I think it's used in image processing, right? Like applying filters to all pixels at once?

Exactly, Student_1! In deep learning, it's very common for matrix multiplications to be performed using SIMD. This allows us to handle large datasets efficiently. Remember, SIMD is like a 'single chef cooking the same dish for multiple guests'!

So, with SIMD, we can process multiple pieces of data really quickly, right?

Yes, that's right! It makes operations like training neural networks much faster. Now, what could be a limitation of this approach?

Maybe it can't handle different tasks at the same time?

Great observation, Student_3! SIMD is powerful for uniform tasks but struggles with varied tasks. Let’s recap: SIMD executes one instruction on multiple data points simultaneously and is great for tasks like image processing.
Multiple Instruction, Multiple Data (MIMD)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's switch gears and discuss MIMD, which stands for Multiple Instruction, Multiple Data. This is where different instructions are applied to different data simultaneously. Who can give an example of where this might be used in AI?

Maybe in an AI system that does both image recognition and language processing?

Exactly, Student_4! In such a system, one processor might handle image data while another one manages text data. This is why MIMD is considered more flexible than SIMD. Can anyone tell me how MIMD helps in complex AI applications?

It lets them run different types of tasks at the same time, which is really powerful!

Correct! MIMD can concurrently perform various tasks, which is essential for handling the complexity of modern AI systems. Lastly, remember, MIMD is like a 'team of chefs, each preparing a different dish' for an elaborate banquet!
Data Parallelism vs. Task Parallelism
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's clarify the concepts of data parallelism versus task parallelism. Who knows what data parallelism involves?

I think it's when the same operation is performed on different pieces of data?

Correct! Data parallelism spreads the same task across multiple processors for different data subsets. Can anyone give an example?

It’s like when we do matrix multiplication in deep learning, where each processor works on a different part of the matrix!

Exactly! Now, how about task parallelism? What distinguishes it?

That's when different tasks or functions are distributed across processors!

Exactly! Task parallelism allows different components like data preprocessing and inference to run concurrently, enhancing efficiency in AI systems. Remember, data parallelism is focused on 'same task, different data' while task parallelism is 'different tasks, same time.'
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section details the two main models of parallel processing architectures: Single Instruction, Multiple Data (SIMD) and Multiple Instruction, Multiple Data (MIMD). It discusses how these models apply to AI, especially in tasks like deep learning and image processing, as well as the difference between data parallelism and task parallelism.
Detailed
Principles of Parallel Processing Architectures
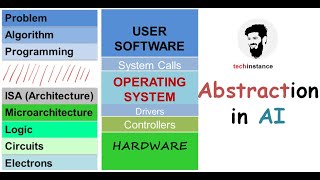
Parallel processing architectures divide computational tasks into smaller, independent subtasks that can be processed simultaneously. The two main models are:
- Single Instruction, Multiple Data (SIMD): In this architecture, a single instruction is executed on multiple data points simultaneously. This makes it particularly suitable for applications where the same operation is performed on many pieces of data, such as in matrix multiplications within deep learning.
- Multiple Instruction, Multiple Data (MIMD): This model allows different processors to execute different instructions on different data. MIMD is more flexible compared to SIMD as it can handle various tasks concurrently, making it ideal for complex AI applications.
The section also distinguishes between Data Parallelism, which involves distributing similar tasks across processing units, and Task Parallelism, where different tasks are distributed among multiple processors, allowing for efficient execution of diverse operations in AI systems. Understanding these principles is crucial for effectively designing and implementing parallel architectures in artificial intelligence.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Parallel Processing Architectures
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Parallel processing architectures are based on the idea of dividing a computational task into smaller, independent subtasks that can be processed simultaneously.
Detailed Explanation
Parallel processing architectures help improve computational efficiency by breaking down complex tasks into smaller, manageable parts. Each subtask can operate concurrently, meaning multiple tasks can be completed at once rather than sequentially. This approach is essential in fields like AI, where extensive computations occur.
Examples & Analogies
Think of parallel processing like a team of chefs in a kitchen. Instead of one chef making an entire meal by themselves (which takes a lot of time), each chef is assigned a specific task, like chopping vegetables, boiling pasta, or grilling meat. As each chef works on their part simultaneously, the meal is prepared more quickly than if just one person was cooking.
Single Instruction, Multiple Data (SIMD)
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In the SIMD architecture, a single instruction is applied to multiple data elements simultaneously. This model is particularly effective in AI applications, such as image processing, matrix operations, and vector computations, where the same operation must be performed on many pieces of data at once.
Detailed Explanation
SIMD allows a single operation to be applied across multiple data points at once. For instance, if you want to adjust the brightness of every pixel in an image, using SIMD means you can apply the brightness adjustment to all pixels simultaneously rather than adjusting them one by one, significantly speeding up processing times.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a factory where the same item is produced in large quantities. Using SIMD is like having one machine that can make 100 toys at once instead of having 100 machines making one toy each. This efficiency allows for faster and more effective production.
Multiple Instruction, Multiple Data (MIMD)
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In MIMD architectures, different processors execute different instructions on different pieces of data. MIMD architectures provide more flexibility than SIMD because they can perform a variety of tasks concurrently, making them ideal for complex AI applications that require handling different types of operations simultaneously.
Detailed Explanation
MIMD enables various processors to carry out different tasks at the same time. While one processor could be analyzing images, another could be processing textual data. This flexibility allows AI systems to tackle more complex activities that cannot be handled by a single type of operation alone.
Examples & Analogies
Think of MIMD as a sports team where each player has a specific role. While one player defends, another attacks, and a third assists. Each player is doing a different task, but they work together simultaneously to win the game, just as different processors work on different tasks in an AI system.
Data Parallelism vs. Task Parallelism
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Data Parallelism: This involves distributing the data across multiple processing units. Each unit performs the same task on different subsets of the data. Data parallelism is widely used in deep learning for operations such as matrix multiplications, convolutions in CNNs, and data loading during training. Task Parallelism: This involves distributing different tasks (or functions) across multiple processors. Task parallelism is useful in AI systems where different components, such as data preprocessing, training, and inference, can be executed concurrently.
Detailed Explanation
Data parallelism focuses on dividing a dataset among various processors where each processor performs the same operation on its data. This approach is commonly used in deep learning. On the other hand, task parallelism distributes different tasks across processors, allowing diverse operations to run concurrently—not just the same operation on different data. Both methods enhance efficiency in AI applications.
Examples & Analogies
Data parallelism can be likened to a school exam where every student answers the same questions separately but simultaneously. Task parallelism, however, is like a school project where different students work on various parts of the project at the same time, each contributing uniquely to the overall completion.
Key Concepts
-
Single Instruction, Multiple Data (SIMD): Architecture where one instruction is applied to multiple data inputs.
-
Multiple Instruction, Multiple Data (MIMD): Architecture allowing different instructions to be processed on different data.
-
Data Parallelism: Distributing the same computational task across multiple processors for different datasets.
-
Task Parallelism: Distributing different tasks among multiple processors to enhance efficiency.
Examples & Applications
In SIMD, matrix operations in deep learning apply the same multiplication across all elements at once.
In MIMD, an AI system could perform image recognition on one processor while handling text analysis on another.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
SIMD runs fast, with one instruction cast, while MIMD does many, keeping tasks diverse and plenty.
Stories
Imagine a restaurant where one chef (SIMD) is cooking the same dish for a large crowd in a short time, while another restaurant has multiple chefs (MIMD) each making different meals, catering to a party's varied tastes.
Memory Tools
For remembering SIMD and MIMD, think 'Same Instruction, Multiple Dishes' for SIMD; 'Multiple Instructions, Many Different Dishes' for MIMD.
Acronyms
SIMD
for Single
for Instruction
for Multiple
for Data - apply the same instruction to many data points.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- SIMD
Single Instruction, Multiple Data; a parallel processing architecture where a single instruction is applied to multiple data elements simultaneously.
- MIMD
Multiple Instruction, Multiple Data; a parallel processing architecture where different processors execute different instructions on different data.
- Data Parallelism
A form of parallel processing where similar tasks are distributed across multiple processors acting on different data subsets.
- Task Parallelism
A form of parallel processing where different tasks or functions are distributed across multiple processors.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
