Conclusion
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Importance of Parallel Processing in AI
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’ll explore why parallel processing architectures are crucial for AI applications. They allow many computations to occur simultaneously.

What do you mean by simultaneous computations?

Good question! It means that instead of performing one task after another, multiple tasks, like training neural networks with different data subsets, can happen at the same time.

That sounds efficient! But are there any challenges to that?

Absolutely. Challenges like synchronization overhead can arise when multiple processors communicate to ensure data consistency.

What about handling large datasets? Are there specific strategies for that?

Great insight! Distributing large datasets across processors to parallelize tasks is key, and this ties into load balancing.

Can you recap that for us?

Certainly! Parallel processing is essential for performance and scalability in AI, but it comes with challenges like synchronization overhead, especially when managing tasks and large datasets.
Hardware and Design Considerations
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

When designing parallel processing systems, hardware selection is crucial. Can anyone name some important hardware for parallel processing?

GPUs and TPUs?

Exactly! GPUs are great for deep learning due to their ability to handle many operations at once. TPUs are specifically designed for AI tasks.

What about FPGAs? How do they fit in?

FPGAs offer flexible parallelism, allowing custom logic for specific tasks, which is essential in edge computing. It’s like having a Swiss Army knife for processing!

What design considerations should we keep in mind?

Good point! We have to focus on memory architecture, load balancing, and scalability to ensure everything runs smoothly.

So, summarizing; the right hardware and design factors are crucial for efficient AI processing.

Nicely put! Remember that the balance of hardware, architecture, and the ability to manage load is key to effective parallel processing systems.
Challenges in Implementing Parallelism
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s now talk about the challenges of achieving effective parallelism. What challenges can you think of?

Synchronization issues, right?

Yes, synchronization overhead can slow down processes. As processors communicate, it can be a bottleneck.

I’ve heard of Amdahl's Law. How does that relate?

Great connection! Amdahl’s Law suggests that the speedup of a program using parallel processing is limited by parts of the program that are inherently serial.

And what about power consumption? Is that a big concern?

Absolutely! High-performance hardware like GPUs can be power-hungry, which is a significant consideration for many applications, especially on the edge.

Can you summarize these challenges?

Sure! Key challenges include synchronization overhead, the limitations described by Amdahl's Law, memory bandwidth bottlenecks, and managing power consumption effectively.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The conclusion emphasizes the critical role of parallel processing architectures in realizing the performance and scalability necessary for advanced AI applications. It also briefly touches on the challenges faced in this domain, including synchronization overhead and power consumption, while highlighting necessary design considerations for effective implementation.
Detailed
Conclusion
Parallel processing architectures are vital for modern AI applications, enabling high performance and scalability by distributing computational tasks across multiple processors or cores. These architectures allow for the efficient handling of large datasets, real-time inference, and optimized model training, crucial for applications ranging from deep learning to real-time processing in autonomous systems. However, the journey towards achieving effective parallelism isn’t without its challenges, such as synchronization overhead, memory bandwidth limitations, and power consumption. By carefully selecting hardware, optimizing memory architecture, balancing loads, and ensuring scalability, engineers can design robust parallel processing systems tailored for the demands of next-generation AI applications.
Youtube Videos
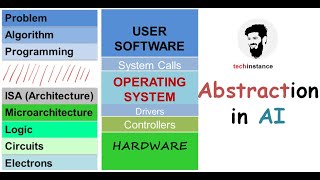

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Importance of Parallel Processing in AI
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Parallel processing architectures are essential for enabling the high performance and scalability required for modern AI applications.
Detailed Explanation
Parallel processing is a method where multiple computations or tasks are executed simultaneously instead of sequentially. This approach is critical for modern AI applications because it helps in managing large amounts of data quickly. For example, when an AI model is being trained, it needs to process millions of data points. Instead of doing this one at a time, parallel processing can divide the work among multiple processors, making the training process much faster and more efficient.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a busy restaurant kitchen. Instead of having one chef cook every meal from start to finish, you have different chefs specializing in different tasks—one for grilling, one for frying, and another for desserts. By working in parallel, they can serve many more customers much faster than if only one chef did everything.
Capabilities of AI Systems
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
By distributing computational tasks across multiple processors or cores, AI systems can handle large datasets, perform real-time inference, and optimize model training.
Detailed Explanation
Distributing tasks means that instead of one processor doing all the work, they share the workload. This allows AI systems not only to process data faster but also to quickly respond to real-time demands, such as in autonomous vehicles that need immediate decisions based on incoming sensor data. Additionally, distributing tasks allows for more efficient model training because different parts of the model can be trained simultaneously, speeding up the process.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a relay race where each runner has a specific segment of the race to run. If each runner takes off at the same time, the team finishes faster than if just one person were to run the entire track. In AI, different processors are like the individual runners, each handling a part of the task to achieve a collective goal more quickly.
Challenges in Parallel Processing
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
However, achieving parallelism in AI circuits comes with challenges such as synchronization overhead, memory bandwidth limitations, and power consumption.
Detailed Explanation
While parallel processing can significantly enhance performance, it isn't without challenges. For instance, synchronization overhead refers to the time lost when processors need to pause and communicate with each other to ensure they are aligned on what they're doing. This can actually slow down the system. Memory bandwidth limitations indicate that if many processors try to access memory at once, there might not be enough bandwidth to accommodate all the requests, causing delays. Lastly, high-performance processors consume substantial energy, which is a critical consideration, especially for battery-operated devices.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a group project in school. If everyone decides to work simultaneously without coordinating, they might end up overlapping tasks, which could lead to confusion or even duplicated efforts. Additionally, if everyone tries to access the same computer to get information at the same time, it might slow down the computer for everyone. It's important to balance teamwork and resource access to maximize efficiency, similar to how parallel processing must manage resources to avoid bottlenecks.
Design Considerations for Efficient Parallel Processing
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
By carefully considering hardware selection, memory architecture, load balancing, and scalability, engineers can design efficient and powerful parallel processing systems that meet the demands of next-generation AI applications.
Detailed Explanation
Designing an efficient parallel processing system requires engineers to make thoughtful choices about the hardware used, how memory is organized, how to distribute workloads evenly across processors, and how to expand the system as demands increase. Each component plays a role in ensuring that computations are carried out quickly and efficiently, leading to better-performing AI applications.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a factory assembly line. If workers are assigned specific tasks without any thought to how the tasks are arranged, some may finish quickly while others might lag, causing delays in production. Designing the assembly line effectively—including which machines to use and how to layout the station—ensures everything runs smoothly and efficiently, just like in parallel processing systems.
Key Concepts
-
Performance: The capability of parallel processing to significantly enhance computational speed and efficiency for AI applications.
-
Scalability: The importance of designing parallel systems that can grow with increasing demand without performance loss.
-
Synchronization Overhead: The potential delays and resource use incurred during communication between processes.
-
Power Consumption: The challenge of managing the energy demands of parallel processing hardware.
Examples & Applications
AI training on deep learning models can utilize GPUs for massive parallelization, leading to faster training times.
Real-time inference in autonomous systems requires low-latency computations, achievable through effective parallel processing architectures.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Parallel tasks run in a line, making AI systems work just fine!
Stories
Imagine a group of friends organizing a party. If they all work simultaneously on different tasks, like sending invites, setting the table, and cooking, the party is prepared much faster!
Memory Tools
Remember 'SCOPE' for challenges in parallel systems: Synchronization, Communication, Overhead, Power, Efficiency.
Acronyms
Remember 'SPICE' for important aspects
Scalability
Power
Integration
Communication
Efficiency.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Parallel Processing
The simultaneous execution of multiple computations or tasks that enhances computational efficiency.
- Synchronization Overhead
The time and resources spent managing communication and coherence between processors in a parallel processing system.
- Amdahl's Law
A formula used to find the maximum improvement of a system when only part of the system is improved.
- Load Balancing
The process of distributing workloads across computing resources to optimize resource use and prevent overload.
- Scalability
The capability of a system to handle a growing amount of work, or its potential to accommodate growth.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
- Parallel Processing - Wikipedia
- Understanding Amdahl's Law
- Introduction to GPUs for AI
- Understanding Load Balancing
- Power Consumption in Parallel Computing
- Scalability in Parallel Computing
- Real-Time Processing in AI
- Tensor Processing Units Overview
- FPGA Basics and Applications
- Challenges in Implementing Parallel Processing
