Scalability
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Scalability
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're diving into scalability in parallel processing systems! Scalability refers to the ability of a system to handle increased loads by augmenting resources. Can anyone tell me why scalability is important for AI?

I think it's important because as AI models grow larger, they need more power to process data!

Exactly, Student_1! A scalable system can adjust to accommodate these growing needs without losing performance. Now, there are two main types of scalability: horizontal and vertical. Can anyone guess what those mean?

Does horizontal scaling mean adding more machines to process data?

Right! Horizontal scaling involves adding more nodes to handle larger workloads. Now, Student_3, can you explain what vertical scaling might involve?

Vertical scaling would mean upgrading existing machines, like getting more powerful GPUs or RAM?

Great explanation! We often use both methods depending on the specific requirements of our AI task. Let's summarize: scalability helps manage increased workload effectively, and we achieve it through horizontal and vertical scaling.
Horizontal Scaling
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s explore horizontal scaling further! Why do you think adding more nodes can improve performance in AI processing?

Adding more nodes means we can divide the workload, so each machine does a part of the processing simultaneously!

Absolutely, Student_4! This distributed approach is particularly effective in large-scale data processing. What are some scenarios you think would benefit from horizontal scaling?

Processing large images or video datasets could benefit because those require a lot of computing power!

Exactly! And large-scale systems can handle tasks that are too big for a single machine. Always remember, **Horizontal Scaling = Adding Nodes**!
Vertical Scaling
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s look at vertical scaling now. Who can remind us what it involves?

It involves making existing machines more powerful, like getting better GPUs with more cores!

That's spot on, Student_2! Vertical scaling lets us enhance performance without the complexity of a distributed system. What do you think could be a downside of relying solely on vertical scaling?

Maybe hardware limits? There's only so much power we can add to a single machine.

Exactly! Vertical scaling has its physical constraints. It's crucial to understand when to scale vertically versus horizontally to maximize efficiency. So remember: **Vertical Scaling = Upgrading Resources**!
Combining Scalability Practices
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand both scaling types, how can we combine them in AI systems for optimal performance?

By using horizontal scaling to add more machines, while making sure each one is powerful enough through vertical scaling!

Excellent thought, Student_4! This mixed approach ensures we have ample power to manage any workload. Can anyone think of an example where both might be applied?

Training a large deep learning model! We could use multiple powerful GPUs in each machine while adding more machines for massive datasets.

Great example! Balancing both scaling strategies leads to remarkable processing capabilities and better resource utilization. Let’s summarize: Combining horizontal and vertical scaling is key to optimizing AI performance!
Reviewing Scalability Concepts
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

As we wrap up our discussion on scalability, can someone remind us what scalability means?

It’s the ability to handle increased workloads as AI systems grow!

Yes! And what are the two main approaches to achieving scalability?

Horizontal scaling adds nodes, while vertical scaling upgrades existing units!

Fantastic! Always remember that both strategies can work together for enhanced performance. Good job, everyone!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses the importance of scalability in parallel processing for AI applications. It highlights horizontal and vertical scaling methods, which allow systems to increase their computational power by adding more nodes or upgrading existing units, respectively.
Detailed
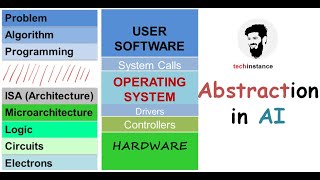
Scalability
Scalability is a crucial aspect of parallel processing systems, especially as the complexity and size of AI models grow. The ability to accommodate increasing data and computational demands is essential for maintaining performance. Scalability can be divided into two main types: horizontal scaling and vertical scaling.
Horizontal Scaling
Horizontal scaling involves adding more nodes or systems to a distributed computing environment. This approach expands computational power by increasing the number of available resources. For instance, when a given AI system cannot handle a dataset due to limits in processing capability, engineers can deploy additional clusters, effectively distributing the workload across multiple systems.
Vertical Scaling
Vertical scaling, on the other hand, refers to upgrading the existing hardware within a system. This could involve enhancing individual processors—like incorporating more cores into GPUs or adding more memory—to boost overall performance. While vertical scaling can improve processing capabilities without changing the architecture, it has its physical limits, making it sometimes less flexible than horizontal scaling.
Importance
Understanding scalability is essential in designing efficient AI systems. As tasks become more demanding, implementing both scaling methods ensures that AI applications remain efficient and effective, leading to improved performance insights, faster processing times, and enhanced capabilities.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Importance of Scalability
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Scalability is critical for parallel processing systems, especially as AI models grow in size and complexity. A scalable system can add more processing units or memory to handle increased data and computational demands without compromising performance.
Detailed Explanation
Scalability refers to the ability of a system to expand and manage growing demands. In the context of parallel processing for AI, as AI models become more complex—processing more data and performing more operations—the system must also grow. This growth can occur in two ways: by adding more units (horizontal scaling) or upgrading existing units (vertical scaling). A scalable system ensures that even as tasks become more demanding, performance remains efficient and effective.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a small coffee shop that starts with one barista. As more customers come in, the owner might first add another barista to speed up service. This is similar to horizontal scaling, where more resources are added to handle increased demand. Eventually, as the shop gets busier, upgrading to a larger espresso machine (vertical scaling) would allow existing staff to operate more efficiently, serving more customers in less time.
Horizontal Scaling
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Horizontal Scaling: This involves adding more nodes to a distributed system to increase computational power.
Detailed Explanation
Horizontal scaling means bringing more 'nodes' into a system. In distributed computing, a node can be understood as an individual computer or server capable of processing data. When the workload increases—say there's more data to analyze or more complex algorithms to apply—adding more nodes allows the workload to be spread among them. This approach can lead to significant increases in computing capacity without altering the existing system architecture drastically.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a delivery service. Initially, one delivery truck can handle deliveries in a small town. But as the service area expands, adding more trucks enables quicker and more efficient delivery. Each truck works independently on different deliveries, which is akin to how horizontal scaling allows tasks to be processed simultaneously by different nodes.
Vertical Scaling
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Vertical Scaling: Vertical scaling involves upgrading individual processing units (e.g., using GPUs with more cores or adding more memory to a system).
Detailed Explanation
Vertical scaling is about enhancing the capacity of existing machines rather than adding new ones. When a server is upgraded—say, by adding more processors or increasing its RAM—this can lead to improved performance without needing to invest in additional hardware. This type of scaling is often limited by the maximum capacity of the current system components but can provide substantial performance boosts for specific tasks.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a personal computer. If a student starts needing more power for gaming or video editing, they might choose to replace their existing graphics card with a more powerful one or add more RAM. This process of upgrading existing components is analogous to vertical scaling, where capabilities are improved without expanding the overall system.
Key Concepts
-
Scalability: The ability of a system to manage increased workload effectively.
-
Horizontal Scaling: Involves adding more nodes to a system to increase performance.
-
Vertical Scaling: Involves upgrading existing hardware to enhance computational capacity.
Examples & Applications
When an AI model grows larger, horizontal scaling can be implemented by adding more servers to distribute the training data.
In a cloud-based AI application, vertical scaling might involve using higher RAM or more powerful CPUs within existing servers for better processing.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Scaling up or scaling wide, choose your path for processing pride!
Stories
Imagine a farmer who needs a bigger barn. He could either build a second barn next to it (horizontal scaling) or make his single barn taller (vertical scaling) to store more hay.
Memory Tools
Use 'H' for Horizontal = 'Add more hardware' and 'V' for Vertical = 'Upgrade existing'.
Acronyms
'HVS' for 'Horizontal and Vertical Scaling' - Remember, both are vital!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Scalability
The ability of a system to handle increased loads by increasing resources without compromising performance.
- Horizontal Scaling
The method of adding more machines or nodes to a system to increase computational capacity.
- Vertical Scaling
The method of upgrading existing hardware to enhance processing capabilities.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
