Advanced Interconnection Topologies
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Series-Parallel Connections
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will discuss series-parallel connections and how they use h-parameters. Can anyone remind me what h-parameters are?

H-parameters define the input-output relationships in two-port networks.

Exactly! When we connect two networks in series-parallel, we can add their h-parameters. What does the combined h-matrix look like?

It would be h_total = h_A + h_B, right?

Correct! This helps us in modeling transistor circuits very effectively. Why do you think this is important?

It allows better design flexibility, especially in amplifiers!

Great point! In addition to flexibility, these configurations can offer improved performance. Remember, the series-parallel method is crucial when dealing with transistor models.

Can we visualize this setup in practical applications?

Definitely! Think about audio amplifiers where various stages might benefit from this method. To summarize, series-parallel connections enhance our design capabilities significantly.
Parallel-Series Connections
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's transition to parallel-series connections. Who can tell me what g-parameters represent?

They define the relationship between output currents and input voltages, right?

Exactly! When we add two networks in a parallel-series configuration, how do we combine their g-parameters?

We can express it as g_total = g_A + g_B.

Correct again! This configuration is particularly useful in feedback networks. What kind of advantages do you think we gain from applying this?

It allows for better control of circuit responses!

Right! By combining g-parameters, we can optimize feedback to stabilize the circuit. As a rule of thumb, always consider how your topology can affect performance.

So, pairs of g-parameters can help us create more robust circuits?

Exactly! The better your understanding of these relationships, the more adept you will become at designing complex systems.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore advanced interconnection topologies of two-port networks. It introduces concepts such as series-parallel connections where h-parameters are added, and parallel-series connections where g-parameters are collectively utilized. Understanding these topologies is essential for designing complex circuits that require precise characteristics while ensuring optimal performance.
Detailed
Advanced Interconnection Topologies
In this section, we delve deeper into the methodologies used for interconnecting two-port networks beyond the basic configurations.
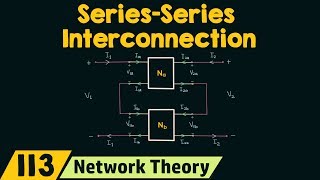
1. Series-Parallel Connection (h-Parameters Add):
In a series-parallel connection, we combine two networks where each contributes to a unified performance based on their h-parameters. The equations governing this topology allow for the addition of the h-parameters of the two networks as:
\[ h_{total} = h_A + h_B \]
This setup is advantageous in transistor modeling and amplifying signal characteristics.
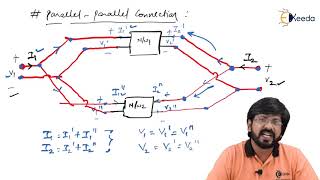
2. Parallel-Series Connection (g-Parameters Add):
In the alternative parallel-series connection, the g-parameters of networks are also combined through addition. This approach proves beneficial particularly in feedback networks that require precise control over output responses. The combined equation for this topology is given by:
\[ g_{total} = g_A + g_B \]
These advanced interconnection methods provide engineers with the flexibility to enhance circuit functionality, improving gain, stability, and overall response, which is significant in applications such as telecommunications, audio processing, and signal integrity. Understanding these topologies helps in selecting the right configurations for specific applications while maintaining reliable performance.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Series-Parallel Connection
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
8.3.1 Series-Parallel (h-Parameters Add)
Network A │ ├─Network B │
- Combined h-Matrix:
\[
h_{total} = h_A + h_B
\]
Detailed Explanation
In a series-parallel connection configuration, two networks (Network A and Network B) are interconnected in such a way that they can operate sequentially while allowing shared connections between them. The h-parameters are used to represent the behavior of these networks under this configuration. When you connect Network A to Network B in this way, their h-parameters can be added together to obtain a single h-matrix that represents the combined system, allowing you to analyze the overall behavior of the interconnected networks.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the series-parallel connection like a relay race. Each runner (network) completes their part of the race (function) while passing the baton (signal) to the next one. The total performance of the team (combined network) can be evaluated by considering how well each runner performed individually and how smoothly they passed the baton.
Parallel-Series Connection
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
8.3.2 Parallel-Series (g-Parameters Add)
Network A │ ┼─Network B │
- Combined g-Matrix:
\[
g_{total} = g_A + g_B
\]
Detailed Explanation
In a parallel-series connection, the networks are organized in a way that allows for concurrent operation while still maintaining a series connection aspect. Here, we utilize g-parameters to characterize how the networks behave in this specific arrangement. Just like in a series-parallel configuration, when the networks are combined, we can add their g-parameters to obtain a new g-matrix representing the overall interconnection, allowing us to analyze inputs and outputs effectively.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of the parallel-series connection as a two-pronged approach to cooking—a kitchen setup where some ingredients are prepared simultaneously (parallel) while others follow a specific sequence (series). Just as the total flavor outcome depends on both the simultaneous and sequential efforts of the chefs (networks), the combined g-matrix gives a full picture of the connected networks' effectiveness.
Key Concepts
-
Series-Parallel Connection: A method of interconnecting networks using h-parameters, enhancing transistor modeling.
-
Parallel-Series Connection: A configuration to interconnect networks using g-parameters, crucial in feedback systems.
Examples & Applications
Example of a series-parallel connection is in transistor amplifiers where performance is optimized by combining h-parameters.
An application of parallel-series connections can be found in audio systems to maintain feedback control.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To connect in series-parallel, h is the key, / Gaining performance, just wait and see!
Stories
Imagine two friends, h-buddy and g-buddy, tasked with building the best robot together. h-buddy connects voltages and currents in perfect harmony while g-buddy makes sure they balance the reactions, creating a robust team.
Memory Tools
Remember: Happy Amplifiers connects like h, while Great feedback is controlled with g.
Acronyms
HAP for Series-Parallel (H-Parameters Add) and GAP for Parallel-Series (G-Parameters Add).
Flash Cards
Glossary
- hParameters
Parameters used to represent the characteristics of two-port networks, specifically in terms of voltage and current relationships.
- gParameters
Parameters that describe the transconductance or input-output characteristics of two-port networks.
- SeriesParallel Connection
An arrangement where two networks are connected in series-parallel fashion allowing their h-parameters to be added.
- ParallelSeries Connection
An arrangement where two networks are connected in parallel-series fashion enabling the addition of their g-parameters.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
