Parallel-Series (g-Parameters Add)
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding g-Parameters
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’re going to explore g-parameters and their significance in parallel-series interconnections. Can anyone explain what g-parameters represent in a network?

Isn't it about how the currents and voltages behave in a two-port network?

Exactly! g-parameters are a way to describe the relationship between the input and output voltages and currents. In a parallel-series configuration, what do you think happens to these parameters?

Do we just add them together?

That's right! The total g-matrix is the sum of the individual g-matrices. Always remember: when dealing with g-parameters, we maintain a specific relationship between voltages. This is critical for circuit calculations.
Application of g-Matrix Addition
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand how to add g-parameters, can someone suggest where this might be useful in real-world applications?

Maybe in feedback networks, where we have to combine different signals?

Excellent point! Feedback networks often use g-parameters to maintain stability while combining the input and output signals. What do you think would happen if we didn't account for these adjustments?

There would be miscalculations in the output, especially with amplification?

Correct! Without properly summing the g-matrices, our output could be inaccurate. Remember, that’s why parallel-series connections are vital for optimized performance.
Example Problem Discussion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s practice a little. Suppose we have two networks with g-parameters of g_A = [1, 2; 3, 4] and g_B = [2, 1; 0, 3]. What is g_total?

We would just add them together, right? So, g_total = [1+2, 2+1; 3+0, 4+3]!

Exactly! This gives us g_total = [3, 3; 3, 7]. Always ensure to double-check your calculations in circuit designs.

Can these kinds of calculations affect the performance of the circuit?

Yes, they do! Effectively combining and analyzing g-parameters will lead to a more robust and efficient network. Remember: accuracy is key in electronics!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The parallel-series interconnection method involves summing the g-parameters from two networks to create a combined g-matrix. This technique ensures that certain electrical characteristics are preserved while enabling complex cascaded designs, particularly in feedback networks.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
The parallel-series interconnection method discussed in this section focuses on how to effectively combine two-port networks using g-parameters. In this approach, the total g-matrix is obtained by simply adding the g-parameters of each individual network. It's essential to note that in this configuration, the input and output voltages are held constant across the combined networks.
The general representation of this methodology is captured in the equation:
$$
g_{total} = g_A + g_B
$$
This addition is vital in understanding how to handle feedback networks where stability and signal integrity are crucial. Understanding the intricacies involved in managing these interconnections allows for effective design and implementation in more complex systems—particularly in scenarios where parallel circuits interact with series connections. This knowledge is foundational when moving forward into practical applications such as designing amplifiers and other complex circuit configurations.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
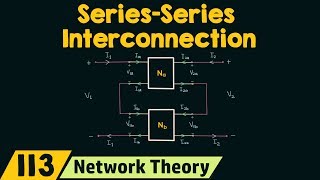
Combined g-Matrix Representation
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Network A │ ┼─Network B │
- Combined g-Matrix:
\[g_{total} = g_A + g_B\]
Detailed Explanation
In this section, we discuss the parallel-series connection of two networks using g-parameters. The visual representation shows how two networks can be interconnected such that Network A and Network B share a common point while still being treated as separate entities. The formula provided indicates how to combine their individual g-parameters into a total g-parameter for the overall system, emphasizing that the total g-parameter is the sum of the individual g-parameters for Networks A and B.
Examples & Analogies
Consider two water tanks connected at the same level. Each tank can independently fill or drain water. Similarly, when analyzing electrical networks connected in parallel-series, we can look at their contributions individually and combine their effects to understand the overall system. If one tank fills faster than the other, we adjust our calculations accordingly, just like we do for the g-parameters in our electrical networks.
Key Concepts
-
g-parameters: Used to relate currents and voltages in two-port networks.
-
Total g-matrix: Derived by adding individual g-parameters of connected networks.
-
Parallel-Series method: A specific topology for combining two-port networks that requires careful consideration of parameters.
Examples & Applications
Example of combining two amplifiers in a feedback network using g-parameters.
Calculating the total voltage across two parallel-connected networks.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In a zig and a zag, we add up our g, keeping voltages steady for you and for me!
Stories
Imagine two rivers of power flowing side by side. When we combine their flows, we need to keep the currents steady to ensure that the ecosystems thrive.
Memory Tools
G-Parameters Addition: Generalize-Add or Stay: Check General Input-Out for stability.
Acronyms
PARA - Parallel-series Approach Requires Addition.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- gparameters
Parameters that describe the relationship between the voltages and currents in a two-port network.
- gmatrix
A matrix representation of the g-parameters of a network, used for analyzing interconnections.
- ParallelSeries Connection
A method of combining two-port networks where certain parameters are summed while holding other parameters constant.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
