SEMI-TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION OF A TYPICAL FLOWERING PLANT
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to the Description of Flowering Plants
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll explore how to effectively describe a flowering plant using various morphological features. Can anyone tell me what we need to start with?

I think we need to start with its habit, right?

What does 'habit' mean in this context?

Excellent question! 'Habit' refers to the general growth form or the ecological niche of the plant. For example, is it a shrub, tree, or herb? Now, after identifying the habit, what comes next?

We would describe the vegetative characters!

Exactly! We focus on the roots, stem, and leaves, discussing their unique features and functions.

What specific traits should we look for in those parts?

That's a great point! The roots can be categorized as tap or fibrous, while the stem can have nodes and internodes. Remember, nodal structures play a crucial role in identifying plants. Let’s summarize: we talked about the importance of starting with the habit, followed by detailed vegetative descriptions.
Floral Characteristics of Flowering Plants
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Having discussed the vegetative parts, we now turn our focus to the floral characteristics. What do we examine in the floral part of a flowering plant?

We need to talk about the inflorescence first!

What is inflorescence exactly?

Inflorescence refers to the arrangement of flowers on a floral axis. There are two main types: racemose, where the main axis continues to grow, and cymose, where the main axis terminates in a flower. Can anyone give examples of these?

Sunflowers are racemose, right?

That's right! Now, once we understand inflorescence, what do we discuss next?

The individual flowers themselves!

Correct! Each flower has a distinctive arrangement of calyx, corolla, androecium, and gynoecium. Remember, the floral formula and diagram we create will depict these details visually.
Floral Diagram and Formula
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Last but not least, let's dive into the floral diagram and formula. Why do you think these tools are useful?

They help simplify complex information!

And they show relationships between different parts of the flower, right?

Exactly! The floral formula uses symbols such as 'K', 'C', 'A', and 'G' for calyx, corolla, androecium, and gynoecium respectively. What does it mean if the formula has brackets or lines?

Brackets indicate fusion of parts, and lines show adhesion between different whorls!

Well said! This representation is essential for understanding floral structure. So, let's summarize: we’ve covered the description, floral characteristics, and the vital tools for representation.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The semi-technical description of a flowering plant includes its habit, vegetative parts like roots, stems, and leaves, followed by floral structures, such as inflorescence and flower parts. It culminates in a floral diagram and formula that succinctly conveys the plant's characteristics.
Detailed
Semi-Technical Description of a Typical Flowering Plant
This section outlines the essential features used in constructing a semi-technical description of a flowering plant. The description is organized sequentially, starting with the plant's habit, which describes its general growth form and habitat. This is followed by detailed descriptions of the vegetative characters, specifically focusing on the roots, stem, and leaves, each of which has distinct characteristics and functions. Next, the floral characters are addressed, including the arrangement of flowers into inflorescence and the details of the flower parts.
To summarize and simplify the morphological complexity, a floral diagram is presented along with a floral formula. The floral formula uses symbols to represent different flower structures—such as 'K' for calyx, 'C' for corolla, 'A' for androecium, and 'G' for gynoecium—and shows relationships between these structures. Through this systematic approach, one can efficiently convey the morphology of flowering plants, aiding in identification and classification.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Description Methodology
Chapter 1 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Various morphological features are used to describe a flowering plant. The description has to be brief, in a simple and scientific language and presented in a proper sequence.
Detailed Explanation
To describe a flowering plant, we look at its morphology, which includes its shape, structure, and growth patterns. The description must be concise and scientific, meaning we should use clear and accurate language. Moreover, it should follow a specific order: starting with the plant's habit (its general growth form), followed by its vegetative characters like roots, stems, and leaves, and finally its floral characters, which include the arrangement of flowers (inflorescence) and details about the flower itself.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are describing a new friend to someone. You might start with how they look (general appearance), then talk about their outfit and accessories (details about their makeup or jewelry), and finally mention their habits or interests (what they like to do or how they spend their time). In a similar way, we describe a plant starting from its overall appearance to specific details.
Sequence of Description
Chapter 2 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The plant is described beginning with its habit, vegetative characters – roots, stem and leaves and then floral characters inflorescence and flower parts.
Detailed Explanation
The process of describing a flowering plant involves a systematic approach. We first identify the 'habit' which is how the plant generally grows (like whether it’s a tree, shrub, or herb). Then, we delve into the 'vegetative characters,' detailing the roots, stems, and leaves. This provides basic information about how the plant sustains itself and how its structures serve its functional needs. Finally, we describe the 'floral characters' including the arrangement of flowers (inflorescence) and the parts of flowers, which are crucial for reproduction.
Examples & Analogies
If you visit a zoological park, you first see the type of animal (its habit), then what it looks like (its size and color), and finally how it behaves or interacts with its surroundings (its reproductive habits or social structure). This makes it easier to understand the animal's place in the ecosystem, just like understanding a plant.
Floral Diagram and Formula
Chapter 3 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
After describing various parts of plant, a floral diagram and a floral formula are presented. The floral formula is represented by some symbols.
Detailed Explanation
Once the plant has been described, a floral diagram and floral formula illustrate the details of the flower’s structure. The floral formula uses specific symbols to succinctly convey information about the flower's different parts, such as calyx (K for sepals), corolla (C for petals), androecium (A for stamens), and gynoecium (G for carpels). This formula captures essential information about the flower’s composition and characteristics in a compact form.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a floral formula like a recipe card for a cake. The recipe might have shorthand notations, like 'C' for cup of sugar or 'B' for baking time. Similarly, the floral formula is a shorthand for the characteristics of a flower, allowing botanists to share detailed information efficiently.
Understanding Symbols in Floral Formula
Chapter 4 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In the floral formula, Br stands for bracteate K stands for calyx , C for corolla, P for perianth, A for androecium and G for Gynoecium.
Detailed Explanation
The floral formula uses a variety of symbols to convey complex information quickly. For instance, 'Br' refers to the presence of bracts (leaf-like structures), while 'K' denotes the calyx or sepals, 'C' specifies the corolla or petals, 'P' indicates the perianth (when calyx and corolla are not distinguished), 'A' symbolizes the androecium (male parts), and 'G' indicates the gynoecium (female parts). This classification helps clarify which parts of the flower are being described and how they relate to each other.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how road signs use symbols to communicate important information quickly—like a stop sign or a detour sign. Just like road signs, the symbols in a floral formula convey critical characteristics of a flower, making it easier to understand its structure without needing extensive text.
Indicating Ovary Position and Flower Types
Chapter 5 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
G for inferior ovary, for male, for female, for bisexual plants, ⊕ for actinomorphic and for zygomorphic nature of flower.
Detailed Explanation
The floral formula includes information about the position of the ovary as well as the flower's gender and symmetry. An 'inferior' ovary occurs when the other floral parts appear to emerge above it, while 'superior' indicates the opposite. Symbols are also used to indicate whether the flower is male, female, or bisexual. Furthermore, the symbols ⊕ and indicate the flower's symmetry—actinomorphic flowers (which can be divided into symmetrical halves) versus zygomorphic flowers (asymmetrical). This helps in understanding the reproductive mechanisms of different flowers.
Examples & Analogies
Think about how you might order food at a restaurant. You might specify whether you want it spicy or mild (like determining a flower's male or female status) and whether it’s vegetarian or not (symmetry of the dish). This specificity ensures you know exactly what you will be getting, just as floral formulas let botanists know the specifics of a flowering plant.
Representation of Floral Structure in Diagrams
Chapter 6 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
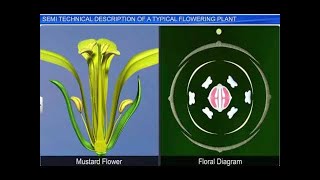
A floral diagram provides information about the number of parts of a flower, their arrangement and the relation they have with one another.
Detailed Explanation
A floral diagram visually represents the components of a flower, illustrating not only how many parts it has but also how they are arranged relative to each other. Each part of the flower—like the sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels—is depicted in concentric circles or whorls, providing a clear reference to their spatial relationship, which is important for understanding how the flower functions.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine following instructions to build furniture from a flat-pack store. The instruction manual often includes a diagram showing how pieces fit together. Similarly, a floral diagram shows how the various parts of a flower connect, ensuring students accurately understand the plant's shape and function.
Example: Mustard Plant
Chapter 7 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The floral diagram and floral formula in Figure 5.16 represents the mustard plant (Family: Brassicaceae).
Detailed Explanation
As a practical illustration, the floral diagram and formula for the mustard plant exemplify how to apply the concepts discussed. In this example, the representation showcases the specific floral characteristics of the mustard plant, including how its parts are arranged. This real-world application of the floral formula facilitates easier identification and understanding of floral structures in this family of plants.
Examples & Analogies
Think of using a map to navigate a new city. The mustard plant serves as a landmark; by studying this example in detail, you can learn how to identify other plants in the same family by understanding their floral characteristics.
Key Concepts
-
Floral Diagram: A visual representation showing the arrangement and relation of floral parts.
-
Floral Formula: A symbolic representation of a flower’s structure, useful for summarizing complex information.
Examples & Applications
For instance, the mustard plant's floral diagram can be used to explain its morphological features.
When describing a sunflower, we can illustrate its racemose inflorescence clearly using a floral diagram.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To remember floral parts, sing with glee: Calyx and corolla, from A to Z!
Stories
Imagine a plant party where each flower part introduces itself: 'I'm Calyx, all covered up, and here's Corolla dressed for fun!'.
Memory Tools
Remember the acronym 'A CAG' for the flower structure: Androecium, Corolla, And Gynoecium.
Acronyms
The acronym 'FLO' can help you recall Flower, Leaf, and Ovary as key components of flowering plants.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Habit
The general growth form or lifestyle of a plant, e.g., shrub, tree, or herb.
- Inflorescence
The arrangement of flowers on the floral axis.
- Calyx
The outermost whorl of a flower, composed of sepals.
- Corolla
The whorl of petals in a flower, often brightly colored.
- Androecium
The whorl of stamens in a flower, representing the male reproductive part.
- Gynoecium
The female reproductive part of a flower composed of carpels.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
