Venation
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Venation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to explore the concept of venation in plants. Can any of you tell me what venation means?

Does it have to do with the veins in the leaves?

Exactly, venation refers to the arrangement of veins and veinlets in the leaf lamina. So, why do you think the structure of these veins might matter?

I guess it helps with how the leaf gets nutrients?

Right! The veins help distribute water and nutrients throughout the leaf. Now, there are two main types of venation: reticulate and parallel. Let’s dive deeper into these.

What’s the difference between them?

Great question! Reticulate venation looks like a network of veins, typically found in dicots, while parallel venation has veins running parallel to each other, commonly seen in monocots. Can anyone give me an example of each?

Would a rose be an example of reticulate venation?

Yes, fantastic! Now summarize what we’ve learned about venation today.
Characteristics of Venation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In our last session, we talked about the types of venation. What might be the functional advantages of reticulate and parallel venation?

Maybe it affects how efficiently the leaf collects sunlight or water?

Exactly! The design of the venation impacts how well the leaf can manage resources. Reticulate venation provides structural support, while parallel venation often enhances the leaf’s ability to cope with mechanical stress. Which plants do you think use these adaptations?

I think palms and grasses would be monocots, right?

You’re correct! Palms and grasses exhibit parallel venation. It’s essential to recognize that these adaptations enable plants to thrive in their respective environments.

Can we observe these differences in real life?

Absolutely! Observing leaf samples in nature allows you to identify venation type real-time. Can someone summarize the two types of venation?

Reticulate is a network in dicots, and parallel runs next to each other in monocots.
Practical Applications of Venation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

As we wrap up our discussions on venation, let’s look at how it helps us in plant identification. Why can knowing about venation be vital for this?

It helps us recognize plants based on their leaf structure!

Exactly! Certain plant families have characteristic types of venation. Knowing this aids in categorizing and identifying them.

Are there other traits we should look for?

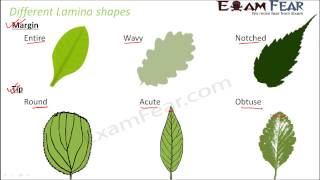
Certainly! Other traits include leaf shape, margin, and apex, but venation is a crucial starting point.

So, if I found a leaf having reticulate venation, I might expect it to be from a plant like a rose or a guava tree?

Exactly right! Excellent deduction. Keep observing the variations in nature, and you'll grow your identification skills.

This adds so much more than just looking at the flowers!

Indeed! All plant structures are intricately connected. Who can give a summary of what we have learned today?
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Different types of venation feature prominently in plant morphology, where reticulate venation forms a network of veins and parallel venation has veins running parallel to each other. Dicotyledons typically display reticulate venation, while monocotyledons exhibit parallel venation.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
Venation is a key structural characteristic of leaves, specifically referring to the arrangement of veins and veinlets within the lamina. Two primary types of venation are discussed:
- Reticulate Venation: This type forms a network pattern where the veins interconnect, providing a rich supply of nutrients and supporting structure. It is predominantly found in dicotyledonous plants.
- Parallel Venation: In this arrangement, the veins run parallel to each other, offering streamlined support and is characteristic of most monocotyledons.
Understanding these types of venation helps in identifying plant types and understanding their physiological adaptations. The distinction between facilitated nutrient distribution and structural integrity of the leaf morphology is crucial for plant survival and adaptability.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Venation
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The arrangement of veins and the veinlets in the lamina of leaf is termed as venation.
Detailed Explanation
Venation refers to the pattern in which the veins and smaller branches (veinlets) are organized within the leaf blade (lamina). This pattern is essential for the leaf's function, as veins transport nutrients and water, and provide structural support.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the veins in a leaf as the highways and streets in a city. Just as highways allow for the quick transportation of goods and people across long distances, the veins in a leaf distribute water and nutrients to where they're needed, while the smaller veinlets resemble local streets that take resources to each part of the leaf.
Types of Venation
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
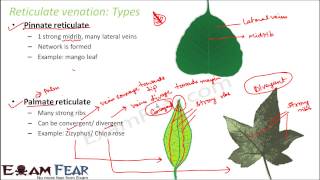
When the veinlets form a network, the venation is termed as reticulate. When the veins run parallel to each other within a lamina, the venation is termed as parallel.
Detailed Explanation
There are two primary types of venation: reticulate and parallel. Reticulate venation occurs when the veins intertwine to form a net-like structure, which is common in dicotyledons. In contrast, parallel venation is characterized by veins that run alongside each other without forming a network, which is typical in monocotyledons. This structural difference results in varying leaf shapes and functions.
Examples & Analogies
Think of reticulate venation as a complex public transportation network, with various routes connecting in multiple locations, allowing for multiple pathways to reach a destination. Parallel venation, on the other hand, resembles a straight highway with lanes running side by side, directing traffic in one direction.
Functional Implications of Venation
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Leaves of dicotyledonous plants generally possess reticulate venation, while parallel venation is the characteristic of most monocotyledons.
Detailed Explanation
The type of venation can impact how a plant functions and thrives in its environment. Dicotyledonous plants with reticulate venation may be better equipped for support and resource distribution across a more expansive surface area of the leaf. Monocotyledons with parallel venation tend to have long, narrow leaves that can be beneficial in environments where wind resistance is a factor, such as grasslands.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how certain vehicles are designed for different purposes. Sports cars (like narrow-leaved monocotyledons) are built for speed and aerodynamics, while SUVs (reflecting the stability of broad-leaved dicotyledons) are constructed for versatility and carrying capacity. Each is optimized for its specific environment and function.
Key Concepts
-
Venation: Patterns of veins in leaves that can aid in nutrient distribution and structural integrity.
-
Reticulate Venation: A network of interconnected veins typical of dicots.
-
Parallel Venation: Characterized by parallel veins found in monocots.
Examples & Applications
Example of reticulate venation: Rose leaves.
Example of parallel venation: Grass leaves.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Reticulate veins intertwine, in a network they're just fine!
Stories
Imagine a city where roads crisscross (reticulate) or run straight (parallel) - both get you where you need!
Memory Tools
Remember 'R' for 'Reticulate' and 'Roses' - they go hand in hand!
Acronyms
RAP for Reticulate And Parallel
Recognizing patterns helps in plant identification!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Venation
The arrangement of veins and veinlets within the leaf lamina.
- Reticulate Venation
A network pattern of veins found typically in dicotyledonous plants.
- Parallel Venation
A type of venation where the veins run parallel to each other, commonly found in monocotyledonous plants.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
