Types of Leaves
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Leaf Types
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll be discussing the two main types of leaves - simple and compound. Can anyone tell me what distinguishes a simple leaf from a compound leaf?

A simple leaf has one blade or lamina, right?

Correct! A simple leaf has an entire lamina or incisions that do not reach the midrib. Now, can someone explain what a compound leaf is?

I think a compound leaf has multiple leaflets that can touch the midrib.

Exactly! The leaflets of a compound leaf break off at the midrib into multiple sections. This is important for plant classification.

To remember this, you can think of the acronym 'SIMPLE' for Simple leaves: **S**ingle blade, **I**ntact, **M**idrib untouched, **P**etiole attached, **L**amina single, **E**ntire or incised.

That's a great way to remember it!

Let’s summarize: Simple leaves are whole or slightly incised; compound leaves are made of multiple leaflets. Next, we will dive deeper into the types of compound leaves.
Types of Compound Leaves
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's explore the types of compound leaves in detail. Who can explain what a pinnately compound leaf looks like?

It's when leaflets are arranged on either side of a central rachis like a feather, right?

Well explained! An example of a pinnately compound leaf is the neem leaf. What about palmately compound leaves?

Those have leaflets that arise from the tip of the petiole, like fingers from a hand.

Exactly! A great example would be the silk cotton leaf. Can anyone remember the key difference?

Pinnately compound has a central rachis, while palmately compound has all leaflets at the same point.

Correct! Let's remember this by the phrase 'PIN the RACHIS' for pinnately compound leaves and 'PALM your HAND' for palmately compound leaves!

To recap, we’ve discussed the two types of compound leaves: pinnately and palmately. Next, we will delve into phyllotaxy.
Understanding Phyllotaxy
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Moving on to phyllotaxy, who can describe what this term means?

It's how leaves are arranged on the stem!

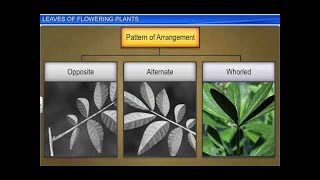
Correct! There are three main types of phyllotaxy: alternate, opposite, and whorled. Can someone give examples of each type?

Alternate is like in mustard or sunflower. Opposite is in guava and whorled is seen in Alstonia.

Well done! To remember, think of the acronym 'AOW' for **A**lternate, **O**pposite, **W**horled.

That's really useful!

Great! To summarize, phyllotaxy is the arrangement of leaves; alternate, opposite, and whorled are the three types. Remember 'AOW' to help memorize these!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section explains the classification of leaves into simple and compound categories, outlining the differences in their structures, including pinnately and palmately compound leaves and the concept of phyllotaxy.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
Leaves, which are essential for photosynthesis in plants, can be classified into two main types: simple leaves and compound leaves. A simple leaf has a single blade that is entire or may be incised but does not reach the midrib. Conversely, a compound leaf consists of multiple leaflets, which are segments that may divide the leaf's lamina up to the midrib, effectively creating multiple blades attached to a common petiole.
Types of Compound Leaves:
- Pinnately Compound Leaf: In these leaves, leaflets are arranged along a common axis called the rachis, similar to the structure of a feather. An example would be the neem leaf.
- Palmately Compound Leaf: In this type, all leaflets originate from a single point at the tip of the petiole. The silk cotton leaf is an example
Furthermore, the arrangement of leaves on a stem is known as phyllotaxy. Phyllotaxy can be classified into three types:
1. Alternate: One leaf arises at each node alternately (e.g., China rose).
2. Opposite: A pair of leaves emerges at each node, directly opposite each other (e.g., guava).
3. Whorled: More than two leaves arise from a single node, forming a whorl, characteristic of plants like Alstonia.
Understanding these classifications is crucial for studying plant morphology and taxonomy as it helps in identifying and categorizing different plant species.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Understanding Simple Leaves
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A leaf is said to be simple, when its lamina is entire or when incised, the incisions do not touch the midrib.
Detailed Explanation
A simple leaf is characterized by having a single blade or lamina. This blade can either be fully intact (entire) or if it has cuts (incisions), those cuts do not reach the central vein, known as the midrib. This means that the leaf remains one complete unit without being divided into smaller pieces.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a simple leaf as a single piece of paper. If a paper has a few cuts in it that don’t go all the way to the edge, it's still considered one sheet, just like a simple leaf with some small incisions.
Characteristics of Compound Leaves
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
When the incisions of the lamina reach up to the midrib breaking it into a number of leaflets, the leaf is called compound.
Detailed Explanation
A compound leaf is one where the blade is divided into multiple sections, or leaflets. These leaflets branch out from a common central point or axis, making the whole structure appear as if it has multiple leaves combined together. In this case, the incisions penetrate all the way to the midrib, creating distinct leaflets that can still be considered part of a single leaf structure.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a hand with fingers spread out; each finger represents a leaflet of a compound leaf. Even though the fingers are separate, they all connect back to the palm, which acts like the leaf’s base.
The Axillary Bud in Leaves
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A bud is present in the axil of petiole in both simple and compound leaves, but not in the axil of leaflets of the compound leaf.
Detailed Explanation
Both simple and compound leaves have an axillary bud located in the angle between the leaf stem (petiole) and the stem of the plant. This bud is critical for plant growth as it can develop into a new branch or flower. However, in the case of compound leaves, individual leaflets do not bear axillary buds, as they are merely subdivisions of a single leaf.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the axillary bud like a light switch on a lamp. In a simple leaf, just like a lamp connected directly to the power source, you can easily turn it on or off. In a compound leaf, the leaflets are like different bulbs on a string of lights; while they each can shine, they don’t have individual switches because they’re still part of the same overall circuit.
Types of Compound Leaves
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The compound leaves may be of two types: pinnately compound leaf and palmately compound leaf.
Detailed Explanation
There are two main types of compound leaves. Pinnately compound leaves have multiple leaflets arranged along a central axis (rachis), resembling a feather. In contrast, palmately compound leaves have all their leaflets attached at a single point at the tip of the petiole, similar to the fingers on a hand stemming from the palm.
Examples & Analogies
Pinnately compound leaves can be visualized as feathers on a bird where the shaft is central, while palmately compound leaves resemble the shape of a hand where fingers radiate from the palm. For example, the neem tree has pinnately compound leaves, while the silk cotton tree features palmately compound leaves.
Key Concepts
-
Types of Leaves: Leaves can be classified into simple and compound based on their structure.
-
Simple Leaves: Single intact blade or slightly incised.
-
Compound Leaves: Composed of multiple leaflets, which can break down into smaller leaflets.
-
Pinnate Structure: Pinnately compound leaves have leaflets arranged on either side of a central rachis.
-
Palmate Structure: Palmately compound leaves have leaflets that originate from a single point.
-
Phyllotaxy: Refers to the arrangement of leaves along the stem, categorized as alternate, opposite, or whorled.
Examples & Applications
Pinnately compound leaf example: Neem leaf.
Palmately compound leaf example: Silk cotton leaf.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
For leaves that are simple, think one cut, / Compound leaves have many; they aren't shut.
Stories
Imagine a tree where simple leaves are like a solitary dancer on stage, while compound leaves are the whole ensemble performing together.
Memory Tools
Remember 'SIMPLE' for Simple leaves: Single blade, Intact, Midrib untouched, Petiole attached, Lamina single, Entire or incised.
Acronyms
Use 'AOW' to memorize types of phyllotaxy
**A**lternate
**O**pposite
**W**horled.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Simple Leaf
A leaf with a single, undivided lamina.
- Compound Leaf
A leaf composed of multiple leaflets attached to a single petiole.
- Pinnately Compound Leaf
A compound leaf where leaflets are arranged on either side of a central axis or rachis.
- Palmately Compound Leaf
A compound leaf where all leaflets arise from a single point at the petiole.
- Phyllotaxy
The arrangement of leaves on the stem or branch.
- Rachis
The central axis of a pinnately compound leaf.
- Leaflet
A segment or subdivision of a compound leaf.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
