The Fruit
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Definition of Fruit
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will learn about fruits, which are the mature ovaries of flowering plants developed after fertilization.

Can a fruit form without fertilization?

Great question! Yes, it's called a parthenocarpic fruit.

What does parthenocarpic mean?

Parthenocarpic means a fruit that develops without fertilization, resulting in seedless fruit.

So, do all fruits have seeds?

Not necessarily. While most fruits have seeds, parthenocarpic fruits, like bananas and seedless watermelons, do not.
Pericarp Structure
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

The fruit typically includes a pericarp, which can be either dry or fleshy. Can anyone tell me the layers of a fleshy fruit?

Are there three layers? Epicarp, mesocarp, and endocarp?

Correct! The epicarp is the outermost layer, the mesocarp is the fleshy part, and the endocarp surrounds the seed.

Can you give examples of each type of fruit?

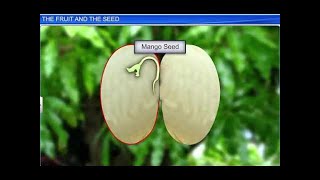
Sure! For example, the mango is a drupe with a well-differentiated pericarp, while the coconut also falls under drupes with fibrous mesocarp.

What about dry fruits?

Dry fruits do not have fleshy tissues and can be classified into types such as capsules, legumes, and nuts. Each type has distinct characteristics.
Types of Fruits
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's explore how we classify fruits. They can be classified as fleshy or dry, with fleshy fruits being often more attractive and edible.

What is the purpose of these fleshy fruits?

Fleshy fruits often attract animals, which help in seed dispersal after consuming the fruit.

Do dry fruits have any advantage?

Yes, dry fruits often protect their seeds from harsh conditions and may aid in mechanical seed dispersal.

Can you summarize this information for us?

Absolutely! Fruits are categorized into fleshy and dry types. Fleshy fruits have a structure that aids in attracting animals, while dry fruits protect seeds and assist in their dispersal. Remember the layers of the pericarp!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses the structure and types of fruits in flowering plants, highlighting their development from the ovary after fertilization, and differentiating between fleshy and dry fruits based on the pericarp's characteristics.
Detailed
The Fruit
The fruit is a defining characteristic of flowering plants, representing the mature ovary developed after fertilization. If a fruit arises without fertilization, it is termed parthenocarpic. Typically, a fruit comprises a wall, termed the pericarp, and seeds. The pericarp can be classified into two categories: dry or fleshy. In fleshy fruits, such as drupes, the pericarp is further divided into three layers: the outer epicarp, the middle mesocarp, and the inner endocarp. For example, the mango and coconut are characterized as drupes, developing from monocarpellary superior ovaries and containing a single seed. In mango, the pericarp is distinctly differentiated, while in coconut, the mesocarp is fibrous.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to the Fruit
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The fruit is a characteristic feature of the flowering plants. It is a mature or ripened ovary, developed after fertilisation. If a fruit is formed without fertilisation of the ovary, it is called a parthenocarpic fruit.
Detailed Explanation
In flowering plants, a fruit is what we recognize as a mature ovary that results from the fertilization process. The fertilization occurs when pollen meets the ovule in the ovary, which leads to the formation of seeds inside the fruit. Interestingly, some fruits can develop even if fertilization does not happen; these are known as parthenocarpic fruits. They can still grow and be edible, for example, bananas.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a situation where you plant a seed and nurture it until it grows into a flowering plant. When the flower is fertilized, it develops into a fruit (like an apple), containing seeds that can grow into new plants. If you have a banana, it can also be thought of as a fruit that develops without fertilization, making it unique.
Structure of the Fruit
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Generally, the fruit consists of a wall or pericarp and seeds. The pericarp may be dry or fleshy. When pericarp is thick and fleshy, it is differentiated into the outer epicarp, the middle mesocarp, and the inner endocarp.
Detailed Explanation
Fruits are composed of two main parts: the pericarp, which is the fruit wall, and the seeds inside. The pericarp can vary in texture; it might be dry, like in nuts, or fleshy, like in peaches. When fleshy, the pericarp is usually divided into three layers—the epicarp (the outer layer), the mesocarp (the middle fleshy part), and the endocarp (the innermost layer that directly surrounds the seeds). This layered structure plays a crucial role in protecting the seeds and aiding in their dispersal.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine biting into a peach. The juicy part you taste is the mesocarp, while the skin you first touch is the epicarp. The hard pit inside is the endocarp, which protects the seed. Each layer serves a different purpose, from attracting animals to eat the fruit and disperse seeds to providing protective barriers.
Types of Fruits
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In mango and coconut, the fruit is known as a drupe. They develop from monocarpellary superior ovaries and are one-seeded. In mango, the pericarp is well differentiated into an outer thin epicarp, a middle fleshy edible mesocarp and an inner stony hard endocarp. In coconut which is also a drupe, the mesocarp is fibrous.
Detailed Explanation
Fruits can be categorized into different types based on their structure and characteristics. A drupe, for example, is a type of fruit that has a single seed encased in a hard shell. In the case of mangoes and coconuts, both are classified as drupes. In mangoes, the fleshy part we eat is the mesocarp, while the hard part surrounding the seed is the endocarp. Coconuts share this structure, but instead of a fleshy mesocarp, they have a fibrous layer, which aids in water retention and its ability to float, ensuring seed dispersal via water.
Examples & Analogies
Think of mangoes as nature's candy with a sweet, juicy exterior (the mesocarp) layered over a protective shell (the endocarp) that guards its valuable seed. Coconuts are like the beach's version of a fruit with a dense outer layer that floats on water, allowing the seed to travel long distances and take root on new shores.
Key Concepts
-
Fruits are the mature ovaries of flowering plants developed post-fertilization.
-
Pericarp is the fruit wall consisting of epicarp, mesocarp, and endocarp.
-
Fruits can be classified into fleshy and dry fruits, with fleshy fruits often attracting animals for seed dispersal.
Examples & Applications
Mango: A drupe with a fleshy pericarp consisting of an outer epicarp, a fleshy mesocarp, and a stony endocarp.
Coconut: Another type of drupe where the mesocarp is fibrous.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Fruits are sweet and oh so neat, from ovaries they're complete!
Stories
Once upon a time, in a garden so bright, a mango and a coconut shared a delightful sight, they spoke of their layers; epicarp, mesocarp, endocarp, creating tales of fruit and trees together in the park.
Memory Tools
Drupe M.E.E. (Mango, Epicarp, Mesocarp, Endocarp) for remembering the layers of a drupe.
Acronyms
F.R.O.P. (Fruit, Ripened Ovary, Pericarp) to remember that fruit is a ripened ovary with a pericarp.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Fruit
The mature or ripened ovary of a flowering plant developed after fertilization.
- Pericarp
The fruit wall, which can be dry or fleshy and is further divided into layers such as the epicarp, mesocarp, and endocarp.
- Parthenocarpic fruit
A fruit formed without fertilization, resulting in a seedless fruit.
- Drupe
A type of fruit with a fleshy exterior and a hard stone containing the seed.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
