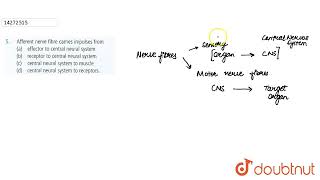
Afferent Fibres
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Afferent Fibers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we are going to dive into the world of afferent fibers, which play a critical role in informing our brain about sensations from our body. Can anyone tell me what they think afferent fibers do?

Afferent fibers send signals to the brain from the body, right?

Exactly! Afferent fibers are like messengers, carrying information from your organs and tissues to the brain. Does anyone know what kind of information they transmit?

They must transmit sensory information like touch and pain.

Yes! They are primarily responsible for relaying sensory signals related to touch, temperature, pain, and other sensations. A simple way to remember this is that 'A' in afferent stands for 'arrival'—these signals are arriving at the brain. Let's explore more about their role in the nervous system.
Structure and Function of Afferent Fibers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Can anyone suggest how afferent fibers are structured to perform their functions?

Maybe they have long extensions to reach different parts of the body?

Great observation! Afferent fibers consist of long axons that help transmit signals over long distances. Each fiber has sensory receptors at their terminals. What do you think these receptors do?

They probably detect stimuli from the environment.

Correct! These receptors respond to various stimuli and convert them into electrical signals that travel along the fibers to the CNS. Understanding their structure is crucial because it determines how effectively they can convey information. What might happen if these fibers are damaged?
Types of Afferent Fibers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Afferent fibers can be categorized into different types. Does anyone know how they can be classified?

I think they could be classified based on the type of sensation they transmit.

Exactly! There are fibers for pain, touch, temperature, and proprioception. For example, A-delta fibers are responsible for fast pain signaling while C fibers handle slow pain. Remembering this can be done with the phrase, 'A for speed, C for... slow!' What implications do you think this has for our understanding of pain management?
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The afferent fibers of the peripheral nervous system play a vital role in relaying sensory impulses from various tissues and organs to the central nervous system, thus enabling the body to respond appropriately to internal and external stimuli.
Detailed
Afferent fibers are specialized nerve fibers responsible for transmitting sensory impulses from peripheral tissues and organs to the central nervous system (CNS). They form an integral part of the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which is divided into afferent (sensory) and efferent (motor) divisions. Afferent fibers are essential for receiving sensory inputs such as touch, temperature, and pain and relay these signals to the CNS for interpretation and response. This transmission is critical for maintaining homeostasis and allowing for coordinated bodily functions.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Difference Between Afferent and Efferent Fibres
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
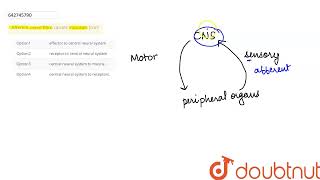
The afferent nerve fibres transmit impulses from tissues/organs to the CNS and the efferent fibres transmit regulatory impulses from the CNS to the concerned peripheral tissues/organs.
Detailed Explanation
Afferent fibers and efferent fibers are two types of nerve fibers in the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Afferent fibers are responsible for carrying sensory information from the body's tissues and organs to the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord. This information can include sensations like touch, temperature, and pain. In contrast, efferent fibers carry messages from the CNS to peripheral tissues and organs, instructing them on how to respond, such as moving muscles or regulating organ functions. Essentially, afferent fibers bring information in, while efferent fibers send information out.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a post office in a city. The afferent fibers are like mail carriers who bring letters and packages (sensory information) from various locations (the body's tissues) to the main post office (the CNS) where information is processed. The efferent fibers are like the delivery trucks that take decisions and packages (regulatory impulses) from the central post office back out to various addresses (the body's organs) to execute certain actions, like delivering a letter that asks someone to move or respond to a stimulus.
Types of Nerve Fibres
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The nerve fibres of the PNS are of two types: (a) afferent fibres (b) efferent fibres.
Detailed Explanation
Nerve fibers are classified into two major types within the peripheral nervous system: afferent fibers and efferent fibers. Afferent fibers are exclusively sensory, and their primary role is to transmit signals from sensory receptors located throughout the body to the CNS. This allows the brain to receive input from the environment and the body's internal state. Efferent fibers, on the other hand, are involved in carrying motor commands from the CNS to the muscles and glands, enabling the body to react to stimuli in a coordinated manner. This classification helps to understand how nervous system functions are organized.
Examples & Analogies
Think about a dial on a car's dashboard showing speed (afferent) and a car's engine responding by accelerating (efferent). Afferent fibers are like the speedometer, indicating how fast the car is going based on sensor input, which informs the driver. Efferent fibers represent the accelerator pedal, which pushes more fuel to the engine and makes the car move faster based on decisions made in response to that speed.
Function of the Peripheral Nervous System
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The PNS comprises of all the nerves of the body associated with the CNS (brain and spinal cord).
Detailed Explanation
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) plays a crucial role in connecting the central nervous system (CNS) to the limbs and organs. It consists of all the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. This network is responsible for relaying information to and from the CNS, enabling the body to respond to changes in both the internal and external environment. Whether it's feeling a touch, sensing a change in temperature, or moving a muscle, the PNS is active in all these processes. One way to categorize PNS is its division into sensory (afferent) pathways and motor (efferent) pathways, providing a clear route for communication between the body and the brain.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the PNS as a telephone network, where the central office (CNS) connects to numerous individual homes and businesses (the body's organs and tissues). The network cables (nerves) facilitate calls (signals), allowing you to convey information (sensations) from one place to another. When you touch something hot, for example, that's like making a phone call to alert someone about a fire; the sensory nerve is sending the urgent message to the brain for action to be taken.
Key Concepts
-
Afferent Fibers: Nerve fibers that carry sensory information to the CNS.
-
Sensory Receptors: Structures that detect stimuli and initiate nerve impulses.
-
CNS and PNS: The organization of the nervous system into central (brain and spinal cord) and peripheral systems (nerves).
Examples & Applications
Afferent fibers responsible for transmitting signals from the skin to the brain to indicate temperature changes.
The role of sensory receptors in detecting pain when a finger touches something hot.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Afferent fibers bring the news, about sensations we can't lose.
Stories
Imagine a postal worker delivering important parcels from the body's sensations to the brain's address; that's what afferent fibers do!
Memory Tools
Use the acronym 'S.A.F.E.' - Sensory Afferent Fibers Enter - to remember that sensory information travels via afferent fibers to the brain.
Acronyms
A.S.P. - Afferent Sends Positively to the brain.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Afferent Fibers
Nerve fibers that transmit sensory impulses from tissues and organs to the central nervous system.
- Central Nervous System (CNS)
The part of the nervous system that includes the brain and spinal cord, responsible for processing information.
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
The part of the nervous system that includes all the nerves outside the CNS.
- Sensory Receptors
Specialized cells or structures that detect specific types of stimuli and convert them into nerve impulses.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
