Central Neural System (CNS)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Overview of the CNS
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to explore the Central Neural System, or CNS. Can anyone tell me what the CNS comprises of?

It includes the brain and spinal cord, right?

Exactly, Student_1! The CNS includes the brain and spinal cord, and it’s essential for controlling and coordinating almost all bodily functions. Now, what do you think the main functions of the CNS are?

I think it processes information and sends instructions to the body.

Great answer! It processes sensory information and coordinates motor actions, among many other roles. We can remember this by using the acronym ‘CIPS’ which stands for Control, Integration, Processing, and Sensory data processing.

That’s an easy way to remember it!

Absolutely! Before we continue, what part of the brain do you think is responsible for higher cognitive functions?

The cerebrum?

Correct, Student_4! The cerebrum handles functions like memory, reasoning, and emotions. Let’s summarize: The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord and is responsible for control, integration, processing, and sensory data processing.
Brain Structure
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s dive into the structure of the brain. Can someone mention the major parts of the brain?

The forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain.

Exactly! Each part has distinct roles. The forebrain includes the cerebrum, thalamus, and hypothalamus. What about the midbrain?

It connects different parts of the brain, right?

Yes! It plays a crucial role in relaying information. And the hindbrain?

It controls vital functions like heart rate and breathing.

Exactly! It contains the medulla and pons. You can remember these three parts by the mnemonic 'Funky Monkeys Hibernate' where 'Funky' stands for Forebrain, 'Monkeys' for Midbrain, and 'Hibernate' for Hindbrain. Summarizing, the brain comprises the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain, each with specific functions.
Functions of the CNS
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

What would you say is the most important function of the CNS?

Controlling and coordinating body activities?

Correct! Control is one of the primary functions. Can anyone think of an example of how the CNS controls body activities?

Like when you touch something hot and pull your hand away!

Exactly! That’s a reflex action, demonstrating the CNS's swift response capabilities. We can remember this with the acronym ‘CARS’: Control, Assessment, Response, and Sensory input regarding the CNS. Each aspect highlights its critical role. In summary, the CNS controls, assesses, responds, and processes sensory input.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The Central Neural System (CNS) encompasses the brain and spinal cord, serving as the primary control center for information processing and coordination of body functions. It forms part of the larger human neural system, which also includes the Peripheral Neural System (PNS), and collaborates with the endocrine system to maintain homeostasis.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
The Central Neural System (CNS) plays a crucial role in human functioning by integrating sensory information and coordinating motor responses. It comprises two main structures: the brain and the spinal cord. The CNS is responsible for high-level functions such as cognition, memory, and emotional regulation, while also managing involuntary body processes through mechanisms such as the autonomic nervous system.
Key Components of CNS:
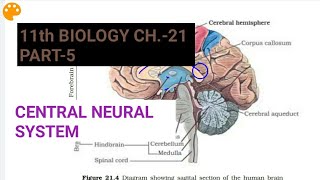
- Brain: Divided into several parts, including the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain, each responsible for specific functions ranging from sensory processing to motor control and autonomic regulation.
- Spinal Cord: Acts as a conduit for signals between the brain and the rest of the body and is involved in reflex actions.
The CNS works in concert with the Peripheral Neural System (PNS) to ensure rapid feedback and efficient coordination of body functions, emphasizing the importance of the neural system in maintaining homeostasis.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to the Human Neural System
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The human neural system is divided into two parts:
(i) the central neural system (CNS)
(ii) the peripheral neural system (PNS)
Detailed Explanation
The human neural system is organized into two main parts: the Central Neural System (CNS) and the Peripheral Neural System (PNS).
- The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord, which serve as the primary processing centers for information and coordination of bodily functions.
- The PNS, on the other hand, includes all the nerves that connect the CNS to the rest of the body, enabling communication between the two systems.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the CNS as the central office of a company where all major decisions are made, while the PNS acts like the network of employees who communicate the decisions to all departments across the company.
Components of the CNS
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The CNS includes the brain and the spinal cord and is the site of information processing and control.
Detailed Explanation
The Central Neural System (CNS) is critical for processing information and executing control functions within the body.
- The Brain: This is the control center of the nervous system, responsible for processing sensory data, sending out motor commands, and supporting other cognitive functions such as memory, thinking, and emotions.
- The Spinal Cord: This acts as a communication highway between the brain and the rest of the body, transmitting signals to and from the brain and coordinating reflexes.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the brain as a computer's CPU processing data and the spinal cord as the USB cables that connect peripherals such as a printer and a keyboard, allowing the computer to communicate effectively with various devices.
Types of Nerve Fibers in PNS
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The nerve fibres of the PNS are of two types: (a) afferent fibres (b) efferent fibres
Detailed Explanation
The Peripheral Neural System (PNS) is made up of different types of nerve fibers that serve distinct functions.
- Afferent Fibres: These fibers carry sensory information from peripheral tissues and organs to the CNS. For example, when you touch a hot surface, afferent fibers transmit the sensation of heat to your brain.
- Efferent Fibres: These fibers transmit commands from the CNS to various body parts, such as muscles or glands. For instance, if the brain decides to move your hand away from that hot surface, the efferent fibers send the appropriate motor signal to the arm muscles.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of afferent fibers as messengers delivering messages from the countryside (your body) to the town hall (CNS), where decisions are made, while efferent fibers are like the town hall sending orders back out to the countryside.
Divisions of the PNS
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The PNS is divided into two divisions called somatic neural system and autonomic neural system.
Detailed Explanation
The Peripheral Neural System is functionally divided into two main systems:
- Somatic Neural System: This system is responsible for voluntary muscle movements. It relays impulses from the CNS to skeletal muscles, enabling us to consciously control movements like walking or writing.
- Autonomic Neural System: This system controls involuntary functions like breathing, heart rate, and digestion. It transmits impulses from the CNS to organs and smooth muscles without conscious effort. The autonomic system is further split into:
- Sympathetic Neural System: Prepares the body for 'fight or flight' responses during stressful situations.
- Parasympathetic Neural System: Helps the body to 'rest and digest', promoting restful functions.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the somatic nervous system as the conductor of an orchestra who directs all the musicians, making sure they play at the right moment. Meanwhile, the autonomic system is like the music playing in the background at a party—it's happening automatically without anyone needing to be aware of it.
Visceral Nervous System
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Visceral nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that comprises the whole complex of nerves, fibres, ganglia, and plexuses by which impulses travel from the central nervous system to the viscera and from the viscera to the central nervous system.
Detailed Explanation
The visceral nervous system is a crucial aspect of the Peripheral Nervous System, responsible for regulating internal organ functions.
- It connects the CNS to the internal organs (viscera), enabling feedback and communication. For instance, it plays a role in controlling the heart and digestive organs by sending signals that help manage their functions based on the body's current needs.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the visceral nervous system as the control room of a factory that monitors and manages various machines (your organs), ensuring they operate smoothly and can respond to changes in the factory's environment.
Key Concepts
-
CNS: Comprises the brain and spinal cord.
-
Brain Functions: Involved in processing sensory information and controlling responses.
-
Spinal Cord: Transmits signals between the brain and body.
-
Three Major Parts of Brain: Forebrain, Midbrain, Hindbrain.
Examples & Applications
The CNS enables quick reflex actions, such as pulling the hand away from a hot surface.
Different regions of the brain work together to perform tasks, like memory recall or motor coordination.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
CNS is the brain and spine, processing signals all the time.
Stories
Imagine a chief in a command center, the brain, guiding the actions of the soldiers, the spinal cord, receiving and relaying every order.
Memory Tools
CIPS - Control, Integration, Processing, Sensory.
Acronyms
Funky Monkeys Hibernate - Forebrain, Midbrain, Hindbrain.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Central Neural System (CNS)
The part of the nervous system that consists of the brain and spinal cord, responsible for processing and integrating sensory information and controlling motor functions.
- Brain
The central organ of the CNS that processes information and controls bodily functions.
- Spinal Cord
The cylindrical structure that transmits signals between the brain and the body and facilitates reflex actions.
- Forebrain
The part of the brain responsible for higher cognitive functions and includes structures such as the cerebrum.
- Hindbrain
The part of the brain responsible for involuntary actions and vital functions, including the medulla and cerebellum.
- Midbrain
The part of the brain that acts as a relay center for information and is involved in various reflex actions.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
