Forebrain
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to the Forebrain
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are diving into the forebrain, which is composed of three main parts: the cerebrum, thalamus, and hypothalamus. Can anyone tell me what role you think the cerebrum plays in our brain?

Isn't the cerebrum the part that controls our thoughts and actions?

Exactly! The cerebrum is responsible for higher brain functions, including thought, movement, and sensory processing. It is divided into two hemispheres, connected by the corpus callosum, which facilitates communication between them.

And how does it connect to the cerebrum?

Great questions! The thalamus acts as a relay station for sensory information, processing and transmitting it to the cerebral cortex. It helps coordinate several brain functions.

I heard the hypothalamus is important too. Why is that?

Yes, indeed! The hypothalamus regulates critical functions like body temperature, hunger, and thirst. It also plays a role in emotional responses. This is tied to the limbic system, which interacts with the hypothalamus.

So the forebrain is quite central to our everyday functions!

Absolutely! To summarize, the forebrain processes information from our senses, manages our body functions, and manages emotional responses, making it crucial for our daily lives.
Exploring the Cerebrum
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's delve deeper into the cerebrum. It's divided into lobes, each responsible for different functions. Can anyone name them?

I think there are frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes?

Perfect! The frontal lobe is associated with reasoning and planning, the parietal lobe processes sensory information, the temporal lobe deals with auditory signals and memory, and the occipital lobe is focused on vision.

How do these areas communicate with each other?

Communication is facilitated by white matter, consisting of myelinated axons. These connections ensure that various regions of the cerebrum share information efficiently.

And what does the cerebral cortex do exactly?

The cerebral cortex is crucial for processing sensory information and performing complex functions, like language and problem-solving. Remember, its gray matter appearance comes from neuron cell bodies!

So can we summarize that the cerebrum is essential for both basic and complex tasks?

Exactly! The cerebrum handles a wide array of functions, from basic sensory perception to higher-level cognitive processes. It's quite remarkable.
Role of the Thalamus and Hypothalamus
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Moving on, let's discuss the functions of the thalamus and hypothalamus. What do you think connects these two structures?

I believe both are involved in sensory processing, right?

Correct! The thalamus processes sensory signals before passing them to the cerebrum. In contrast, the hypothalamus regulates vital functions. For instance, can anyone name one?

Body temperature control?

Yes, the hypothalamus is key for thermoregulation. It helps maintain homeostasis in the body.

What about emotions? How are they related to these areas?

Excellent point! The limbic system, which includes the hypothalamus, influences our emotional responses—such as fear and pleasure—helping regulate motivation and behavior.

This system sounds essential for our daily experiences.

Indeed, and to recap: the thalamus coordinates sensory data, the hypothalamus regulates several body functions including emotions, making them critical components of the forebrain.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The forebrain is the largest part of the human brain, comprising the cerebrum, thalamus, and hypothalamus. It manages higher functions, including sensory perception, voluntary movements, temperature regulation, and emotional responses.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of the Forebrain
The forebrain, primarily composed of the cerebrum, thalamus, and hypothalamus, is crucial for various functions in the human brain.
Cerebrum
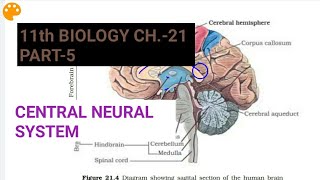
- The cerebrum constitutes the largest part of the brain, divided into left and right hemispheres connected by the corpus callosum.
- The cerebral cortex, characterized by its gray matter, covers the surface with folds, hosting areas responsible for both sensory and motor functions, as well as higher cognitive tasks handled by the association areas.
Thalamus
- The thalamus acts as a key relay station for sensory and motor signals, coordinating information before it reaches the cerebral cortex.
Hypothalamus
- Located beneath the thalamus, the hypothalamus controls essential processes such as body temperature, hunger, thirst, and emotional responses.
- It houses neurosecretory cells that secrete hormones vital for various bodily functions.
Limbic System
- The inner parts include structures like the amygdala and hippocampus, forming the limbic system, crucial for emotional regulation and memory processing.
Overall, the forebrain is a significant region responsible for processing and integrating essential functions and higher-order interactions within the human body.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of the Forebrain
Chapter 1 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The forebrain consists of cerebrum, thalamus and hypothalamus.
Detailed Explanation
The forebrain is a significant part of the human brain that includes three main structures: the cerebrum, thalamus, and hypothalamus. Each of these structures has distinct functions that contribute to the overall operation of our nervous system.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the forebrain as an orchestra, where each section plays its unique part to create harmonious music. The cerebrum is like the lead musician, carrying out complex tasks, while the thalamus and hypothalamus ensure that everything runs smoothly.
Cerebrum Structure and Function
Chapter 2 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Cerebrum forms the major part of the human brain. A deep cleft divides the cerebrum longitudinally into two halves, which are termed as the left and right cerebral hemispheres.
Detailed Explanation
The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain and is divided into two halves known as the left and right cerebral hemispheres. This division allows the brain to compartmentalize different functions, with the left hemisphere typically associated with logical reasoning and language, while the right hemisphere is linked to creativity and spatial awareness.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the cerebrum as a control tower in an airport, where each half manages different flight operations. The left side might handle the arrivals and the right side the departures, ensuring everything is coordinated and organized.
Corpus Callosum
Chapter 3 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The hemispheres are connected by a tract of nerve fibres called corpus callosum.
Detailed Explanation
The corpus callosum is a thick band of nerve fibers that connects the left and right hemispheres of the cerebrum. This connection enables communication between the two sides of the brain, allowing them to work together efficiently.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the corpus callosum as a bridge that connects two islands (the hemispheres), allowing information to flow back and forth freely, ensuring that both islands function as a cohesive unit.
Cerebral Cortex: Grey Matter
Chapter 4 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The layer of cells which covers the cerebral hemisphere is called cerebral cortex and is thrown into prominent folds. The cerebral cortex is referred to as the grey matter due to its greyish appearance.
Detailed Explanation
The cerebral cortex is the outer layer of the cerebrum, often referred to as grey matter owing to the concentration of neuron cell bodies. This layer is thrown into folds which increase its surface area, allowing for more neurons to be packed within it, facilitating complex processing functions such as thinking, learning, and memory.
Examples & Analogies
You can compare the cerebral cortex to a crumpled piece of paper; when crumpled, it provides more surface area for details rather than being flat, just like how it allows more neurons to exist which enhances brain processing.
Cerebral Cortex: White Matter
Chapter 5 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Fibres of the tracts are covered with the myelin sheath, which constitute the inner part of cerebral hemisphere. They give an opaque white appearance to the layer and, hence, is called the white matter.
Detailed Explanation
The inner part of the cerebral hemisphere consists of white matter, which is made up of myelinated axon fibers. The myelin sheath around these fibers gives them their characteristic white appearance, and these fibers facilitate rapid transmission of nerve impulses between different parts of the brain and between the brain and the spinal cord.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of white matter as the highways of the brain, where heavily traveled roads (myelinated fibers) allow vehicles (nerve impulses) to travel quickly to their destinations, compared to side roads (unmyelinated fibers) that might take longer to traverse.
Thalamus Function
Chapter 6 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The cerebrum wraps around a structure called thalamus, which is a major coordinating centre for sensory and motor signaling.
Detailed Explanation
The thalamus acts as a relay station for sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex. It filters information and sends it to the appropriate areas of the brain for processing, playing a crucial role in sensing the environment and coordinating responses.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of the thalamus as a receptionist at a busy office, who directs incoming calls (sensory signals) to the correct departments (cerebral cortex areas), ensuring that every signal is appropriately handled.
Hypothalamus: Regulation Centre
Chapter 7 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Another very important part of the brain called hypothalamus lies at the base of the thalamus. The hypothalamus contains a number of centres which control body temperature, urge for eating and drinking.
Detailed Explanation
The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus and serves as a homeostatic control center for various bodily functions, including the regulation of temperature, hunger, thirst, and circadian rhythms. It plays a vital role in maintaining balance within the body's internal environment.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the hypothalamus as a thermostat in your house, which regulates temperature — if it gets too hot, it cools down (sweating), and if it gets too cold, it warms up (shivering); likewise, it prompts us when to eat or drink to maintain internal balance.
Limbic System: Emotions and Memory
Chapter 8 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The inner parts of cerebral hemispheres and a group of associated deep structures like amygdala, hippocampus, etc., form a complex structure called the limbic lobe or limbic system.
Detailed Explanation
The limbic system, which includes structures such as the amygdala and hippocampus, plays a significant role in regulating emotions, behavior, memory, and motivation. It is essential for forming memories and emotional responses to stimuli.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of the limbic system as a movie theater, where sensory experiences (movies) are processed and linked with emotions (audiences’ reactions), creating memorable experiences that influence how we feel and behave in real life.
Key Concepts
-
Forebrain: Comprised of the cerebrum, thalamus, and hypothalamus; manages complex brain functions.
-
Cerebrum: The largest brain part, responsible for higher cognitive functions and sensory processing.
-
Thalamus: It serves as a relay for sensory and motor signals.
-
Hypothalamus: Controls involuntary functions like temperature and hunger.
-
Limbic System: Regulates emotions and memory through structures like the amygdala and hippocampus.
Examples & Applications
The cerebrum allows us to engage in critical thinking during problem-solving tasks.
The thalamus plays a vital role when we perceive sensations like touch and pain before they reach the cerebral cortex.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the forebrain's sprawl, where functions call, / Cerebrum rules, thalamus stands tall, / Hypothalamus keeps us in line, / For body needs, it's truly divine!
Stories
Imagine a city where the cerebrum is the mayor, overseeing all citizens (neurons), the thalamus is the messenger delivering requests, and the hypothalamus is the caretaker ensuring everyone is fed and at the right temperature.
Memory Tools
Remember 'C-T-H' for Cerebrum, Thalamus, Hypothalamus to recall the components of the forebrain.
Acronyms
C-T-H helps you remember the three main parts of the forebrain.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Cerebrum
The largest part of the brain responsible for higher brain functions such as thought, action, and sensory processing.
- Thalamus
A brain structure that relays sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex.
- Hypothalamus
A region of the forebrain that controls involuntary functions like hunger, thirst, and body temperature.
- Cerebral Cortex
The outer layer of the cerebrum, involved in complex brain functions such as perception and cognition.
- Limbic System
A complex system responsible for emotional regulation, memory, and motivation.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
