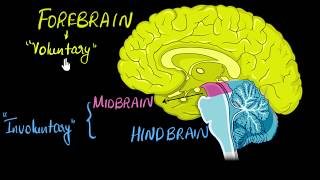
Hindbrain
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Overview of the Hindbrain
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will discuss the hindbrain, which is a crucial part of our brain. Who can tell me what structures are included in the hindbrain?

Is it the pons, cerebellum, and medulla?

That's correct! The hindbrain consists of the pons, cerebellum, and medulla oblongata. Let’s explore each of these parts. What do you think the pons does?

Maybe it connects different parts of the brain?

Exactly! The pons acts as a communication bridge within the brain. Remember the acronym 'PC'M for Pons, Cerebellum, and Medulla. What about the cerebellum? Any ideas?

Isn't it about balancing and coordinating movements?

Yes! The cerebellum helps coordinate voluntary movements and maintains balance. This is very important for activities like playing sports or riding a bike. Lastly, what do you know about the medulla?

I think it controls involuntary actions like breathing?

Exactly! The medulla controls vital functions such as respiration and heart rate. Great job, everyone! Now, let’s summarize: The hindbrain plays a crucial role in essential life functions.
Functions of the Medulla
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we've covered the hindbrain overview, let’s delve deeper into the medulla oblongata. Can anyone tell me how the medulla contributes to survival?

It controls breathing and heartbeat!

Correct! The medulla regulates critical autonomic functions. Together with these functions, it also manages reflex actions like swallowing and sneezing. Can anyone think of why it's essential for the medulla to function properly?

If it doesn’t work, we might stop breathing or our heart might not beat!

Exactly! Dysfunction here can be life-threatening. Always remember: the medulla is a ‘life-saver’ by autonomously managing vital functions. Can anyone summarize what we learned about the medulla?

It controls breathing, heart rate, and reflex actions.

Well done! The medulla's role is indeed crucial for our survival.
Role of the Cerebellum
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s explore the cerebellum now. Who can share its main functions?

It coordinates movements and helps with balance.

Great! The cerebellum integrates sensory input and coordinates muscle activity for smooth motion. Can you think of activities that might involve the cerebellum?

Like playing a musical instrument or dancing!

Exactly! Those activities require precise coordination. Remember the phrase ‘Cerebellum = Coordination’ to help remember its function. How about if someone had a cerebellum injury; what could happen?

They might have trouble walking or moving smoothly.

Correct! Injuries to the cerebellum can severely affect movement and balance. Let’s wrap up: the cerebellum is vital for coordination and maintaining balance.
Functions of the Pons
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s now focus on the pons. What do you think is its importance in the brain?

It connects different parts of the brain, right?

Exactly! The pons helps relay signals between the cerebellum and the cerebrum, playing a critical role in motor control and sensory analysis. How does this feature of the pons benefit our daily activities?

I guess it helps us perform activities that need different parts of our brain to work together.

Yes! It’s essential for smooth execution of movements. Can you remember the acronym we formed earlier for parts of the hindbrain?

PC'M!

Well remembered! Lastly, the pons also plays a role in regulating sleep and arousal. So to summarize: the pons is a vital connector in the hindbrain, aiding communication within the brain.
Integration of the Hindbrain Functions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s connect everything we’ve learned about the hindbrain. How do the pons, cerebellum, and medulla work together?

They coordinate to control body functions and movements.

Exactly! They ensure that everything runs smoothly from our breathing to our movements. Can anyone explain how the loss of one of these parts could affect us?

If the cerebellum is affected, we might stumble while walking or even struggle with our coordination.

Correct! Any disturbance in the hindbrain can lead to significant issues. Let’s conclude our lesson: the interconnectedness of the hindbrain structures is key for our survival and well-being.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The hindbrain consists of three main structures: the pons, which interconnects brain regions; the cerebellum, responsible for movement coordination; and the medulla, controlling autonomic functions like respiration and cardiovascular reflexes, forming a crucial part of our central nervous system.
Detailed
Hindbrain
The hindbrain, one of the three major divisions of the human brain, includes the pons, cerebellum, and medulla oblongata. This section of the brain plays a vital role in coordinating essential bodily functions and integrating motor control.
- Pons: This structure consists of fiber tracts that interconnect various parts of the brain, facilitating communication between different brain regions.
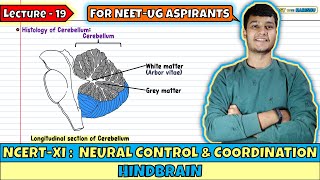
- Cerebellum: Notably characterized by its convoluted surface, the cerebellum is crucial for the coordination of voluntary movement, balance, and fine motor skills by processing sensory information from the body.
- Medulla (Medulla Oblongata): Connecting the brain to the spinal cord, the medulla contains centers regulating automatic functions like respiration, heart rate, and blood pressure. It is vital for sustaining life and responding to physiological changes.
Together, these components form the brain stem, which is essential for survival, forming the bridge between the brain and spinal cord, functioning as the control center for basic life processes.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Structure of the Hindbrain
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The hindbrain comprises pons, cerebellum and medulla (also called the medulla oblongata).
Detailed Explanation
The hindbrain consists of three main parts: the pons, the cerebellum, and the medulla oblongata. These structures work together to maintain essential bodily functions.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the hindbrain as a control center for vital functions, similar to a conductor leading an orchestra, where each instrument plays a crucial role in creating harmonious music.
Function of Pons
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Pons consists of fibre tracts that interconnect different regions of the brain.
Detailed Explanation
The pons serves as a bridge connecting different parts of the brain. It facilitates communication between various brain regions, which is vital for coordinated responses and functions.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the pons as a busy highway interchange, directing traffic between multiple routes, ensuring that information flows smoothly between different areas of the brain.
Function of Cerebellum
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Cerebellum has a very convoluted surface in order to provide the additional space for many more neurons.
Detailed Explanation
The cerebellum’s convoluted surface allows for a greater number of neurons, which enhances its ability to process information related to coordination and balance. It plays a critical role in motor control and ensuring smooth movements.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the cerebellum as a highly skilled pianist whose fingers move gracefully and accurately over the keys, enabling precise and well-coordinated performances.
Function of Medulla Oblongata
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The medulla contains centres which control respiration, cardiovascular reflexes and gastric secretions.
Detailed Explanation
The medulla oblongata is essential for regulating autonomic functions, such as breathing and heart rate. It houses centers that monitor and control these involuntary processes, keeping the body alive without conscious effort.
Examples & Analogies
The medulla can be likened to an automatic pilot in an aircraft, ensuring that essential operations like altitude and speed are maintained without the pilot having to manually adjust them constantly.
Brain Stem Connection
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Three major regions make up the brain stem; mid brain, pons and medulla oblongata. Brain stem forms the connections between the brain and spinal cord.
Detailed Explanation
The brain stem is composed of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata, serving as a vital pathway for communication between the brain and the spinal cord. It is crucial for transmitting signals that control both involuntary functions and higher brain processes.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the brain stem as the main railway station in a city, where all the train lines converge, allowing for efficient transport of information to and from various destinations in the neural network.
Key Concepts
-
Hindbrain: The hindbrain comprises the pons, cerebellum, and medulla, crucial for coordinating automatic functions and voluntary movements.
-
Pons: Connects different regions of the brain and regulates sleep and arousal.
-
Cerebellum: Responsible for coordination of movements and balance, integrating sensory information.
-
Medulla: Controls vital functions including respiration, heart rate, and autonomic reflexes.
Examples & Applications
An example of the pons’ function is its role in sleep regulation, affecting how rested one feels.
The cerebellum is actively involved when you learn to ride a bicycle, helping you balance and coordinate your movements.
A practical example of the medulla's function is when you breathe automatically without conscious effort.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the hindbrain, pons relay, cerebellum helps play, medulla keeps alive our way.
Stories
Imagine a conductor at a concert – the pons connects musicians, the cerebellum ensures they play in sync, and the medulla keeps the music flowing by controlling the tempo.
Memory Tools
Remember 'PCM' for Pons, Cerebellum, Medulla to recall hindbrain parts.
Acronyms
HPC
Hindbrain's Pons Connect to manage brain communication.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Pons
Part of the hindbrain involved in relaying signals between different regions of the brain.
- Cerebellum
A brain structure that coordinates voluntary movements and maintains balance.
- Medulla Oblongata
Part of the brain responsible for controlling vital autonomic functions such as breathing and heart rate.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
