Midbrain
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to the Midbrain
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome, everyone! Today, we're diving into the midbrain. It's located between the forebrain and hindbrain. Can anyone tell me what they might think its function could be?

Maybe it helps with coordination since it connects two major brain parts?

That's spot on! The midbrain serves as a conduit, relaying information between the forebrain and hindbrain. It plays an important role in processing visual and auditory information. Remember, it's crucial for your reflexes.

What areas specifically in the midbrain are responsible for those functions?

Great question! The corpora quadrigemina, composed of two pairs of swellings, handles that. The superior colliculi manage visual reflexes, and the inferior colliculi manage auditory reflexes!

To help remember these parts, think of the acronym 'VARS' – Visual for superior, Auditory for inferior, Reflexes for both. Any questions before we wrap up this session?

So the midbrain is essentially a sensory integration center?

Absolutely! It integrates and processes sensory information before it reaches other parts of the brain. Excellent job!
Role of Midbrain in Reflex Actions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's talk more about reflex actions and the midbrain's role. Can anyone explain what reflex actions are?

They are quick responses to stimuli without conscious thought, right?

Exactly! The midbrain is crucial for this because it processes the sensory information and quickly sends out the motor response. Why do you think this is important?

To help us react quickly to danger or other stimuli?

Exactly right! This rapid processing helps us protect ourselves. The visual reflexes are vital, especially for activities like avoiding obstacles. Let's remember this by associating 'quick reactions' with the midbrain. Anyone else?

So, without the midbrain, our reactions would be slower?

Yes, indeed! The midbrain is like a rapid-response team in our brains. Great understanding, everyone!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
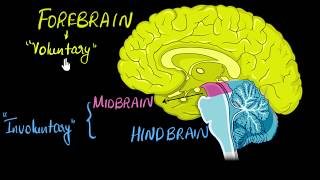
Located between the thalamus/hypothalamus of the forebrain and the pons of the hindbrain, the midbrain contains essential structures like the corpora quadrigemina, which are involved in sensory processing and reflex actions. It also acts as a pathway for nerve impulses traveling between the forebrain and the hindbrain.
Detailed
Midbrain
The midbrain is a vital component of the central nervous system, situated between the forebrain and hindbrain. Its position allows it to act as a conduit for information traveling between these two major parts of the brain. At its core, the midbrain contains several critical structures, including the corpora quadrigemina, which consists of four prominent bulges. These bulges play a significant role in processing various types of sensory information, specifically in visual and auditory reflexes. For example, the superior colliculi are involved in visual reflexes, while the inferior colliculi are responsible for auditory reflexes.
Through these functions, the midbrain helps to integrate sensory input and contributes to the control of movements, maintaining coordination and response to stimuli. Given its role in the processing of crucial sensory information, the midbrain is fundamentally important for daily activities that require quick reflexes and responses.
Youtube Videos




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Location and Structure of the Midbrain
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The midbrain is located between the thalamus/hypothalamus of the forebrain and pons of the hindbrain.
Detailed Explanation
The midbrain serves as a critical connection between the forebrain and hindbrain. It exists at a central point in the brain, which allows for the integration of signals coming from various parts of the brain. Understanding its position can help students visualize how signals flow through the brain—essentially being a middle ground where various functions and pathways converge.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of the midbrain as a train station that connects different train lines (forebrain and hindbrain). Just like trains come together at a station before being sent to their next destination, nerve signals converge in the midbrain before moving to other brain regions.
Cerebral Aqueduct
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A canal called the cerebral aqueduct passes through the midbrain.
Detailed Explanation
The cerebral aqueduct is an important structure within the midbrain that allows the flow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)—the fluid that cushions the brain and spine. CSF plays a crucial role in protecting the brain from injury, removing waste, and providing nutrients. Understanding this canal’s purpose helps illustrate how the body maintains a stable environment for brain function.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the cerebral aqueduct as a water pipeline in a city. Just like water flows through pipes to provide access to clean water for residents, the CSF flows through the cerebral aqueduct ensuring the brain stays hydrated and protected.
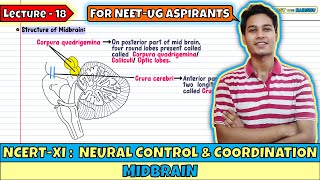
Corpora Quadrigemina
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The dorsal portion of the midbrain consists mainly of four round swellings (lobes) called corpora quadrigemina.
Detailed Explanation
The corpora quadrigemina are critical for processing sensory information, specifically related to vision and hearing. It comprises two pairs of lobes: the superior colliculi (involved in visual processing) and the inferior colliculi (involved in auditory processing). Each set of lobes plays a role in reflex responses to visual and auditory stimuli, helping us react quickly to our environment.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the corpora quadrigemina like a home security system. The superior colliculi act like cameras watching for movement (visual stimuli), while the inferior colliculi are like microphones listening for sounds (auditory stimuli). When something triggers the sensors, both visual and auditory systems alert us about potential dangers, allowing us to respond effectively.
Key Concepts
-
Sensory Processing: The midbrain integrates and processes sensory information for quick reflex responses.
-
Corpora Quadrigemina: The structure in the midbrain responsible for visual and auditory processing.
-
Visual Reflexes: Functions of the superior colliculi to coordinate responses based on visual stimuli.
-
Auditory Reflexes: Functions of the inferior colliculi to respond to auditory stimuli.
Examples & Applications
When you touch a hot surface and withdraw your hand quickly without thinking, that's a reflex action mediated by the midbrain.
If you hear a loud noise and turn your head towards it, this action is governed by the auditory reflexes in the midbrain.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Midbrain's main, is a sensory train, reflexes work fast, never last!
Stories
Imagine a knight who must react quickly to danger. His eyes spot a dragon (visual) and he hears its roar (auditory). The midbrain tells him to quickly draw his sword without thinking!
Memory Tools
M.A.R.V. - Midbrain, Auditory, Reflex, Visual. Remember the primary roles of the midbrain!
Acronyms
C.V.V.A. - Corpora Quadrigemina, Visual, and Auditory functions in the midbrain.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Midbrain
The midbrain is the middle portion of the brain located between the forebrain and hindbrain, involved in sensory processing and reflex control.
- Corpora Quadrigemina
A set of four round swellings located on the dorsal side of the midbrain that process sensory inputs.
- Superior Colliculi
Part of the corpora quadrigemina that is involved in processing visual information and reflexes.
- Inferior Colliculi
Part of the corpora quadrigemina that processes auditory information and reflexes.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
