Characteristics
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Plant Growth Regulators
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll discuss plant growth regulators, or PGRs, which are essential in guiding plant growth and development. Can anyone tell me what they think these molecules do?

Are they like hormones in animals? Do they control growth?

Exactly! PGRs function similarly to hormones by regulating growth processes. They can influence processes like cell division and flowering. Let's remember this with the acronym 'GROW' - Growth Regulators Organize Wonder!

What types of PGRs are there?

Great question! PGRs can be classified mainly into two groups: growth promoters and growth inhibitors. Let's remember this structure with the acronym 'GPI' - Growth Promoters and Inhibitors.
Types of Plant Growth Regulators
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive deeper into each type of PGR. Who can name a growth promoter?

Auxins! I remember those from our earlier lessons.

Exactly right! Auxins are crucial for cell elongation and promoting root growth. What about growth inhibitors?

Abscisic acid? I think it helps plants with stress.

Yes, it acts as a stress hormone and helps in seed dormancy. Remember this with the mnemonic 'A.A.A.' – Abscisic Acid for Adaptation!

Are there other groups?

Yes! We also have gibberellins, cytokinins, and ethylene. Each has unique roles. Let's summarize these by thinking of it as 'A, G, C, E' – representing Auxins, Gibberellins, Cytokinins, and Ethylene!
Discovery of Plant Growth Regulators
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Did you know that the discovery of PGRs was often accidental? For instance, auxin was identified by Charles Darwin's observations. Why do you think such discoveries are crucial?

They help us understand plant behavior and improve crops!

Absolutely! These discoveries have vast implications for agriculture. We should keep in mind that the impact of these regulators can be both positive and negative depending on the context.

What about gibberellins? How were they discovered?

Gibberellins were found from a fungal pathogen affecting rice – showing how closely plant health can relate to other organisms. Let's memorize: 'Gibberellins for Growth Galore!'
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section explores the characteristics of plant growth regulators (PGRs), describing their chemical composition, functional classifications, and the significance of each group in plant growth and development.
Detailed
Characteristics of Plant Growth Regulators
Plant growth regulators (PGRs) are small, simple molecules that exhibit diverse chemical compositions. These compounds play crucial roles in managing growth and developmental processes in plants. The major types of PGRs include auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, abscisic acid, and ethylene, each exhibiting unique physiological effects.
Classification of PGRs
PGRs can be broadly categorized into two groups:
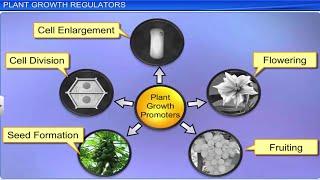
- Growth Promoters - These PGRs stimulate growth-related processes like cell division, flowering, and fruit formation. Examples include auxins and gibberellins.
- Growth Inhibitors - These compounds help plants respond to stress, assisting in dormancy and abscission. An example is abscisic acid, known for its role in stress responses.
Additionally, the discovery of major PGRs has been rooted in both experimental observations and accidental findings, highlighting their importance in plant biology. The distinct pathways through which these molecules influence plant physiology make them essential for agricultural practices and understanding plant life cycles.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Plant Growth Regulators
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The plant growth regulators (PGRs) are small, simple molecules of diverse chemical composition.
Detailed Explanation
Plant growth regulators, often referred to as PGRs, are crucial for the growth and development of plants. These molecules can vary significantly in their chemical structure and composition, which allows them to perform different functions in a plant's life cycle. Examples of PGRs include indole compounds like indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), adenine derivatives such as kinetin, and gases like ethylene.
Examples & Analogies
Think of PGRs as the 'management team' of a plant. Just like a manager can influence different parts of a business to optimize performance, PGRs can stimulate or inhibit various growth processes in plants, ensuring they grow strong and healthy.
Classification Based on Functions
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The PGRs can be broadly divided into two groups based on their functions in a living plant body.
Detailed Explanation
PGRs are categorized into two main groups: those that promote growth and those that inhibit growth. Growth-promoting PGRs include auxins, gibberellins, and cytokinins, which are involved in activities such as cell division, elongation, flowering, and fruit formation. On the other hand, growth-inhibiting PGRs, like abscisic acid, respond to plant stresses and control dormancy and abscission (the shedding of leaves or fruits).
Examples & Analogies
Imagine plants as actors in a play. The growth promoters are like directors who guide the actors to perform their best, while the inhibitors act like producers who step in when the show needs to be paused or adjusted.
Diverse Functions of Plant Growth Regulators
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
One group of PGRs are involved in growth promoting activities, while the other group plays an important role in plant responses to wounds and stresses of biotic and abiotic origin.
Detailed Explanation
The diverse functions of PGRs allow plants to adapt and respond effectively to their environments. Growth promoters enhance crucial processes such as cell expansion, fruit growth, and flowering. Conversely, growth inhibitors help the plant deal with stress, whether from environmental factors like drought or external agents like pests, allowing it to conserve energy when necessary.
Examples & Analogies
Think of PGRs like a team of emergency responders. The growth promoters act like first responders rushing to help areas that are growing and thriving, while the inhibitors are like a crisis management team that steps in during tough times to ensure the plant survives the challenges it faces.
Key Concepts
-
PGRs are crucial for plant growth and development.
-
They are classified into growth promoters and growth inhibitors.
-
Each type of PGR has unique physiological effects.
Examples & Applications
Auxins are used in propagating plant cuttings to induce root growth.
Gibberellins increase grape cluster length in the fruit industry.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Growth is grand, regulators stand, guiding plants across the land!
Stories
Once, in a vast garden, tiny messengers called PGRs guided every flower's bloom, each fruit's ripening, ensuring life thrived beautifully.
Memory Tools
'A G C E' – Auxins, Gibberellins, Cytokinins, Ethylene, to remember the main types of PGRs.
Acronyms
'GPI' – Growth Promoters and Inhibitors, to recall the classification of PGRs.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Plant Growth Regulators (PGRs)
Small, simple molecules that influence plant growth and development processes.
- Auxins
A group of PGRs that promote cell elongation and growth.
- Gibberellins
PGRs that stimulate growth processes such as internode elongation.
- Cytokinins
PGRs that promote cell division and shoot development.
- Abscisic Acid (ABA)
A PGR involved in stress response, helping regulate dormancy.
- Ethylene
A gaseous PGR that regulates fruit ripening and senescence.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
