PLANT GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Plant Growth
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to explore the fascinating concept of plant growth. Can anyone tell me what we mean by growth in plants?

I think it’s how plants get bigger, right?

Exactly! Growth is an irreversible, permanent increase in size. It can be observed in organs, parts, or individual cells. We often measure growth using parameters like fresh weight, length, and cell number. Remember, growth in plants is unique because it’s indeterminate, meaning they continue to grow throughout their lives.

So, plants can keep growing forever?

In a way, yes! This continuous growth is due to the presence of meristems, which are specialized regions in a plant. Can you recall what a meristem is?

Meristems are where new cells are produced, right?

Perfect! Meristematic cells divide continuously, allowing plants to grow taller or wider over time. Just remember the acronym 'M.E.A.' for Meristem, Elongation, and Area to connect these ideas.

That's a cool way to remember it!

Let's summarize. Plant growth is indeterminate, facilitated by meristematic cells, and can be measured in various ways. Next, we'll discuss the different growth phases.
Phases of Growth
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s talk about the phases of growth in plants, which are divided into three main types. Who can name them?

I know! They are meristematic, elongation, and maturation!

Great job! The meristematic phase involves actively dividing cells, the elongation phase is where cells expand and increase in size, and the maturation phase involves cells reaching their full functional potential. Which phase do you think is the most critical for overall plant growth?

Maybe the elongation phase? That's where they get bigger!

That’s a valid point! Each phase plays a vital role, but the elongation phase is indeed where significant size increases occur. Let's practice remembering these with a mnemonic. How about ‘M.E.M. - My Elongating Metamorphosis’?

I like that! Easy to remember!

Excellent! Each stage is crucial for the plant's development. Now, let’s discuss the factors affecting growth.
Factors Influencing Growth
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Which factors do you think influence plant growth the most?

I think water is really important.

Absolutely! Water is essential as it aids in cell turgidity and enzymatic activity. Apart from water, plants also rely on nutrients, sunlight, and temperature. Can anyone explain the difference between intrinsic and extrinsic factors?

Intrinsic factors are internal, like hormones, and extrinsic are external, like light and temperature, right?

Spot on! Intrinsic factors include plant growth regulators, which directly impact growth and development. Let’s remember this with the mnemonic ‘I’m Highly Effective’ - Intrinsic factors: Hormones, Enzymes, Environmental factors! By understanding these factors, you can better grasp the plant’s response to its environment.

I get it! So, the environment plays a huge role.

Yes, it’s all interconnected! In summary, both intrinsic and extrinsic factors significantly influence plant growth.
Plant Growth Regulators (PGRs)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's shift our focus to plant growth regulators, or PGRs. What role do you think these chemicals play?

They must help plants grow better, right?

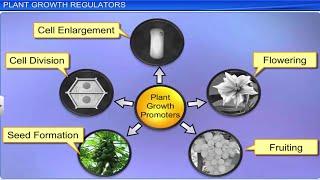
Exactly! PGRs are responsible for regulating various aspects of growth and response to environmental stimuli. There are five major groups: auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, ethylene, and abscisic acid. Can anyone name one function of auxins?

Auxins help with root development!

Right again! They also influence flowering and prevent the dropping of immature fruits. Let’s use the acronym ‘A.G.C.E.A’ to remember them—Auxins, Gibberellins, Cytokinins, Ethylene, Abscisic acid. Each plays a unique role in plant growth.

What about ethylene? What does it do?

Ethylene is crucial for fruit ripening and leaf abscission. It's a gas that affects many aspects of growth. Remember its wide impact by saying, ‘E for Everything!’. So let’s wrap up the key points learned about PGRs.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section delves into how plants grow from a zygote to maturity through the processes of growth, differentiation, and development. It also explores how plant growth is controlled by various external and internal factors, emphasizing the role of plant growth regulators.
Detailed
In this section, we examine the fundamental aspects of plant growth and development, highlighting key concepts such as growth, differentiation, dedifferentiation, and redifferentiation. Growth in plants is characterized as indeterminate, facilitated by the presence of meristems. The section delineates how growth can be measured and categorized into distinct phases—meristematic, elongation, and maturation—each playing a crucial role in plant development. Furthermore, the mechanisms governing growth rates, types of growth (arithmetic and geometric), and the conditions necessary for optimal growth are elaborated upon. The interplay between differentiation, dedifferentiation, and redifferentiation reflects the dynamic nature of plant structure and function. The integration of intrinsic factors (like genetic influences) and extrinsic factors (such as light and nutrients) through plant growth regulators (PGRs) further emphasizes the complexity of plant development. This section serves as a foundational overview of how plants interact with their environment and adapt through various phases of growth and development.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Growth
Chapter 1 of 9
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Growth is regarded as one of the most fundamental and conspicuous characteristics of a living being. What is growth? Growth can be defined as an irreversible permanent increase in size of an organ or its parts or even of an individual cell.
Detailed Explanation
Growth is a key feature of every living organism. It means that an organism, or its parts, becomes larger or increases in number in a permanent way. For example, when a tree grows taller or when a leaf expands, this is considered growth. Similarly, when a single cell divides and increases in number, that too is growth.
Examples & Analogies
Think of growth like feeding a puppy. As you feed the puppy, it grows bigger and stronger. Just like the puppy grows and changes size, plants grow and develop, becoming larger over time.
Indeterminate Growth in Plants
Chapter 2 of 9
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Plant growth is unique because plants retain the capacity for unlimited growth throughout their life. This ability of the plants is due to the presence of meristems at certain locations in their body.
Detailed Explanation
Unlike animals that grow to a certain size and then stop, many plants can keep growing indefinitely because they have special tissues called meristems. These meristems are found in parts of the plant that keep dividing and producing new cells. This allows plants to grow taller or expand their girth continuously throughout their lifetime.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a plant as a set of building blocks. As long as you keep adding blocks (through meristems), the tower (the plant) keeps growing taller! Unlike a statue that won’t get any bigger once it’s done, a plant can keep growing and changing as long as it has these building blocks.
Measuring Growth
Chapter 3 of 9
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Growth, at a cellular level, is principally a consequence of increase in the amount of protoplasm. Growth is measured by a variety of parameters such as increase in fresh weight, dry weight, length, area, volume and cell number.
Detailed Explanation
When we want to know how much a plant has grown, we cannot just look at it; instead, scientists measure different things. These measurements include how much it weighs, how tall it is, or how many cells it has. Each of these measurements helps to show how the plant is increasing in size or mass.
Examples & Analogies
Think about how you measure your own growth. You might step on a scale to see how much you weigh, or stand back-to-back with a friend to see who is taller. Just like this, scientists use various methods to see how much the plant has 'grown up.'
Phases of Growth
Chapter 4 of 9
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The period of growth is generally divided into three phases, namely, meristematic, elongation and maturation.
Detailed Explanation
Plant growth occurs in three distinct phases. The first phase, 'meristematic,' consists of cells that are constantly dividing. In the second phase, 'elongation,' the cells increase in size. Finally, during 'maturation,' the cells develop into specialized cells with specific functions, such as making leaves or roots.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a person learning to play basketball. At first, they practice basic skills (meristematic phase), then they grow taller and become more coordinated (elongation phase), and finally, they learn advanced plays and strategies (maturation phase) to become skilled players.
Growth Rates
Chapter 5 of 9
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The increased growth per unit time is termed as growth rate. The growth rate shows an increase that may be arithmetic or geometrical.
Detailed Explanation
The speed at which something grows is called its growth rate. In plants, this can happen in two ways: arithmetic growth, where growth happens at a steady pace, and geometric growth, where growth starts slowly and then speeds up dramatically.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a movie. At first, there are just a few viewers in the theater (slow growth). But as word spreads and more people start watching, the audience fills the seats fast (rapid growth). In plants, something similar happens: they can grow steadily at one time and then, when conditions are right, they can grow much faster!
Conditions for Growth
Chapter 6 of 9
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The plant cells grow in size by cell enlargement which in turn requires water. Turgidity of cells helps in extension growth.
Detailed Explanation
For a plant to grow, it needs certain conditions to be just right. Water is crucial because it helps plant cells fill up and become turgid, allowing them to expand. Without enough water, plants struggle to grow and may wilt. They also need nutrients and the right temperature to thrive.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how you feel when you're thirsty; you might feel weak and tired. Just like when you drink water to feel better, plants need water to grow strong and healthy. If they don’t get it, they can’t grow properly.
Differentiation, Dedifferentiation, and Redifferentiation
Chapter 7 of 9
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The cells derived from root apical and shoot-apical meristems and cambium differentiate and mature to perform specific functions. This act leading to maturation is termed as differentiation.
Detailed Explanation
Differentiation is the process where cells become specialized to carry out specific tasks in the plant. For example, some cells might become root cells that absorb water, while others become leaf cells that capture sunlight. Sometimes, cells can change back to a less specialized state (dedifferentiation) if the plant needs to adapt, then they can become specialized again (redifferentiation).
Examples & Analogies
Think of a group of friends who start playing different roles in a play. At first, they can all do anything (like undifferentiated cells), but then they choose to take specific roles, such as a hero or a villain (differentiated cells). If someone needs to switch roles, they can, just like how plant cells can change back to a less specific form!
Development in Plants
Chapter 8 of 9
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Development is a term that includes all changes a plant undergoes during its life cycle from germination of the seed to senescence.
Detailed Explanation
The term 'development' encompasses all the changes a plant goes through from a tiny seed to a fully grown plant and, eventually, to the end of its life. This includes germinating from a seed, growing roots and leaves, producing flowers, and eventually aging.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of a plant's development like a child growing up. They start as a baby (seed), learn to walk and talk (germination and early growth), go to school (developing leaves and flowers), and eventually grow into adults with complex lives (mature plants). Each stage is important in their overall development.
Summary of Plant Growth and Development
Chapter 9 of 9
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Growth, differentiation and development are very closely related events in the life of a plant. Broadly, development is considered as the sum of growth and differentiation.
Detailed Explanation
In summary, the life stages of a plant involve growing larger (growth), changing tissues to perform different functions (differentiation), and going through various life stages (development). All these processes are interconnected and essential for the plant to thrive and adapt over time.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine building a house. First, you need to lay the foundation (growth), then build the walls with different rooms for different purposes (differentiation), and finally furnish and finish the interiors (development). Each step is necessary to create a solid, functioning home, just as each step is crucial for a plant's life.
Key Concepts
-
Indeterminate Growth: Plants continue to grow throughout their lives due to the presence of meristems.
-
Phases of Growth: Growth is categorized into three main phases—meristematic, elongation, and maturation.
-
Plant Growth Regulators (PGRs): Chemical substances that regulate physiological processes in plants.
-
Differentiation: The process by which cells become specialized in structure and function.
-
Open Differentiation: Refers to how cells from the same meristem can mature differently based on their location.
Examples & Applications
A seed germinates and grows into a plant when provided with water, sunlight, and nutrients.
The growth of roots in response to gravity (gravitropism) showcases the effect of environmental signals.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To grow, plants know, where meristems show, new roots and leaves will grow.
Stories
Once a tiny seed found itself in a rich garden. With the right water, nutrients, and light, it called on its helpers, the PGRs, to start growing. It felt the warmth of the sun and started to stretch taller each day, becoming part of the beautiful garden.
Memory Tools
A.G.C.E.A. for Plant Growth Regulators: Auxins, Gibberellins, Cytokinins, Ethylene, Abscisic Acid.
Acronyms
M.E.M. for Growth Phases
Meristematic
Elongation
Maturation.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Growth
An irreversible permanent increase in size of an organ, part, or cell.
- Meristem
A region of undifferentiated plant cells capable of cell division.
- Differentiation
The process by which generic cells become specialized for specific functions.
- Dedifferentiation
The process through which mature cells regain the ability to divide.
- Redifferentiation
The phenomenon where dedifferentiated cells mature again to perform specific functionalities.
- Plant Growth Regulators (PGRs)
Chemical substances that influence plant growth and development processes.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
