Development
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Development
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Good morning, everyone! Today, we’ll explore the concept of development in plants. Development refers to the entire lifecycle of a plant, from germination to senescence. Why do you think this full process is crucial for plants?

I think it shows how plants grow and change over time!

Exactly! It helps plants adapt to their environment and fulfill their roles in ecosystems. Can anyone define what we mean by 'plasticity' in plant development?

Isn't it the ability of plants to change their growth forms based on their surroundings?

Well done! That’s a perfect explanation. Plasticity allows plants to survive in varying conditions.
Growth and Differentiation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand plasticity, let's talk about growth and differentiation. Can someone explain growth in the context of plants?

I remember growth as an increase in size, right? It's irreversible.

Correct! It leads to larger roots, stems, or leaves over time. And differentiation allows these new cells to take on specialized roles. What do you think would happen if growth occurred without differentiation?

Maybe we'd have a plant that keeps growing but doesn’t develop any useful structures?

Exactly! You all are catching on quickly. Let’s review some key terms: Growth = increase in size; Differentiation = specialization.
Intrinsic and Extrinsic Factors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, we consider intrinsic and extrinsic factors. Can anyone describe intrinsic factors?

Those would be internal, like genetic components and plant growth regulators.

Exactly! Now, what about extrinsic factors?

External factors like light, temperature, and water!

Great job! These factors all interact creatively to drive the plant’s development. Can you think of an example of how these might come into play?

A plant might grow towards light, right? That's a response to the environment!

Very insightful! It's called phototropism, and it shows how flexible and responsive plants can be.
Summary and Review of Development Concepts
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

As we wrap up, let’s recap what we’ve learned about development today. What key points stand out to you?

The relationship between growth and differentiation!

And how both intrinsic and extrinsic factors impact development!

Absolutely! Understanding these relationships helps us appreciate how plants thrive and adapt. Remember: development is a continuous process influenced by many factors.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Development in plants includes the processes from seed germination through maturity to senescence, influenced by intrinsic and extrinsic factors. It is characterized by plasticity, allowing plants to adapt their growth and structures to environmental conditions.
Detailed
Development in Plants
Development is defined as the series of changes that an organism undergoes throughout its life cycle, starting from seed germination and continuing to senescence. In this context, development includes both growth and differentiation processes, leading to the creation of various structure types in plants. The development of plants is characterized by:
- Plasticity: Plants exhibit the ability to change their growth patterns based on environmental conditions, such as light and water. For example, plants may have different leaf shapes (heterophylly) in juvenile versus mature stages or when grown in water versus air.
- Integration of Growth and Differentiation: Development involves coordinated growth (an irreversible increase in size) and differentiation (the process through which generic cells become specialized in structure and function). Both processes are influenced by intrinsic factors like genetics and hormones, and extrinsic factors such as temperature, light, and moisture.
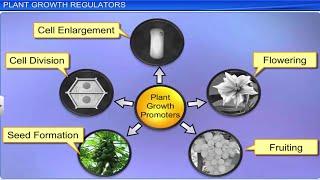
- Control Mechanisms: The development of plants is regulated by various plant growth regulators (PGRs) such as auxins, gibberellins, and cytokinins, which interact to promote or inhibit growth activities.
In summary, development is a complex and flexible process that allows higher plants to adapt to their environment and fulfill their life cycle efficiently.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Development
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Development is a term that includes all changes that an organism goes through during its life cycle from germination of the seed to senescence.
Detailed Explanation
Development in plants refers to the entire series of changes that occur from the moment a seed germinates until the plant reaches the end of its life cycle, which includes aging (senescence). This means that development encompasses every stage, such as cell division, growth, and differentiation throughout the plant's life.
Examples & Analogies
Think of development like the journey of a person from birth to old age. Just as people grow, learn, and go through various life stages, plants also undergo transformations from a tiny seed to a mature plant, eventually aging and dying.
Pathways and Plasticity
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Plants follow different pathways in response to environment or phases of life to form different kinds of structures. This ability is called plasticity, e.g., heterophylly in cotton, coriander and larkspur.
Detailed Explanation
Plants can adapt their growth and development based on external conditions, which is referred to as plasticity. For example, certain plants, like larkspur, can produce different leaf shapes depending on environmental factors. This versatility allows plants to optimize their growth in varying conditions, enhancing survival and reproduction.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a chameleon changing its color to blend in with its environment. Similarly, plants adjust their structural features, like leaf shapes, to better suit their surroundings, helping them thrive.
Interrelation of Growth, Differentiation, and Development
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Thus, growth, differentiation, and development are very closely related events in the life of a plant. Broadly, development is considered as the sum of growth and differentiation.
Detailed Explanation
Growth, which is the increase in size, and differentiation, which is the process by which cells become specialized for different functions, are essential components of development. Essentially, development can be viewed as a combination of these two processes, occurring simultaneously throughout the life of a plant to ensure it can successfully adapt and thrive.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a child learning to walk (growth) and gradually being able to perform different tasks like running, playing, and learning (differentiation). In plants, as they grow, they also develop various functions that allow them to perform tasks such as photosynthesis, reproduction, and nutrient uptake.
Influence of Intrinsic and Extrinsic Factors
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Development in plants (i.e., both growth and differentiation) is under the control of intrinsic and extrinsic factors.
Detailed Explanation
The development of plants is influenced by both internal (intrinsic) and external (extrinsic) factors. Intrinsic factors include genetic and hormonal influences within the plant, while extrinsic factors comprise environmental conditions like light, temperature, and water. These influences determine how a plant grows and develops at each stage of its life cycle.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a plant as a student in a classroom. The student (the plant) brings their own abilities and learning style (intrinsic factors) but is also influenced by the teaching methods, school environment, and resources available (extrinsic factors) which affect how they learn and grow.
Key Concepts
-
Development: All changes from germination to senescence.
-
Plasticity: Ability to change adaptations based on environment.
-
Growth: Irreversible increase in size.
-
Differentiation: Process of specialization within cells.
-
Intrinsic Factors: Genetics and hormones affecting development.
-
Extrinsic Factors: Environmental influences on plant growth.
Examples & Applications
A plant showing heterophylly, with juvenile leaves differing in shape from mature leaves.
Phototropism, where plants grow towards a light source to maximize exposure.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Growth is how plants get big, while differentiation's like a jig; one sizes up, the other’s specialized, together in life, plants are realized!
Stories
Once in a garden, a seed sprouted, filled with dreams of growth and clouted. It saw sunlight and stretched high, while roots dug deep, it waved goodbye! Through seasons, it changed, adjusting its form to thrive in the rain or the sun warm.
Memory Tools
Remember 'GIDE' for plant change: Growth, Intrinsic, Development, Extrinsic.
Acronyms
P.E.D. - Plasticity, Environment, Development define how plants evolve!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Development
The series of changes that an organism undergoes throughout its life cycle, including growth and differentiation.
- Plasticity
The ability of plants to change their growth patterns and structures in response to environmental factors.
- Growth
An irreversible increase in the size or mass of an organ or an organism.
- Differentiation
The process where cells become specialized in structure and function.
- Intrinsic Factors
Internal aspects, such as genetic makeup and hormones, that influence development.
- Extrinsic Factors
External elements, like light, temperature, and nutrients, that affect growth and development.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
