Cytokinins
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Cytokinins
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're focusing on cytokinins, a crucial group of plant hormones. Can anyone tell me what they know about them?

I think they help plants grow. Like, they support cell division?

Exactly, Student_1! Cytokinins are very much involved in promoting cytokinesis or cell division. They were discovered in herring sperm. Kinetin is one of the early examples, found from purified DNA.

So, where exactly are cytokinins made in the plant?

Great question, Student_2! Cytokinins are primarily synthesized in areas of active growth, such as the root apices and young fruits. This allows them to play a critical role in growth regulation.

To help remember this, think of 'C' for Cytokinesis and 'C' for Cell growth! Can you all come up with another point about cytokinins?

Uh, do they help with the growth of shoots too?

Yes! Cytokinins promote lateral shoot growth as well, which often helps overcome apical dominance by encouraging side shoot development. Remember the acronym 'LAD' for Lateral shoot and Apical dominance.

Key points here: cytokinins support cell division, are synthesized in growing tissues, and encourage lateral growth!
Functions of Cytokinins
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s delve into the physiological functions of cytokinins. They help delay leaf senescence, but how does that work?

Is it related to how they help with nutrient mobilization?

Exactly right, Student_4! Cytokinins promote nutrient mobilization from other parts of the plant to the leaves, delaying aging. Can anyone think of why delaying senescence might be beneficial?

It could help the plant gather more sunlight or energy before it starts dying?

Exactly! Longer-lasting leaves mean more photosynthesis and better growth potential. Now, let’s summarize the effects of cytokinins: they promote cell division, lateral shoot growth, and delay leaf senescence.
Application of Cytokinins in Agriculture
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s talk about the practical applications of cytokinins in agriculture. How might farmers use cytokinins?

Maybe to increase the yield of certain crops?

Correct again, Student_2! Farmers can use cytokinins to boost crop yields by promoting healthier, stronger plants. This includes enhancing flowering, fruit set, and even extending the harvesting period.

What about when it comes to plant tissue culture?

Excellent point, Student_3! Cytokinins are essential in plant tissue culture as they stimulate cell division and help in the development of new plants from cells. To help you remember, think of 'CTC'—Cytokinins in Tissue Culture!

So in summary: cytokinins are key in agriculture for yield improvement and are vital in plant propagation technology.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Cytokinins, first discovered in herring sperm DNA, are essential for stimulating cytokinesis, promoting lateral shoot growth, and delaying leaf senescence. They are synthesized in rapidly dividing tissues and can help in overcoming apical dominance, playing a vital role in plant development and growth regulation.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of Cytokinins
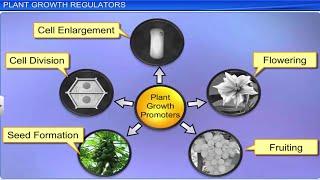
Cytokinins are a class of plant growth regulators primarily known for their ability to promote cell division (cytokinesis). They were first identified from kinetin derived from herring sperm DNA and later, zeatin was discovered in corn and coconut milk. These hormones are synthesized in areas of active growth, such as root apices and developing shoots. Cytokinins play several critical roles in plants, including:
- Promotion of Cell Division: They stimulate the division of plant cells, making them crucial during the development of new tissues and organs.
- Influencing Shoot Growth: Cytokinins promote the growth of lateral shoots, effectively overcoming apical dominance where the main shoot inhibits the growth of side shoots.
- Delaying Senescence: By promoting nutrient mobilization, cytokinins help delay leaf senescence, thus prolonging the life of leaves and improving overall plant vitality.
Their significance extends to agricultural applications, where they are used to enhance crop yield and manage plant growth more effectively. A deeper understanding of their mechanisms can provide ways to optimize plant growth and health.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Discovery of Cytokinins
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Cytokinins have specific effects on cytokinesis, and were discovered as kinetin (a modified form of adenine, a purine) from the autoclaved herring sperm DNA. Kinetin does not occur naturally in plants. Search for natural substances with cytokinin-like activities led to the isolation of zeatin from corn-kernels and coconut milk.
Detailed Explanation
Cytokinins are a type of plant growth regulator that play a vital role in cell division (cytokinesis). The discovery of these compounds began with kinetin, which is a synthetic version derived from DNA of herring sperm. Although kinetin is not naturally found in plants, researchers sought natural equivalents and found zeatin, which is present in corn kernels and coconut milk. This highlights the journey of scientific exploration in plant biology.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine discovering a new type of nutrient for plants similar to finding an alternative energy drink that boosts energy in athletes. Just as athletes seek out the best supplements based on research, scientists sought natural compounds in plants that enhance growth and vitality.
Functions of Cytokinins
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Since the discovery of zeatin, several naturally occurring cytokinins, and some synthetic compounds with cell division promoting activity, have been identified. Natural cytokinins are synthesised in regions where rapid cell division occurs, for example, root apices, developing shoot buds, young fruits etc.
Detailed Explanation
Cytokinins are produced in areas of the plant that are actively growing, such as the tips of roots and shoots, and in young fruits. This production supports the plant's ability to develop new tissues. When cytokinins are present, they stimulate the formation of new leaves and help in the growth of shoots. They are essentially growth boosters for developing plant tissues.
Examples & Analogies
Think of cytokinins as plant fertilizers that are specifically designed to promote new growth. Just as gardeners add fertilizer to boost flower blooms or vegetable growth, cytokinins enhance the plant's ability to create new structures and sustain life.
Role in Overcoming Apical Dominance
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Cytokinins help overcome the apical dominance. They promote nutrient mobilisation which helps in the delay of leaf senescence.
Detailed Explanation
Apical dominance is the phenomenon where the main bud of a plant suppresses the growth of lateral buds. Cytokinins counteract this effect, allowing lateral buds to grow, which leads to a more bushy and fuller plant appearance. They also assist in moving nutrients within the plant, which not only supports growth but also helps keep leaves alive longer before they fall off.
Examples & Analogies
This situation can be compared to a family where the oldest sibling tends to take charge, controlling the younger siblings' activities. If support (cytokinins) is provided to the younger siblings, they can flourish and show their potential just as the lower buds on a plant can grow when apical dominance is reduced.
Key Concepts
-
Cytokinins: Plant hormones that primarily promote cell division.
-
Kinetin: The first identified cytokinin.
-
Zeatin: A naturally occurring cytokinin in corn.
-
Apical Dominance: The suppression of side shoots by the main shoot.
-
Nutrient Mobilization: How cytokinins help in moving nutrients to delay leaf senescence.
Examples & Applications
Use of cytokinins in tissue culture to develop new plant tissues.
Application of cytokinins in agriculture to increase crop yields by promoting lateral growth.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Cytokinins grow stems and leaves, helping plants achieve their heaves.
Stories
Imagine a garden where little green sprouts come to life as cytokinins work their magic, giving energy and strength to those tiny shoots reaching towards the sun.
Memory Tools
Remember 'C.A.L.S.' for Cytokinins, Apical dominance, Lateral growth, and Senescence delay.
Acronyms
Cytokinins = 'C' for Cell division, 'Y' for Young tissues, 'T' for Tissue culture applications.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Cytokinins
A group of plant hormones that promote cell division and affect growth and development.
- Cytokinesis
The process of cell division, resulting in the formation of two daughter cells.
- Apical Dominance
The phenomenon where the main shoot suppresses the growth of lateral shoots.
- Senescence
The process of aging in plants, leading to the eventual death of tissues.
- Kinetin
The first cytokinin discovered, derived from herring sperm DNA.
- Zeatin
A naturally occurring cytokinin found in corn and coconut milk.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
