Conditions for Growth
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Importance of Water for Growth
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's explore why water is crucial for plant growth. Can anyone tell me how water affects plant cells?

I think it helps them become turgid, which supports their structure!

Exactly, Student_1! Water indeed helps maintain cell turgidity. Remember, we can use the acronym 'WET' to recall that water is essential for extension and turgidity. Can anyone elaborate on another function?

It also provides a medium for enzymatic reactions.

Correct! Enzymatic processes are vital for metabolic activities. So, what do we conclude about water's role?

Water is fundamental for cell growth and functioning!

Great summary! Now let’s move to the role of oxygen.
The Role of Oxygen
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Why is oxygen essential for plant growth? Anyone?

Isn't oxygen important for respiration?

Absolutely! Oxygen supports aerobic respiration, which is how plants release energy for growth. Remember the mnemonic 'O2 for Growth' — it reminds us that oxygen is key for sustaining life and energy release. Can anyone think of the consequences of low oxygen levels in soil?

Plants might not grow well and could even die, right?

Precisely! Lack of oxygen can lead to poor root growth and affect the overall plant health. Now, let’s wrap this session up. What have we learned about water and oxygen?

Both are vital for growth processes and overall plant health!
Need for Nutrients
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

What can you tell me about nutrients and why they are important?

Plants need nutrients to grow strong and healthy, and they are used in making protoplasm.

Correct! Macronutrients and micronutrients are both vital. Here’s a mnemonic to remember some key nutrients: 'N-P-K-Ca-Mg' for nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, and magnesium. What happens if there's a nutrient deficiency?

The plant may exhibit stunted growth or yellowing of leaves.

Exactly! Nutrients are essential for metabolic functions and growth. Let's summarize the importance of nutrients, water, and oxygen in plant development at the end of this section.
Temperature and Environmental Factors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s touch on temperature. What should plants have in terms of temperature for optimal growth?

Plants have an optimal temperature range, and anything outside that range can be harmful.

Correct! Just like humans, plants prefer their comfortable climate. Furthermore, what are some environmental signals that affect plant growth?

Light and gravity!

Exactly! Light is vital for photosynthesis, and gravity helps in orienting growth direction. Before we conclude this session, can anyone summarize how temperature and environmental factors contribute to plant growth?

Both help ensure that plants grow in the best conditions possible!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
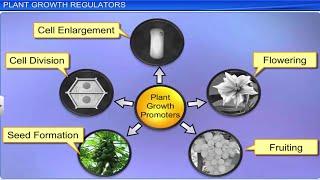
Plants require specific conditions for growth including adequate water, oxygen, and nutrients. These conditions enable cell enlargement and metabolic energy release, ultimately influencing growth rates and developmental processes. Additionally, optimal temperature ranges and environmental signals such as light and gravity are critical for growth.
Detailed
Conditions for Growth
Plant growth is fundamentally dependent on certain necessary conditions, as highlighted in this section. The essential elements for growth include:
- Water: Required for cell enlargement and maintaining turgidity, which supports extension growth. Water also acts as a medium for crucial enzymatic activities that drive growth.
- Oxygen: Important for the release of metabolic energy, facilitating various growth activities in plants.
- Nutrients: Both macronutrients (like nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium) and micronutrients (like iron, copper) are vital for protoplasm synthesis and energy production.
Moreover, each plant has an optimum temperature range that supports its growth, with deviations potentially harmful. Environmental factors such as light and gravity also play crucial roles, affecting different growth phases and overall development. Understanding these conditions helps in optimizing plant cultivation and enhancing growth strategies.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Essential Elements for Plant Growth
Chapter 1 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Why do you not try to write down what you think are necessary conditions for growth? This list may have water, oxygen and nutrients as very essential elements for growth. The plant cells grow in size by cell enlargement which in turn requires water.
Detailed Explanation
Plants need certain conditions to grow effectively. The most critical elements are water, oxygen, and nutrients. Water is fundamental because it allows plant cells to enlarge—a process known as cell turgidity. Turgidity is essential as it helps cells maintain their shape and provides the necessary pressure for growth. Oxygen is vital for plants because it helps them release energy through respiration, thus powering their growth processes.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a sponge. It expands when soaked in water, similar to how plant cells swell and elongate when they take in water. Without sufficient water, the sponge—and the plant—would remain small and inflexible.
Role of Water in Growth
Chapter 2 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Turgidity of cells helps in extension growth. Thus, plant growth and further development is intimately linked to the water status of the plant. Water also provides the medium for enzymatic activities needed for growth.
Detailed Explanation
The turgidity of plant cells, which is their swelling due to water intake, contributes to their ability to grow and extend. This process is critical because the internal pressure from turgidity keeps the plant upright and supports cell expansion, allowing the plant to grow taller and sprout new leaves and stems. Moreover, water is crucial as it serves as the medium for enzymes that facilitate biochemical reactions needed for growth and metabolic processes.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how a soda can pops open and releases fizz when you shake it. The carbonation is under pressure—water in cells acts similarly, and when it is available, the cells push outward and grow, making the plant stand tall, much like the fizz rising to the top of the can.
Importance of Oxygen for Metabolic Energy
Chapter 3 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Oxygen helps in releasing metabolic energy essential for growth activities.
Detailed Explanation
Oxygen is essential for aerobic respiration in plants, a process where cells break down glucose from photosynthesis to release energy. This energy is crucial for various growth activities including nutrient transport, cell division, and overall plant vitality. Without adequate oxygen, these processes are hindered, stunting growth.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to run a race while holding your breath. You would quickly tire and slow down, similar to how plants cannot perform efficiently without enough oxygen. Just as you need air, plants need oxygen to grow effectively.
Nutrients Required for Growth
Chapter 4 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Nutrients (macro and micro essential elements) are required by plants for the synthesis of protoplasm and act as source of energy.
Detailed Explanation
Plants require various nutrients to thrive. Macro and micro nutrients play critical roles in the synthesis of protoplasm, which is the living content of the cell that encompasses all organelles. These nutrients help in processes such as photosynthesis and energy production. Without them, plants would lack the building blocks they need for growth.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a construction site. Just like a building needs bricks, cement, and other materials to be built strong and stable, plants require nutrients to grow healthy and strong. Without the right materials, the structure—whether it’s a building or a plant—can crumble.
Optimum Temperature for Growth
Chapter 5 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In addition, every plant organism has an optimum temperature range best suited for its growth. Any deviation from this range could be detrimental to its survival.
Detailed Explanation
Each plant species has an ideal temperature range that supports its metabolic processes. Temperatures that are too high or too low can negatively affect growth rates and overall plant health. This impact has to do with the protein and enzyme activities, which are temperature-dependent. If the temperature strays too far from the optimum, plants may stress, leading to poor growth or even death.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to make ice cream on a hot summer day—without the right cold conditions, it won't freeze properly! Similarly, plants need their specific temperature range to thrive; out of this range, they may struggle to grow.
Environmental Signals Impacting Growth
Chapter 6 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Environmental signals such as light and gravity also affect certain phases/stages of growth.
Detailed Explanation
Plants respond to environmental signals like light and gravity, which direct their growth patterns. Light influences processes like photosynthesis and flowering, while gravity affects root growth direction. These environmental cues help plants adapt to their surroundings and optimize their growth.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a sunflower following the sun during the day. This behavior, called phototropism, shows how light can guide growth direction. If a plant didn’t respond to light or gravity, it wouldn't be able to grow efficiently, just as a traveler who ignores road signs may get lost.
Key Concepts
-
Water: Crucial for cell turgidity and enzymatic functions.
-
Oxygen: Essential for aerobic respiration and energy production.
-
Nutrients: Macro and micronutrients are required for growth and metabolic activities.
-
Optimal Temperature: Each plant species has a specific temperature range for best growth.
-
Environmental Signals: Light and gravity influence plant growth and development.
Examples & Applications
A plant deprived of water will exhibit wilting due to loss of turgidity.
Plants growing in an area with constant light tend to grow taller and lean toward the light source (phototropism).
Plants experiencing nutrient deficiencies may show symptoms like yellow leaves, indicating a lack of nitrogen.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Plants need water and air, nutrients are fair; too much heat makes them despair!
Stories
Once upon a time, there was a garden where plants flourished when they had just the right amount of water, nutrients, and light. But when the sun shone too bright or they lacked one of their nutrients, they began to wilt and fade, teaching us the balance required for life.
Memory Tools
Remember 'WON' for Water, Oxygen, Nutrients, essential for plant growth.
Acronyms
Use 'WON-T' — Water, Oxygen, Nutrients, Temperature — for remembering conditions for growth.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Turgidity
The stiffness or swelling of plant cells, resulting from water entering the cell and creating internal pressure.
- Macronutrients
Essential nutrients required in larger amounts for plant growth, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
- Micronutrients
Essential nutrients required in smaller amounts for plant growth, including iron, copper, and zinc.
- Aerobic Respiration
The process by which cells use oxygen to produce energy from food.
- Optimal Temperature Range
The specific range of temperatures where a plant grows best.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
