Gibberellins
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Gibberellins
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will discuss gibberellins, an important class of plant growth regulators. Can anyone tell me what they think gibberellins do in plants?

Are they responsible for making plants grow taller?

Great observation! Yes, gibberellins are known to promote stem elongation. They help in the stretching of stems and can even influence the length of grape stalks.

So, they are important for fruit development too, right?

Exactly! Gibberellins can enhance the shape of fruits and promote parthenocarpy, leading to seedless varieties in crops like grapes and tomatoes. This is vital for farmers!

What else do they do?

They also delay senescence, which means they can keep fruits fresh longer on the tree. For instance, by applying gibberellins, sellers can extend the marketability of fruits.

Wow, that sounds really useful. How are they used in agriculture?

Great question! Gibberellins are used to increase yields in crops, like spraying sugarcane to boost its height and, consequently, the sugar yield. They can also speed up maturity in conifers.

To summarize, gibberellins are vital for plant growth by enhancing stem elongation, fruit development, and delaying senescence. They have significant applications in agriculture.
Physiological Responses of Gibberellins
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's delve deeper into the physiological responses induced by gibberellins. Can anyone tell me how gibberellins affect a plant's lifecycle?

Do they just affect growth or is there more?

They influence many aspects! Gibberellins trigger not only growth in terms of height but also developmental processes like bolting in rosette plants, which is crucial before flowering.

What does bolting mean?

Bolting refers to the rapid elongation of stems that many plants undergo in preparation for flowering, often facilitated by gibberellins.

So, are gibberellins used to induce flowering as well?

Yes! By using gibberellins, we can induce flowering in certain crops, thus affecting their yield significantly. This includes crops like cabbages.

If they can delay aging, what’s that concept called?

That's called senescence. Gibberellins can counteract the natural aging process, allowing fruits to stay viable longer on the tree.

To conclude, gibberellins promote significant physiological changes, including growth, bolting, and delaying senescence, all of which have practical implications for agriculture.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
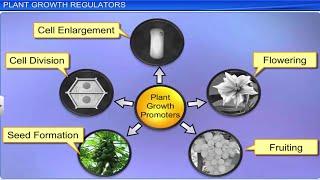
Gibberellins, classified as plant growth regulators, are vital for stimulating various physiological processes in plants, such as promoting stem elongation, enhancing fruit shape, and delaying senescence. With over 100 types identified, gibberellins play essential roles in agriculture and horticulture, affecting growth and improving crop yields.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of Gibberellins
Gibberellins are a group of plant growth regulators (PGRs) that play a crucial role in regulating growth and development in plants. Discovered from the fungal pathogen Gibberella fujikuroi that causes 'bakanae' disease in rice, gibberellins exist in over 100 forms, with gibberellic acid (GA₃) being the most well-studied.
Key Functions of Gibberellins:
- Stem Elongation: They stimulate internode elongation, helping plants grow taller.
- Fruit Development: Gibberellins enhance fruit shape and stimulate seedless fruit development (parthenocarpy) in crops like grapes and tomatoes.
- Delay of Senescence: They can delay the aging process in fruits, extending the shelf life and marketable period by slowing down the ripening process.
- Agricultural Applications: Gibberellins have practical applications in the brewing industry, increasing the yield of sugarcane, and promoting flowering in various plants.
Importance in Agriculture:
Gibberellins significantly influence agricultural practices. For instance, applying gibberellins to sugarcane can boost yield by as much as 20 tonnes per acre, while they also support faster maturity in conifers, leading to earlier seed production.
Gibberellins are integral to plant growth and development, connecting directly to many physiological processes essential for plant fitness and productivity.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Gibberellins
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Gibberellins are another kind of promotory PGR. There are more than 100 gibberellins reported from widely different organisms such as fungi and higher plants. They are denoted as GA1, GA2, GA3, and so on. However, Gibberellic acid (GA3) was one of the first gibberellins to be discovered and remains the most intensively studied form. All GAs are acidic. They produce a wide range of physiological responses in the plants.
Detailed Explanation
Gibberellins are a type of plant growth regulator (PGR) that contribute to plant growth and development. They are found in various organisms, including fungi and higher plants. Among the numerous gibberellins, Gibberellic acid (GA3) is the most researched. All gibberellins are acidic, and they trigger various physiological changes in plants, like growth and development.
Examples & Analogies
Think of gibberellins as a magical growth potion for plants. Just like how a kid might grow taller and stronger after drinking milk, plants use gibberellins to lengthen their stems and grow more robustly.
Functions of Gibberellins
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Their ability to cause an increase in the length of axis is used to increase the length of grapes stalks. Gibberellins, cause fruits like apple to elongate and improve its shape. They also delay senescence. Thus, the fruits can be left on the tree longer so as to extend the market period. GA3 is used to speed up the malting process in the brewing industry.
Detailed Explanation
Gibberellins have several significant roles in plant growth. They help to elongate the stems, which is particularly valuable for crops like grapes, where longer stalks are desired. In fruits such as apples, gibberellins promote elongation, enhancing their shape for better marketability. Additionally, they delay aging, allowing fruits to remain on trees longer, thus prolonging their harvest period. In agriculture, gibberellins also play a role in brewing by accelerating the malting process, which is essential for beer production.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine gibberellins as a plant's personal trainer. Just as a personal trainer can help someone grow stronger and longer over time, gibberellins help plants increase their size, shape, and market readiness.
Impact on Crop Yield
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Sugarcane stores carbohydrate as sugar in their stems. Spraying sugarcane crop with gibberellins increases the length of the stem, thus increasing the yield by as much as 20 tonnes per acre. Spraying juvenile conifers with GAs hastens the maturity period, thus leading to early seed production.
Detailed Explanation
When gibberellins are sprayed on sugarcane, they promote the growth of taller stems, which means the plant can store more carbohydrates in the form of sugar. This can significantly enhance yield, often by up to 20 tonnes per acre. Similarly, juvenile conifers treated with gibberellins mature faster, enabling them to produce seeds sooner. This is beneficial for forestry and agricultural practices where quicker seed production is desired.
Examples & Analogies
Consider gibberellins like fertilizers that boost a plant’s growth potential. Just as better nutrition helps a student finish school faster and achieve better grades, gibberellins help sugarcane and conifers grow better and produce results faster.
Influence on Flowering and Bolting
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Gibberellins also promote bolting (internode elongation just prior to flowering) in beet, cabbages and many plants with rosette habit.
Detailed Explanation
Bolting refers to the rapid elongation of the stem before the plant flowers. Gibberellins encourage this process in several plants such as beets and cabbages, particularly in those that typically have compact growth forms (rosettes). This is crucial for these plants as it helps them prepare for and successfully transition into their flowering phase.
Examples & Analogies
Think of gibberellins as a coach encouraging a runner on the starting line to take that crucial first step. Just like the runner needs that push to get moving, plants rely on gibberellins to help them stretch upward and prepare to bloom.
Key Concepts
-
Gibberellins: Important plant hormones that regulate growth and development.
-
Stem Elongation: Gibberellins stimulate elongation of stem internodes.
-
Senescence: Gibberellins can delay the aging process in fruits.
-
Parthenocarpy: Gibberellins promote seedless fruit development.
Examples & Applications
Gibberellins are sprayed on sugarcane crops to increase yield by enhancing stem length.
In grapes, gibberellins are used to promote elongated shapes and enhance marketability.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
For tall plants, gibberellins call; they help them stand strong and tall.
Stories
Once in a garden, the fruit trees were aging quickly. The wise gardener sprinkled gibberellins, and the fruits stayed fresh and plump, making the trees the envy of the orchard!
Memory Tools
GREAT - Gibberellins Regulate Elongation And Timing (of senescence).
Acronyms
G.A. for Gibberellins Action in growth and development.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Gibberellins
A group of plant hormones that promote growth, especially stem elongation and flowering.
- Senescence
The process of aging in plants that leads to the death of cells or organs.
- Bolting
The rapid elongation of the stem, usually occurring in rosette plants, in preparation for flowering.
- Parthenocarpy
The development of fruit without fertilization, resulting in seedless fruit.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
