Force Law for Simple Harmonic Motion
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Simple Harmonic Force
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to discuss how forces impact simple harmonic motion, or SHM. Can anyone tell me what force means in this context?

Does it mean the push or pull on the object?

Exactly! In SHM, the force responsible for the oscillation is called the 'restoring force' because it acts to return the object back to its equilibrium point. Now, can anyone tell me how we represent this restoring force mathematically?

Isn't it F = -kx?

Close! In terms of SHM, we express it as F(t) = -mω²x(t), where 'x' is the displacement from the equilibrium. This indicates that the force is always directed towards the mean position. Let's remember the force in SHM is negative in relation to the displacement, hinting it's a restoring force!

So the force gets stronger the farther you move away from equilibrium?

Absolutely! This 'spring-like' behavior is fundamental in SHM. Understanding this relationship is key. Great job, everyone!
Applying Newton’s Second Law
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand the restoring force, let’s apply Newton’s second law to derive it. Can anyone remind us what Newton's second law states?

It states that force equals mass times acceleration, right?

Exactly! We use that idea here. If we have our force F = -mω²x, what happens when we substitute F into F=ma?

We can set ma equal to -mω²x, so it simplifies!

Great deduction! So, we find a link between displacement and acceleration via this relationship. Remember: a linear relationship means that the system can perform simple harmonic motion effectively. Can anyone summarize what we've discussed?

The force acting on SHM is proportional to displacement and directed towards equilibrium!

Perfect! That's a comprehensive understanding!
Significance of the Restoring Force
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s delve deeper into the implications of our restoring force. What do you think happens if the restoring force isn’t linear?

Does that mean the motion might be different or not harmonic?

Exactly! If the force deviates from that linear form, like involving x² or higher, we call that a nonlinear oscillator. Can you think of real-world examples where we might encounter these non-linear effects?

Like a swing in strong winds or a musical instrument string?

Spot on! These systems can behave unpredictably. Understanding linear versus non-linear forces helps in designing stable oscillatory systems. As we explore more complex oscillations, these principles will become increasingly relevant!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, the force acting on a particle undergoing simple harmonic motion (SHM) is derived using Newton's second law. The force is characterized as a restoring force, directing the particle towards the equilibrium position, and demonstrates the linearity in relation to displacement, hence defining the motion as harmonic.
Detailed
Force Law for Simple Harmonic Motion
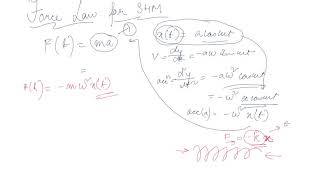
In this section, we explore the dynamics of simple harmonic motion (SHM) through the lens of Newton's second law of motion. When a particle exhibits SHM, the force acting on it can be expressed mathematically as:
F(t) = ma = -mω²x(t)
This equation reveals that the force is proportional to the displacement from the mean position, leading to a restoring nature of the force, hence the term 'restoring force.' Constant 'k' is defined as:
k = mω²
This equation relates the parameters of the system, where 'ω' is the angular frequency. Possessing a restoring force is characteristic of oscillatory systems, defining linear harmonic oscillators. The section also hints at non-linear behaviors in oscillators where the force might involve higher order terms of displacement, such as x² or x³. Understanding these fundamentals provides insights into the nature of SHM and broader oscillatory systems.
Youtube Videos


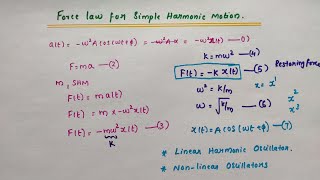




Key Concepts
-
Restoring Force: The force that acts to return the system to its mean position.
-
Newton's Second Law: A foundational principle that links force, mass, and acceleration.
-
Linear vs. Non-linear Oscillators: Linear oscillators follow Hooke's law while non-linear oscillators deal with higher order terms.
Examples & Applications
A mass on a spring exhibits SHM as it oscillates about its equilibrium position when displaced.
A pendulum swinging back and forth in small angles approximates SHM due to the linear restoring force from gravity.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In SHM if you see, force pulls to the mean, it’s strong and it’s clean.
Stories
Think of a swing at a park. The farther you push it away, the stronger it pulls back to the rest, illustrating the restoring force.
Memory Tools
SHM - Simple Harmonic Motion For 'Spring' - Pushing distances simply brings it back.
Acronyms
SHM - 'S' for 'Swing', 'H' for 'Harmonious', 'M' for 'Motion', it's all about balance.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)
A type of periodic motion where the restoring force is directly proportional to the displacement from the mean position.
- Restoring Force
The force that acts to bring a system back to its equilibrium position.
- Newton’s Second Law
A principle stating that the acceleration of an object is proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass.
- Linear Harmonic Oscillator
An oscillator that operates under a restoring force proportional to its displacement.
- Nonlinear Oscillator
An oscillator where the restoring force involves higher-order terms in displacement, deviating from the linear relationship.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
