CALORIMETRY
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Heat Transfer
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will discuss calorimetry, which is the study of heat transfer. Can anyone tell me what heat is in this context?

I think heat is the energy that moves from a hot object to a cool one.

Exactly! Heat moves from areas of higher temperature to areas of lower temperature until thermal equilibrium is reached. Why is this important in calorimetry?

Because it helps us measure how much heat is being transferred between substances?

Correct! And in a calorimeter, heat gained by one substance equals the heat lost by another. Let's remember this as H_gain = H_loss. Now, can anyone explain what an isolated system is?

It's a system where no heat flows in or out, right?

Yes, that's the idea! In an isolated system, all heat exchange occurs internally.

So, if I measure two substances, one hot and one cold, I can find their specific heat capacities?

Yes! You can use the heat exchange formula to solve for specific heat capacity. Great observations, everyone!
Calorimeter Design
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s talk about how a calorimeter is designed. What materials do you think are used for the calorimeter vessel and why?

Is it made of metal like copper or aluminum?

Exactly! Metals are good conductors of heat, which helps in efficiently measuring temperature changes. And why do we use an insulating jacket?

To prevent heat from escaping?

Right! It helps keep the heat within the system, ensuring accurate measurements. We should also think about the stirrer's role. What does it do?

It helps mix the contents for even heat distribution?

Precisely! An even distribution is key for accurate readings in calorimetry.
Calculating Specific Heat Capacity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s work through an example of calculating specific heat capacity using calorimetry. Can someone summarize what we need to find?

We need to determine the heat lost by the hot object and the heat gained by the cold one?

Very good! If we take a sphere of aluminum and place it in water, we can set up the equation H_cold = H_hot. Does anyone remember the formula for calculating heat?

It’s Q = mcΔT!

That's right! So if we apply that to both substances in our calorimeter, we can find the specific heat capacity of aluminum using the mass and temperature change.

And we set the heat gained equal to the heat lost to find the unknown?

Exactly! Great connections being made today!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section introduces calorimetry as the study of heat transfer when bodies at different temperatures come in contact. It discusses heat loss and gain in an isolated system, the role of calorimeters, and provides an example of calculating specific heat capacity.
Detailed
Calorimetry
Calorimetry is the measurement of heat transfer in a system. When different parts of an isolated system are at different temperatures, heat transfers from the part with a higher temperature to the part with a lower temperature.
In this context, the heat lost by the hotter part equals the heat gained by the colder part, assuming no heat loss to the environment. A calorimeter is a device used to measure this heat transfer, consisting of a vessel and a stirrer, often made of metals like copper or aluminum, housed in an insulating jacket to reduce heat loss.
Through practical examples, such as determining the specific heat capacity of materials like aluminum, the principle of heat exchange is illustrated, emphasizing the equality between heat lost and heat gained.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Calorimetry
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A system is said to be isolated if no exchange or transfer of heat occurs between the system and its surroundings. When different parts of an isolated system are at different temperatures, a quantity of heat transfers from the part at higher temperature to the part at lower temperature. The heat lost by the part at higher temperature is equal to the heat gained by the part at lower temperature.
Detailed Explanation
Calorimetry is the scientific measurement of heat. It relies on the principle that in an isolated system, heat will flow from the hotter part to the cooler part until both parts reach the same temperature. This principle is crucial in understanding how heat is transferred and helps in calculating the specific heat capacities of substances through careful measurement.
Examples & Analogies
Think of an ice cube in a warm drink. The heat from the drink warms the ice cube (which is colder), causing it to melt. The drink loses some heat, while the ice cube gains heat until both reach the same temperature. This is like how a game of tag works—heat is 'tagged' from the warmer drink to the cooler ice.
Understanding Calorimeters
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
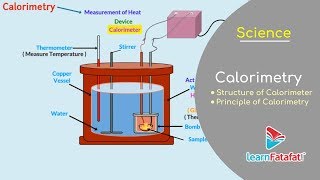
Calorimetry means measurement of heat. When a body at higher temperature is brought in contact with another body at lower temperature, the heat lost by the hot body is equal to the heat gained by the colder body, provided no heat is allowed to escape to the surroundings. A device in which heat measurement can be done is called a calorimeter. It consists of a metallic vessel and stirrer of the same material, like copper or aluminium. The vessel is kept inside a wooden jacket, which contains heat insulating material, like glass wool etc. The outer jacket acts as a heat shield and reduces the heat loss from the inner vessel. There is an opening in the outer jacket through which a mercury thermometer can be inserted into the calorimeter.
Detailed Explanation
A calorimeter is an essential tool for measuring heat changes during chemical reactions or physical changes like melting and boiling. The design of the calorimeter helps to ensure that heat does not escape to the environment, allowing accurate measurements of heat transfer. The use of a stirrer ensures even distribution of temperature within the calorimeter.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a thermal coffee cup designed to keep your coffee hot. Just like a calorimeter, it has insulating layers to maintain temperature. When you pour hot coffee inside, it stays hot longer because the heat doesn't escape as quickly.
Example of Specific Heat Capacity Determination
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The following example provides a method by which the specific heat capacity of a given solid can be determined by using the principle, heat gained is equal to the heat lost. Example 10.3: A sphere of 0.047 kg aluminium is placed for sufficient time in a vessel containing boiling water, so that the sphere is at 100 °C. It is then immediately transferred to 0.14 kg copper calorimeter containing 0.25 kg water at 20 °C. The temperature of water rises and attains a steady state at 23 °C. Calculate the specific heat capacity of aluminium.
Detailed Explanation
In this example, the aluminum sphere, after being heated, is placed in a cooler environment (the calorimeter with water). Here, we assume that heat lost by the aluminum sphere equals the heat gained by the water and the calorimeter. Using the formula for heat transfer and substitution with known quantities, we can solve for the specific heat capacity of aluminum. This example illustrates the principle of conservation of energy in calorimetry.
Examples & Analogies
Think of this like a game of hot potato, where the hot potato (aluminum sphere) is passed around. As it moves from one player (the boiling water) to another (the cooler water), it cools down while the other players warm up, all while keeping track of the temperature shifts.
Key Concepts
-
Calorimetry: The science of measuring heat transfer.
-
Calorimeter: A device designed to measure how much heat is transferred between bodies.
-
Heat exchange: In an isolated system, heat lost by one part equals heat gained by another.
-
Specific heat capacity: The heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of a substance by 1 °C.
-
Insulation: Important in calorimetry to prevent heat loss from the measurement system.
Examples & Applications
An aluminum sphere at 100 °C is placed in a calorimeter with water at 20 °C, reaching a final temperature of 23 °C. By calculating heat lost and gained, we can determine the specific heat capacity of aluminum.
Using a calorimeter, if 0.047 kg of aluminum loses heat equal to the heat gained by 0.25 kg of water heated from 20 °C to 23 °C, the calculation involves setting up the heat transfer equations.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In a chamber cool, the hot and cold, heat they share, tale unfolds.
Stories
Once in a lab, a brave scientist used his trusty calorimeter to understand how heat travels between bodies. One day, he noticed how an aluminum sphere warmed the cold water and wondered about the specifics of heat!
Memory Tools
Heat Always Goes from Hot To Cold (HAGH2C).
Acronyms
C.H.E.A.T - Calorimetry, Heat Exchange, And Transfer.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Calorimetry
The measurement of heat transfer in a system.
- Calorimeter
A device used for measuring heat transfer.
- Isolated System
A system where no heat transfers in or out.
- Heat Capacity
The quantity of heat required to change the temperature of a substance.
- Specific Heat Capacity
The amount of heat per unit mass required to change the temperature of a substance by one degree.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
