LiDAR and 3D Sensing
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to LiDAR Technology
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Good morning class! Today we are diving into LiDAR technology. What do you think LiDAR is used for?

Isn’t it how self-driving cars see their surroundings?

Exactly! LiDAR helps in mapping environments using light. It stands for Light Detection and Ranging. Can anyone tell me how LiDAR detects distances?

It measures how long it takes for light to bounce back?

Great answer! This time delay is critical for determining the distance to various obstacles, which is crucial for navigation. Let's remember this with the acronym "LIT": Light, Interactive, and Time.

So, the more precise the light measurement, the better the detection capabilities?

Exactly! Precision is key in autonomous vehicle navigation.

To recap, LiDAR uses light to measure distances interactive and precisely. Next, we’ll explore the types of semiconductors used.
VCSELs and Photodetectors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's discuss the semiconductor technologies essential for LiDAR. Can anyone tell me what VCSEL stands for?

Is it Vertical-Cavity Surface-Emitting Lasers?

Correct! VCSELs are integral to emitting light in LiDAR systems. Can anyone think of a reason why they might be preferred?

Maybe they are more efficient than other types of lasers?

Yes, they are efficient and compact! Now, what about photodetectors? What materials are often used?

InGaAs and GaAs, right?

Exactly! InGaAs is known for its sensitivity to infrared light, which is beneficial for accuracy in LiDAR. Remember the phrase "IGAS" for InGaAs and GaAs semiconductors.

In summary, VCSELs and photodetectors like InGaAs are crucial for LiDAR technology's efficiency and effectiveness.
Applications of LiDAR in Autonomous Systems
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s discuss how LiDAR affects various technologies. What is one application you know of?

For self-driving cars, I think?

Absolutely right! LiDAR enables these vehicles to understand their environment. Why is that important?

Because it helps avoid obstacles and navigate safely!

Correct! This safety aspect is paramount. Now, can anyone relate LiDAR to augmented reality?

It helps create a 3D map of the environment for AR applications!

Exactly! It aids in integrating digital content with the real world. Let’s remember "3D-ARM": 3D mapping, Augmented Reality, and Mapping.

So, we learned that LiDAR is crucial in both self-driving cars and AR applications. Let’s recap the impactful applications.
Impact of LiDAR on Future Technologies
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's think about the future. How do you think LiDAR will shape new technologies?

More advanced autonomous vehicles and maybe even smart cities?

Excellent insight! Smart cities could utilize LiDAR for traffic management and urban planning. Can anyone imagine a unique application?

What about enhanced security systems?

Yes! LiDAR can improve surveillance through better obstacle detection and depth mapping. Remember "SECURE": Safety Enhancement through Compound Utility and Real-time Evaluation.

To summarize, LiDAR will significantly impact future technologies, especially in autonomous systems and urban planning.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses the role of compound semiconductor technologies, particularly VCSELs and photodetectors, in advancing LiDAR and 3D sensing applications vital for autonomous vehicles, augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and facial recognition, enabling improved depth sensing and obstacle detection.
Detailed
LiDAR and 3D Sensing
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) and 3D sensing are pivotal applications in the realm of emerging technologies powered by compound semiconductors. This section highlights:
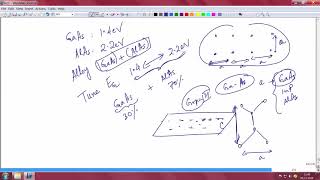
- Semiconductor Devices: The use of Vertical-Cavity Surface-Emitting Lasers (VCSELs) and photodetectors made from materials like InGaAs and GaAs.
- Applications: These technologies play critical roles in navigating autonomous vehicles, enhancing augmented and virtual realities, and enabling advanced facial recognition systems.
- Key Capabilities: By providing accurate depth sensing, obstacle detection, and spatial mapping, LiDAR and 3D sensing technologies significantly contribute to the functionality and safety of autonomous systems. Their integration enables these systems to interact intelligently with their environments, enhancing user experiences across multiple sectors.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to LiDAR and 3D Sensing
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
LiDAR and 3D Sensing
● VCSELs and photodetectors (InGaAs, GaAs)
● Critical for autonomous vehicles, AR/VR, face recognition
Detailed Explanation
LiDAR stands for Light Detection and Ranging. It is a technology that measures distances by illuminating a target with a laser and analyzing the reflected light. In this section, we are discussing how specific types of lasers and sensors—such as Vertical-Cavity Surface-Emitting Lasers (VCSELs) and photodetectors made from materials like Indium Gallium Arsenide (InGaAs) and Gallium Arsenide (GaAs)—are important in applications such as autonomous vehicles, augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and facial recognition. These technologies help in creating detailed 3D maps of environments.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine driving a car with a superpower that allows you to 'see' the world in 3D, even at night or in fog. That's what LiDAR does for autonomous vehicles, acting like a special pair of eyes that can measure distances very accurately, ensuring the vehicle knows where everything is around it.
Applications of LiDAR
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Enable depth sensing, obstacle detection, spatial mapping
Detailed Explanation
LiDAR technology has critical functions, such as depth sensing, which allows devices to understand how far away objects are. This is essential for obstacle detection since autonomous vehicles need to know about any potential barriers in real-time. Spatial mapping involves creating a detailed map of the environment, which is vital for applications like AR and VR, where accurate representation of the space can elevate user experience.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like a video game where your character can maneuver around a virtual world. The game needs to know where all the walls and obstacles are to guide the character correctly. LiDAR performs a similar task in real life by helping vehicles navigate safely through their surroundings.
Key Concepts
-
LiDAR: A technology using light to measure distances for environmental mapping.
-
VCSEL: An efficient semiconductor laser crucial for driving LiDAR systems.
-
Photodetectors: These capture reflected light, converting it into signals for analysis.
-
InGaAs: A semiconducting material favored for infrared light sensitivity.
-
Applications of LiDAR: Include autonomous navigation, AR, VR, and security.
Examples & Applications
LiDAR is used in self-driving cars to detect obstacles and navigate streets safely.
In augmented reality applications, LiDAR provides accurate spatial mapping, allowing for better immersion.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
LiDAR sees far, like a guiding star, measuring depth near and far.
Stories
Imagine a car that can see, using light to know what will be, it maps the world as it drives swiftly, avoiding obstacles efficiently.
Memory Tools
For LiDAR applications, think 'SAFETY': Self-driving cars, Augmented reality, Facial recognition, Enhanced navigation, Technologies in smart cities, and Yielding improvements.
Acronyms
Remember 'LIT' for LiDAR
Light
Interactive
Time.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- LiDAR
A method for measuring distances using light waves, to navigate and map environments.
- VCSEL
Vertical-Cavity Surface-Emitting Laser, an efficient type of semiconductor laser used in LiDAR systems.
- Photodetector
A device that converts light into an electrical signal, essential for detecting reflected light in LiDAR technology.
- InGaAs
Indium Gallium Arsenide, a semiconductor material known for its sensitivity to infrared light.
- GaAs
Gallium Arsenide, a compound semiconductor often used in photodetectors.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
