Quantum and Neuromorphic Computing
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Quantum Computing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’re diving into quantum computing. Can anyone tell me what a qubit is?

Isn't it a quantum version of a regular bit? It can be both 0 and 1?

Exactly! This property is called superposition. In terms of materials, we use compounds like InAs and GaSb to create topological qubits. Can anyone explain why these materials are important?

They’re more resistant to errors, so they’re better for maintaining qubit states!

Spot on! And integrating these materials with silicon helps us develop quantum interconnects. Let’s remember this with the acronym QIS: Quantum, Integration, Stability. Can anyone recall this acronym?

Quantum, Integration, Stability!

Great job! So, let’s summarize today’s discussion: Qubits are the core of quantum computing, and materials like InAs/GaSb are vital due to their error-resistant properties.
Applications of Quantum Computing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's discuss applications. Why are quantum computers important for cryptography?

Because they can crack encryption methods much faster than classical computers!

Correct! Additionally, quantum computers can simulate complex molecules effectively. What does this lead to?

Advancements in drug discovery and materials science!

Exactly right! Let’s connect this with a memory aid: 'QCS' - Quantum Computers Simulate. Use this to remember the impact of quantum computing!

QCS - got it!

To wrap up, quantum computing enables breakthroughs in cryptography and molecular simulation, enhancing various fields.
Neuromorphic Computing Overview
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s shift gears to neuromorphic computing! What do you think this means?

It’s where computers mimic brain activity, right?

Exactly! It aims to replicate how our brains process information. Compound semiconductor photonics are integral here. Student_2, can you explain how?

They allow for ultrafast processing of information!

Right! Let’s use the mnemonic 'Nifty CPUs' to remember that Neuromorphic Computing is all about efficient processing! Can you repeat that?

Nifty CPUs - great!

To summarize, neuromorphic computing uses advanced materials for brain-like processing speeds and efficiency.
Significance and Implications of Neuromorphic Computing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s talk about the implications! How could neuromorphic computing change industries?

It could revolutionize artificial intelligence and machine learning!

Absolutely! With faster processing, we could handle data in real-time. How about applications like driverless cars or real-time navigation?

Yes, they would need fast, efficient processing from neuromorphic systems!

Great insights! Remember this with the term 'RACE' - Real-time AI and Computing Efficiency! Can someone repeat RACE?

RACE - Real-time AI and Computing Efficiency!

Perfect! So, in summary, neuromorphic computing is set to revolutionize multiple sectors by enhancing efficiency and speed.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Compound semiconductors are instrumental in advancing quantum and neuromorphic computing technologies. This section highlights specific materials and applications, such as topological qubits and ultrafast neural networks, that leverage the unique properties of these materials to enhance computational efficiency and capabilities.
Detailed
Quantum and Neuromorphic Computing
In the realm of advanced computing, compound semiconductors play a critical role, particularly in quantum computing and neuromorphic computing.
Quantum Computing
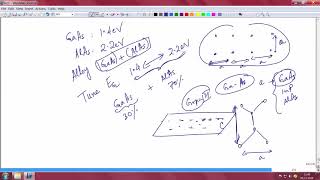
- Topological Qubits: These are quantum bits (qubits) that are particularly robust against certain types of errors. They are achieved through materials like InAs/GaSb and HgTe/CdTe quantum wells, which allow for the manipulation of quantum states crucial for the development of quantum computers.
- Integration with Silicon: The integration of these advanced materials with silicon-based systems aids in the creation of quantum interconnects, which are essential for the scalability of quantum computers.
Neuromorphic Computing
- This refers to computing that mimics the architecture and functioning of the human brain. Compound semiconductor photonics are used to create ultrafast neural networks. These networks can process information at speeds far exceeding traditional architectures, making them suitable for applications that require high efficiency and speed.
- Applications: The implications of these technologies extend into domains such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and real-time data processing, providing significant improvements in performance and efficiency.
In summary, as the demand for advanced computing paradigms increases, the integration of compound semiconductors in quantum and neuromorphic computing remains pivotal, marking a significant evolution in how computational tasks are approached and executed.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Topological Qubits
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
InAs/GaSb and HgTe/CdTe quantum wells for topological qubits
Detailed Explanation
Topological qubits are a type of quantum bit that leverage the unique properties of certain materials to store and process information. The materials mentioned, InAs/GaSb and HgTe/CdTe, are specifically chosen because they can exhibit 'topological' states. These states are less susceptible to errors due to external disturbances, making them promising candidates for stable quantum computing.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to balance a pencil on your finger. If you’re careful, the pencil can stay upright. However, the moment you shake your hand or make a sudden movement, the pencil will likely fall. Topological qubits are like a specially designed pencil that can remain upright despite the shakiness around it, providing more stability in a qubit's operation.
Ultrafast Neural Networks
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Compound semiconductor photonics for ultrafast neural networks
Detailed Explanation
Ultrafast neural networks utilize high-speed data processing capabilities afforded by compound semiconductor photonics. This technology enables the implementation of artificial neural networks that can operate at exceptionally high speeds, leading to faster decision-making processes and the ability to handle vast amounts of data all at once. The speed of light is leveraged to transfer information in these networks, drastically reducing latency.
Examples & Analogies
Think of traditional neural networks as cars traveling on a highway. Some cars are fast, but they still get stuck in traffic. Now, imagine if those cars could travel on a special lane where there are no traffic jams and they can move at the speed of light. That’s what ultrafast neural networks achieve—they avoid the slowdowns and operate smoothly, providing quicker responses to challenges.
Integration with Silicon
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Integration with silicon for quantum interconnects
Detailed Explanation
Integrating quantum devices with silicon technology is essential for developing functional quantum computing systems. Silicon is the backbone of conventional electronics, and connecting quantum chips with silicon allows for effective communication between quantum bits (qubits) and classical computational systems. This integration helps bridge the gap between traditional computing and advanced quantum processing.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a city where you have high-speed trains (the quantum systems) that need to connect with regular buses (the silicon systems) to transport people across various parts of the city. If these two transportation modes can work together seamlessly, it would allow for efficient travel across all areas of the city, similar to how quantum interconnects allow for smooth data exchange between quantum and classical computing systems.
Key Concepts
-
Topological Qubits: A robust qubit type enabled by certain semiconductor materials.
-
Neuromorphic Computing: A computing style that mimics brain functioning for efficient information processing.
-
Ultrafast Neural Networks: Advanced networks utilizing fast processing offered by compound semiconductors.
Examples & Applications
InAs/GaSb composite structures for topological qubits help reduce error rates in quantum computing.
Use of compound semiconductor photonics in neuromorphic systems for real-time AI processing.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In quantum land, it's not a fad, qubits are here to make us glad!
Stories
Imagine a world where bits don’t just choose sides but can dance between states, like a qubit at a party!
Memory Tools
Remember 'TRACE': Topological, Robust, Advanced, Coherent, Efficient for topological qubits.
Acronyms
NAI
Neuromorphic AI - integrating neural processes for fast computing.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Quantum Computing
A type of computation that uses quantum bits, or qubits, capable of representing and processing information in ways traditional computers cannot.
- Topological Qubits
Types of qubits derived from materials that are less susceptible to certain errors, enabling more stable quantum computations.
- Neuromorphic Computing
An approach that mimics the operations of the human brain to process information more efficiently.
- Ultrafast Neural Networks
Artificial neural networks that process information at extremely high speeds using advanced material systems.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
