Heterogeneous Integration with Silicon
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Heterogeneous Integration
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to talk about heterogeneous integration with silicon. This is a vital technology that combines CMOS logic with III-V semiconductors. Can anyone tell me what CMOS stands for?

I think it stands for Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor!

Correct! CMOS is critical because it is used in many modern electronic devices. Heterogeneous integration allows us to add functionalities like high-speed electronics and optics onto a single chip, which enhances device performance. Why do you think that would be important?

Maybe because we can get more capabilities in a smaller size?

Exactly! This leads to more compact and efficient devices. Let's summarize: Heterogeneous integration merges CMOS with III-V semiconductors to create multifunctional chips.
Benefits of Heterogeneous Integration
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we've established what heterogeneous integration is, let's discuss its key benefits. One major advantage is performance improvement. Can anyone comment on how this integration enhances performance?

I think it improves processing speeds by using faster III-V materials.

Right! III-V materials like GaN can handle high frequencies better than silicon alone. What do you think the versatility of this technology means for different applications?

It could allow companies to design more advanced communication systems that are also smaller!

Exactly! To recap, heterogeneous integration provides performance improvements, versatility, and reduces size—all essential for next-gen tech.
Integration Platforms
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's move to the platforms used in heterogeneous integration. Can anyone name one of the platforms used for integrating III-V semiconductors with silicon?

GaN-on-Si?

Exactly! GaN-on-Si is one platform. What do you think makes this advantageous?

It's probably cost-effective and scalable compared to other methods.

Great insight! Other platforms include InP-on-Si and GaAs-on-SOI. These allow varying functionalities and cost efficiencies. Can anyone summarize the key points discussed today?

Heterogeneous integration combines CMOS and III-V for better performance, has several key platforms, and supports diverse applications!

Excellent summary! Remember, this technology is pushing boundaries in many sectors.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section explains heterogeneous integration, highlighting its importance in integrating complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) technology with III-V semiconductors. It discusses the benefits and platforms for monolithic integration, which enable enhanced performance in photonics, RF, and logic applications.
Detailed
Heterogeneous Integration with Silicon
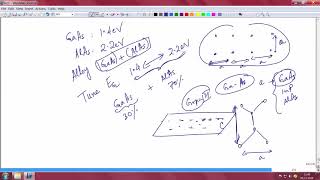
Heterogeneous integration refers to the advanced integration process that combines traditional silicon-based CMOS technology with III-V compound semiconductors, such as Gallium Nitride (GaN) and Indium Phosphide (InP). This integration allows for monolithic solutions combining high-speed electronics and optoelectronics on a single chip, which is essential for next-generation electronic devices.
Key Benefits of Heterogeneous Integration:
- Performance Improvement: Enhances the overall performance of semiconductor devices by leveraging the high-speed characteristics of III-V materials alongside the scalability of silicon.
- Versatility: Enables the embedding of diverse functionalities, including photonic circuits, RF components, and digital logic, facilitating advanced applications in communications, sensing, and computing.
- Integration Platforms: Common platforms for this integration include:
- GaN-on-Si
- InP-on-Si
- GaAs-on-SOI
These platforms allow for cost-effective fabrication and scalability, which are crucial for commercial applications.
Overall, heterogeneous integration represents a promising direction in semiconductor technology, significantly pushing the boundaries of performance in various applications, particularly in the fields of telecommunications and data processing.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Heterogeneous Integration
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Combines CMOS (logic) with III-V semiconductors (high-speed/optoelectronics)
Detailed Explanation
Heterogeneous integration refers to the combination of different types of semiconductor materials on a single chip. In this case, it merges Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS) technology, which is widely used for logic circuits, with III-V semiconductors, which are known for their high-speed capabilities and optoelectronic properties. This integration allows for the creation of more advanced and efficient devices.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like a hybrid car that combines an electric motor and a traditional gasoline engine. Just as this combination allows the car to be both efficient and powerful, the integration of CMOS and III-V semiconductors enables chips to deliver both logic processing and high-speed communication capabilities.
Benefits of Heterogeneous Integration
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Enables monolithic integration of photonics, RF, and logic on the same chip
Detailed Explanation
One of the significant advantages of heterogeneous integration is that it allows for the on-chip integration of photonics, radio frequency (RF), and logic circuits. This means that a single chip can handle light signals (like those used in fiber optics), radio signals (used in wireless communication), and processing tasks (like computing), which significantly boosts the performance and efficiency of electronic devices. This integration reduces the need for multiple chips and connections, leading to smaller and more efficient devices.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a smartphone that can take photos, make calls, and play videos all from one application instead of needing separate applications for each task. Heterogeneous integration in semiconductors works similarly by allowing multiple functions to exist seamlessly within one chip.
Platform Examples for Integration
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Platforms: GaN-on-Si, InP-on-Si, GaAs-on-SOI
Detailed Explanation
There are specific platforms where this heterogeneous integration occurs. For example, GaN-on-Si combines Gallium Nitride (GaN) with silicon substrates, which allows for high-performance RF applications. InP-on-Si and GaAs-on-SOI (Silicon-On-Insulator) are other examples, facilitating various communication technologies. These platforms provide different benefits based on the material properties and application needs, making it possible to advance technologies in telecommunications and other fields.
Examples & Analogies
Think of choosing different types of ingredients to create a recipe. Using GaN, InP, or GaAs as the 'ingredients' lets engineers create semiconductor 'dishes' tailored for specific applications like high-speed internet or efficient power management, depending on the 'flavor' they are after.
Key Concepts
-
Heterogeneous Integration: Combining CMOS and III-V semiconductors to enhance performance.
-
CMOS: A prevalent technology in integrated circuits, allowing for low-power consumption.
-
Platforms for Integration: Different methods like GaN-on-Si, InP-on-Si for effective integration.
Examples & Applications
GaN-on-Si technology enables high-frequency applications while maintaining cost efficiency.
InP-on-Si platforms are crucial for integrating high-speed wireless systems.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Heterogeneous integration, the future's fascination, combines tech with precision, for the best creation.
Stories
Imagine a world where silicon chips come together with light-speed gallium to create faster, smarter devices just like superheroes joining forces to save the day.
Memory Tools
Think of CHIPS to remember the platforms: 'C' for CMOS, 'H' for Heterogeneous, 'I' for Integration, 'P' for Platforms, 'S' for Speed.
Acronyms
Use 'GIPS' to recall key platforms
'G' for GaN
'I' for InP
'P' for Platforms
'S' for silicon substrates.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Heterogeneous Integration
The integration of different semiconductor materials, such as CMOS and III-V semiconductors, to enhance device performance.
- CMOS
Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor, a technology for constructing integrated circuits.
- IIIV Semiconductors
Materials composed of elements from groups III and V of the periodic table, known for their high efficiency in electronic and optoelectronic applications.
- Monolithic Integration
The process of integrating different devices or functionalities onto a single semiconductor chip.
- GaN
Gallium Nitride, a semiconductor material with a wide bandgap, used for high-frequency and high-power applications.
- InP
Indium Phosphide, a III-V semiconductor widely used in high-speed electronics and photonics.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
