Introduction
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Compound Semiconductors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will discuss compound semiconductors, which are materials that consist of two or more elements, unlike silicon which is a pure element. Can anyone tell me why these materials are important in modern technologies?

They have unique physical properties that help improve performance in various applications?

Exactly! They enable devices to operate at higher voltages and frequencies. For instance, the wide bandgap allows them to handle high power applications effectively. Can someone describe what a wide bandgap actually means?

It means the energy gap between the valence band and the conduction band is larger, allowing for better efficiency in high-temperature environments.

Great explanation! This capability opens doors for innovations in telecommunications and renewable energy, as these fields require reliable operation under rigorous conditions.
Applications of Compound Semiconductors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s talk about where we see these compound semiconductors being utilized. Which sectors do you think benefit from these materials?

Telecommunications and renewable energy seem obvious, but what about quantum computing?

Absolutely! Their unique properties allow for advancements in quantum technologies. Can anyone name a few examples of these applications?

I know that they are used in data centers, for 5G technology, and even autonomous vehicles for efficient power systems.

Spot on! Each of these areas requires the unique advantages that compound semiconductors provide, and as we go forward in this chapter, we will delve deeper into each application's innovations.
Future Trends in Compound Semiconductors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let's wrap up by discussing future trends. How do you think compound semiconductors will evolve in the coming years?

I imagine they will be used in more everyday electronics as the technology becomes cheaper and easier to integrate.

And what about sustainability? Are there alternatives to the toxic materials currently used in some compounds?

That’s an important consideration! Researchers are indeed looking for non-toxic alternatives. As we proceed, we’ll explore these innovations, integration strategies, and the overall market trends that will shape the evolution of compound semiconductors.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section introduces the role of compound semiconductors in various fields such as telecommunications, renewable energy, and quantum computing. It highlights the unique physical properties that make these materials superior for new technologies and sets the stage for discussions on recent advancements and future prospects.
Detailed
Introduction to Compound Semiconductors
Compound semiconductors represent a significant advancement in material science, especially with their unique physical properties like wide bandgap, high breakdown voltage, and direct bandgap. These qualities allow them to function efficiently in numerous applications that traditional silicon cannot accommodate. The discussion here emphasizes the importance of compound semiconductors in innovation within telecommunications, renewable energy, quantum computing, and autonomous systems. As the chapter unfolds, it will explore recent developments, future trends, and key applications that these technologies are enabling, thereby shaping the landscape of modern electronic, photonic, and energy systems.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Compound Semiconductors
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Compound semiconductors are at the forefront of innovation across diverse sectors, including telecommunications, renewable energy, quantum computing, and autonomous systems.
Detailed Explanation
Compound semiconductors are special materials that show great promise in many high-tech industries. These are different from traditional silicon-based semiconductors, as they have unique properties that make them suitable for advanced applications. They are used in important sectors such as telecommunications, where fast data transfer is essential, renewable energy systems that convert sunlight into electricity, quantum computing that uses the principles of quantum physics for advanced computation, and autonomous systems like self-driving cars that require sophisticated sensors and processors.
Examples & Analogies
Think of compound semiconductors like a high-performance sports car compared to a standard vehicle. While both can get you from point A to point B, the sports car (compound semiconductors) can do it faster and with more advanced technology, making it better suited for challenging terrains (like cutting-edge applications) than a standard vehicle (traditional silicon semiconductors).
Unique Properties of Compound Semiconductors
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
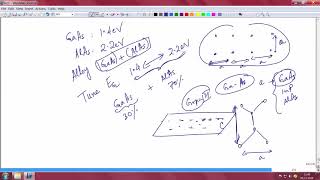
Their unique physical properties—such as wide bandgap, high breakdown voltage, and direct bandgap—enable device capabilities beyond what silicon alone can offer.
Detailed Explanation
Compound semiconductors have distinct physical attributes that give them advantages over silicon. A wide bandgap helps them operate at higher voltages and temperatures, making them ideal for high-power applications. High breakdown voltage allows these materials to withstand more electrical stress without failing. Additionally, a direct bandgap enables efficient light emission, which is essential in optoelectronics like LEDs and laser diodes. Collectively, these properties allow for the creation of devices that are more powerful, efficient, and versatile.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the ingredients in a recipe. If you want to bake a cake, you need flour, eggs, and sugar (silicon for basic applications). But if you want to make a gourmet cake that stands out at a wedding, you might choose to add special ingredients like vanilla extract or gourmet chocolate (the unique properties of compound semiconductors), which will create a much more impressive and effective dessert that can cater to special occasions.
Focus of the Chapter
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
This chapter explores the latest developments and future trends in compound semiconductor technologies and highlights emerging applications that are shaping the next generation of electronic, photonic, and energy systems.
Detailed Explanation
The chapter's aim is to discuss current advancements in compound semiconductors and to look ahead at how these materials will change the landscape of technology in the future. It will cover new innovations, applications that are under development, and the potential impact these technologies will have on various fields such as electronics (like smartphones and computers), photonics (which deals with light and its applications), and energy systems (especially in harnessing renewable energy sources).
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a movie that takes you on a journey through time, showcasing not only how things are now but also revealing glimpses of what could be in the future. Just like the plot unfolds, this chapter will take readers through the story of compound semiconductors, highlighting their current role and the exciting possibilities that lie ahead in transforming modern technology.
Key Concepts
-
Compound Semiconductors: Materials that combine two or more elements, offering unique properties.
-
Wide Bandgap: A key feature that allows semiconductors to operate under extreme conditions of temperature and voltage.
-
Emerging Technologies: Sectors and innovations that leverage the properties of compound semiconductors.
Examples & Applications
GaN (Gallium Nitride) used in RF applications and 5G technology.
SiC (Silicon Carbide) utilized in electric vehicle chargers for improved efficiency.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the world of chips, we find, there's silicon in a bind; but compound ones, so wide and bright, bring innovation to new height.
Stories
Once in a factory far beyond, silicon ruled the land. But then arrived the clever compounds, bringing technology's demand, in phones, cars, and solar farms, they shine with unique charms.
Memory Tools
Remember C-WISE for the benefits: Compound, Wide bandgap, Innovation in sectors, Sustainably harnessed, Efficiency improved.
Acronyms
C.E.E.T
Compound semiconductors drive Change in Electronics
Energy
and Telecommunications.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Compound Semiconductor
A semiconductor material made from two or more elements.
- Wide Bandgap
A property describing a semiconductor’s ability to operate at higher temperatures and voltages due to a larger energy gap.
- Telecommunications
The transmission of information over significant distances by electronic means.
- Quantum Computing
A type of computing that takes advantage of quantum mechanical phenomena to process information.
- Autonomous Systems
Systems that can operate independently without human intervention.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
