Cost Performance Analysis
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Cost of Hardware Components
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

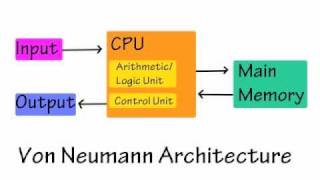
Let's start by looking at the costs associated with different hardware components. Can anyone name a few key components in a computer system?

CPU, memory, and storage.

Exactly! The CPU, memory, and I/O components are essential. CPUs are often the most expensive part of a computer system, followed by memory. How do you think this affects our design choices?

If the CPU is expensive, we might look for cost-effective memory solutions to balance the budget.

Great point! Balancing these costs is key to effective design. Remember, we want to optimize performance without exceeding our budget.
Trade-offs in Design
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's discuss trade-offs. When deciding between a high-performance component and a cheaper alternative, what factors should we consider?

We should think about how much performance we really need for the intended applications.

And the long-term costs too—like maintenance and power consumption!

Exactly! Performance needs can guide us, but Total Cost of Ownership plays a crucial role. Would anyone like to summarize what TCO includes?

It includes maintenance costs, power consumption, and scalability.

Perfect! Keeping TCO in mind helps ensure our design decisions are sustainable.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s delve deeper into Total Cost of Ownership. Why is it more comprehensive than just looking at initial costs?

It considers all costs over the lifespan of the system, not just the purchase price.

Yes! For instance, how might high-performance components influence maintenance costs?

They could lead to higher maintenance costs if they require specialized knowledge or parts.

Exactly! Understanding TCO helps us make better design decisions and find the right balance between cost and performance.
Evaluating Design Options
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let's talk about evaluating our design options. What methods can we use to compare the cost and performance of different components?

We could use performance metrics like throughput and latency in conjunction with cost data.

And create a cost-benefit analysis to visually compare different configurations.

Excellent ideas! By systematically analyzing these factors, we can achieve a well-rounded perspective before finalizing our design.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Cost Performance Analysis emphasizes the importance of evaluating component costs against performance requirements. It discusses hardware costs, design trade-offs, and the concept of Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) in evaluating the economic viability of computer systems.
Detailed
Cost Performance Analysis
In this section, we delve into the critical balance between cost and performance in computer system design. Understanding the cost of hardware components is crucial, as it lays the groundwork for making informed design decisions. We break down the costs associated with key components such as CPUs, memory, and I/O devices. Additionally, we discuss the trade-offs involved in choosing between high-performance, expensive components and low-cost, less capable alternatives. Finally, we introduce the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) concept, which assesses not just the initial costs but also ongoing expenses such as maintenance, power consumption, and scalability. This holistic view is vital for making effective design decisions that meet performance needs while remaining economically feasible.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Cost of Hardware Components
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Breakdown of CPU, memory, and I/O components in terms of cost.
Detailed Explanation
This part discusses how the costs of different hardware components—like the CPU, memory (RAM, etc.), and Input/Output devices (like keyboards and mice)—are assessed. Each of these components plays a critical role in the overall cost of building a computer system. The CPU is typically one of the most expensive components because of its performance capabilities. Memory costs can vary depending on speed and size, while I/O components tend to be relatively less expensive but are essential for user interaction with the computer.
Examples & Analogies
Think of building a custom computer system like constructing a house. The foundation (CPU) is the most crucial and costly part, providing stability and performance. The walls and roof (memory) add substantial costs, depending on the quality and materials chosen. Finally, the doors and windows (I/O components) might not cost as much, but you need them to gain access and function effectively.
Trade-offs in Design
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Choosing between expensive, high-performance components versus low-cost, less powerful options.
Detailed Explanation
In this section, the focus is on the trade-offs that designers must consider. They often have to choose between high-performance components that can improve speed and efficiency but come at a higher cost, and low-cost components that may suffice for basic tasks but could limit overall system performance. The choice can impact the system’s capability, operational efficiency, and longevity, making it crucial for designers to evaluate the intended use of the system before making decisions.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a chef deciding between using top-quality ingredients (high-performance components) or budget options (low-cost components) for a recipe. The top ingredients yield a better dish, attracting customers, but significantly increase costs. On the other hand, budget ingredients might save money but could result in a meal that does not impress, leading to fewer customers.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Including maintenance, power consumption, and scalability in the overall cost evaluation.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk examines the concept of Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which goes beyond the initial cost of purchasing hardware. TCO considers ongoing expenses such as maintenance and repairs, power usage, and how well the system can scale with future demands. Understanding TCO is essential for stakeholders because it often reveals that a cheaper initial investment may lead to higher costs over time, especially if components are less energy-efficient or require more frequent replacements.
Examples & Analogies
Think of buying a car; the sticker price (initial cost) is just one part of the equation. You'll also need to consider fuel costs, insurance, maintenance, and repairs over the years (TCO). A more expensive car might be more fuel-efficient and durable, resulting in lower costs overall, similar to how investing in better components can pay off through lower maintenance and energy costs in computing.
Key Concepts
-
Cost of Hardware Components: Evaluation of the monetary aspects of essential components like CPUs and memory that form the basis of a computer system.
-
Trade-offs in Design: The critical balances necessary in choosing high-performance versus cost-effective options in component selection.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): A model that encapsulates the total costs associated with owning and maintaining computer systems beyond initial purchase prices.
Examples & Applications
Choosing between a high-end CPU designed for gaming and a budget processor for office tasks reflects a trade-off between performance and cost.
A company evaluating two server options may find that a cheaper server has higher power costs over time, altering its TCO.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Cost and power, let’s be wise, choose the bits that win the prize!
Stories
Imagine a chef choosing ingredients: a high-cost spice equals a gourmet dish, but sometimes store-brand spices do just as well for a casual meal!
Memory Tools
C-P-T: Cost, Performance, Total cost - the triangles of tech.
Acronyms
TCO
Total Costs Over time — every cent must align.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Cost of Hardware Components
The monetary value associated with the purchase of essential computer parts, notably the CPU, memory, and I/O components.
- Tradeoffs in Design
The decisions made during design that involve balancing performance with cost and other factors.
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
The comprehensive assessment of both the initial and ongoing costs associated with acquiring and maintaining technology systems.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
