Basic Principles of Computer Design
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Abstraction in Computer Design
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss abstraction in computer design. Abstraction helps us manage complex systems by reducing the details we need to focus on. Can anyone think of an example of abstraction in computing?

Is it like how we use high-level programming languages instead of assembly language?

Exactly! High-level languages abstract the machine details away. They allow us to write code without handling every tiny detail of the hardware.

So, abstraction can be applied at different levels within the system?

Right! We have hardware-level abstractions like CPUs, instruction sets, and even software layers. Each level simplifies the complexity we need to handle.

Can abstraction also lead to issues if not used correctly?

Great question! Yes, it can lead to performance overhead if the abstraction layers are too high. It's all about finding the right balance.

To summarize, abstraction is crucial for managing complexity, allowing us to work at different levels of detail without getting lost in the intricacies of the hardware.
Modularity in Design
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s talk about modularity. Why do you think it’s important in computer design?

I think it makes it easier to replace parts of a system without rebuilding everything.

That's spot on! Modularity promotes reusability. If one component fails or becomes outdated, we can just swap it out. What about examples of modular systems?

Like how we can upgrade RAM in our computers?

Yes! Upgrading RAM is a perfect example of modular design. It allows consumers to enhance their systems without needing to purchase a completely new one.

Does it also help with development time?

Absolutely! Modular components can often be developed in parallel, speeding up the overall design process.

To conclude, modularity makes systems easier to maintain, encourages reusability, and enhances development efficiency.
Scalability in System Design
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's explore scalability. Why do you think scalability is crucial in computer design?

It allows systems to grow with increasing demands, right?

Exactly! A scalable design ensures that systems can adapt to rising demand without needing a total redesign. Can anyone give an example of scalability?

Like cloud computing? You can increase your resources without a new setup.

Perfect example! Cloud services allow for scalable resource allocation. What happens if a company grows suddenly?

They could face issues if they aren't using scalable systems.

Exactly. Non-scalable systems may lead to performance bottlenecks. Remember, scalability is all about future-proofing your designs.

In summary, scalability is vital for handling growth effectively and ensures longevity in system designs.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore the essential principles governing computer design, including abstraction which defines multiple levels of complexity, modularity that encourages reusable components, and scalability which ensures that a system can grow without a complete redesign.
Detailed
Basic Principles of Computer Design
In this section, we delve into the fundamental principles that guide the design of computer systems. Understanding these principles is critical for creating efficient and robust systems in the evolving field of computer architecture. Three central principles are highlighted:
- Abstraction: Abstraction involves constructing models that simplify complex systems by presenting them at different levels of detail. In computer design, this spans multiple levels, including hardware, instruction sets, and software layers. By using abstraction, designers can focus on individual components without getting overwhelmed by the entire system complexity.
- Modularity: Modularity emphasizes the importance of designing systems in interchangeable components or modules. This approach not only promotes reuse but also facilitates easier maintenance and updates. For instance, if a certain hardware module needs upgrading or replacement, it can be done without redesigning the entire system.
- Scalability: Scalability ensures that as demand grows, the system can accommodate additional resources without needing a complete overhaul. In essence, a scalable design should allow for the addition of components or increased capacity, leading to enhanced performance.
By comprehending these three principles—abstraction, modularity, and scalability—students can better appreciate how fundamental design choices impact the overall effectiveness of computer systems.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Abstraction in Computer Design
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Abstraction: Understanding different levels of abstraction in design, such as the hardware level, instruction set, and software layer.
Detailed Explanation
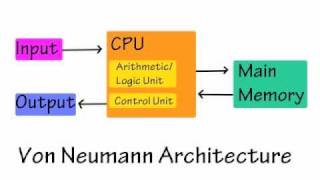
Abstraction in computer design refers to the simplification of complex systems into more manageable, understandable parts. It involves various layers: the hardware level, which includes physical components like processors and memory; the instruction set, detailing how software interacts with hardware; and the software layer, encompassing applications and interfaces that users interact with. By using abstraction, designers can focus on individual layers without needing to understand every detail of others, leading to more efficient development and troubleshooting.
Examples & Analogies
Think of abstraction in computer design like a car. When you drive, you don't need to understand how the engine works or how the fuel system operates; you only need to know how to use the steering wheel, pedals, and gear shift. In the same way, abstraction allows computer designers to build systems where users or developers only interact with the layers they need to.
Modularity in Design
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Modularity: Importance of creating reusable and modular components for efficient design and maintenance.
Detailed Explanation
Modularity is the principle of designing a system in a way that separates it into smaller, interchangeable components or modules. This approach allows designers to develop, test, and maintain each module independently. By creating reusable components, systems become easier to update or fix because modifying one module doesn’t necessarily impact others. This leads to enhanced efficiency in design, as well as a reduction in time and resources spent on maintaining the system.
Examples & Analogies
Consider modularity like building with LEGO bricks. Each brick is a module that can be combined in different ways to create various structures. If one piece is damaged or needs to be changed, you can easily replace it without tearing apart the entire model. This is how modular components work in computer design - they can be easily swapped out or upgraded without major disruptions.
Scalability in System Design
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Scalability: Ensuring the system design can handle increased demand without a complete redesign.
Detailed Explanation
Scalability refers to the capability of a computer system to grow and manage increased demands effectively. A scalable system can adapt to higher loads, whether by upgrading existing components or adding new ones without needing a redesign of the entire system. This is crucial for businesses that expect growth or fluctuations in usage, as it avoids costly overhauls and ensures continued performance.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a small restaurant that originally seated 20 customers. As its popularity grows, it implements a modular seating design that can easily add tables without altering the restaurant's layout significantly. This scalability means that as the demand increases, the restaurant can adapt seamlessly to accommodate more diners, similar to how scalable systems operate in computer design.
Key Concepts
-
Abstraction: Reduces complexity by organizing systems at different levels.
-
Modularity: Promotes the design of interchangeable components for ease of upgrade and maintenance.
-
Scalability: Ensures that systems can adapt to increase demands and function efficiently without reconfiguration.
Examples & Applications
Using high-level programming languages instead of assembly to abstract hardware complexity.
Upgrading a computer's RAM instead of replacing the entire machine.
Cloud computing services like AWS which allow adding server resources as demand grows.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When designing a machine, keep it clean: Abstract it right, modules in sight, scale it wide, and let it glide!
Stories
Imagine a chef in a kitchen where pots represent different parts of a computer. Each pot can be swapped out for a better one (modularity), but the chef can also cook new dishes (abstraction) without changing the kitchen's entire setup (scalability).
Memory Tools
AMS: Abstraction, Modularity, Scalability - the three crucial principles to remember for computer design.
Acronyms
A huge 'AMScape' of computer design with its landscape of modular components and scalable horizons.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Abstraction
A principle in design that simplifies complex systems by presenting them at different levels of detail.
- Modularity
The design principle of creating interchangeable components or modules to enhance reusability and maintenance.
- Scalability
The ability of a system to handle increased demand without a complete redesign.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
