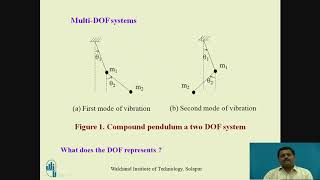
Degrees of Freedom (DOF)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Definition of Degrees of Freedom
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Degrees of Freedom, or DOF, is an essential concept in structural engineering, particularly when analyzing how a structure moves during earthquakes. Can anyone tell me why it's called degrees of freedom?

Is it because it defines how freely the structure can move?

Exactly! It's about the minimum number of independent coordinates needed to describe a system's motion. This can include translations along different axes or rotations. Understanding this helps us model and analyze structures effectively.

So, all buildings have the same degrees of freedom?

Not quite; different structures possess different DOFs. Complex or irregular buildings may have coupled DOFs, meaning they have both translational and rotational movements. Remember, DOF is a key factor in modeling structural response under seismic activity.

Could you give us an example of a building with multiple DOFs?

Sure! A tall, multi-story frame building will typically exhibit more dynamic DOFs due to each floor contributing to lateral movements. This is foundational for understanding seismic design and response.

In summary, DOF defines the possible movements of structures and is crucial for analyzing their seismic response.
Types of Degrees of Freedom
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive into the types of Degrees of Freedom. Can anyone name them?

Translational and rotational DOFs?

"Correct! Translational DOFs are movements along x, y, and z directions, while rotational DOFs are movements around those axes.
Importance of DOF in Earthquake Engineering
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we know what DOFs are and their types, let's discuss why they are crucial in earthquake engineering. How does knowing the DOF impact our ability to analyze structures?

It helps us understand how complex the analysis should be?

Yes! The complexity of the structural analysis is influenced by how many DOFs are present. More DOFs mean more complex analysis. What else does understanding DOF influence?

Natural frequencies?

Exactly! Natural frequencies and mode shapes of structures are determined by their DOFs. This understanding is crucial for selecting appropriate numerical methods for seismic analysis. Can anyone think of a numerical method we might use?

Maybe modal analysis?

Spot on! Modal analysis is one such method that relies heavily on the understanding of DOFs. So, to summarize, DOFs are not just theoretical concepts; they significantly inform our analysis techniques in earthquake engineering. Brilliant discussions today, everyone!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section explores the concept of Degrees of Freedom (DOF) in seismic structural analysis, detailing its definitions, types, and importance. Understanding DOF is crucial for formulating dynamic models, particularly in simplifying structures into Single-Degree-of-Freedom (SDOF) systems, optimizing dynamic analysis methods, and informing the choice of numerical methodologies.
Detailed
Degrees of Freedom (DOF)
Definition
In earthquake engineering, the concept of Degrees of Freedom (DOF) refers to the minimum number of independent coordinates required to define the motion of a system. It encompasses various displacements—both translational and rotational—that a structure may experience.
Types of Degrees of Freedom
- Translational DOF: Movements along x, y, or z directions.
- Rotational DOF: Rotations about the x, y, or z axes.
- Coupled DOFs: Certain systems may exhibit coupling between translational and rotational movements, particularly in irregular or torsionally unbalanced structures.
Importance in Earthquake Engineering
- Understanding DOF informs the complexity of structural analysis needed for evaluating a structure's response to seismic activity.
- It influences natural frequencies and mode shapes, and assists in choosing appropriate numerical methods such as modal analysis and time history analysis.
This foundational understanding enhances the capability of engineers to model seismic impacts effectively.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Degrees of Freedom
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A degree of freedom refers to the minimum number of independent coordinates required to define the motion of a system. In structural engineering, this typically relates to possible displacements (translational or rotational) that a structure can experience.
Detailed Explanation
Degrees of freedom (DOF) represent how many independent movements a system, such as a building, can make. For a structure, this means it can move in certain ways. Think of it like a dancer who can twist and turn in various directions; each unique twist or turn corresponds to a degree of freedom. In buildings, this motion can be translational (moving straight) or rotational (spinning around an axis).
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a toy robot that can move in three ways: forward/backward (x), left/right (y), and rotate (z). Each unique way it can move represents a degree of freedom. If it only moved forward and backward, it would have one degree of freedom.
Types of Degrees of Freedom
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Translational DOF: Movement along x, y, or z directions.
- Rotational DOF: Rotation about x, y, or z axes.
- Coupled DOFs: Some structural systems exhibit coupling between translation and rotation, especially in irregular or torsionally unbalanced buildings.
Detailed Explanation
There are three main types of degrees of freedom. First, translational DOF involves straight movements along three dimensions - left/right, forward/backward, and up/down. Next, rotational DOF includes rotations around these three axes, allowing for twists and turns. Lastly, some structures have coupled DOFs, where the movement in one direction affects movement in another, often seen in buildings that are not perfectly symmetrical.
Examples & Analogies
Combining translational and rotational DOFs is like a modern toy that can both roll across the floor and spin. A regular toy car can move forward or backwards (translational), while a top can spin in circles (rotational). If you have a toy that can do both, like a spinning robot that walks, that showcases coupled DOFs.
Importance in Earthquake Engineering
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Determines the complexity of structural analysis.
- Influences the natural frequencies and mode shapes.
- Helps in selecting appropriate numerical methods (modal analysis, time history, etc.).
Detailed Explanation
Understanding degrees of freedom is critical in earthquake engineering. It dictates how complex a structural analysis has to be – more degrees of freedom means a more complicated situation to analyze. It also affects how a structure behaves during tremors, specifically its natural frequencies and how it vibrates. This understanding helps engineers choose the correct methods for analyzing how a structure will respond to seismic events, ensuring safety and stability.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a playground swing. If the swing only goes back and forth (one degree), it's simpler to analyze than a complex ride with swings that can twist and turn (multiple degrees). Engineers need to know all the ways the structure can move to predict how it will behave during an earthquake.
Key Concepts
-
Degrees of Freedom: Essential for understanding how structures can move during seismic events.
-
Translational and Rotational DOF: The two primary types of motion a structure can experience.
-
Coupled DOFs: Significant for irregular structures; they highlight the interaction between translation and rotation.
-
Importance in Earthquake Engineering: DOFs influence the complexity of analysis and selection of numerical methods.
Examples & Applications
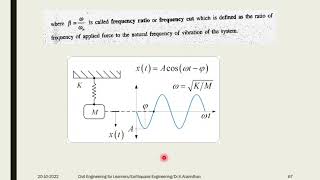
A cantilever beam has one dynamic DOF, representing lateral displacement at the top.
A multi-story frame building exhibits multiple DOFs as each floor contributes to lateral movements.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Degrees of Freedom mean how it can glide, along straight paths and spins with pride.
Stories
Imagine a dancer who can twirl (rotation) and leap (translation) across the stage. That’s how structures move under seismic forces!
Memory Tools
'TR' for Translational and Rotational—remembering the two main types of DOF.
Acronyms
Use 'T&R' to remind you of Translational and Rotational types of DOF.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Degrees of Freedom (DOF)
The minimum number of independent coordinates required to define the motion of a system.
- Translational DOF
Movement along x, y, or z directions in a structure.
- Rotational DOF
Rotation about the x, y, or z axes in a structure.
- Coupled DOFs
Degrees of Freedom that exhibit a coupling between translation and rotation, often found in irregular structures.
- Natural Frequencies
The frequencies at which a system tends to oscillate in the absence of any driving force.
- Mode Shapes
The configuration that a vibrating system assumes at specific natural frequencies.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
