Use of SDOF Systems in Seismic Isolation and Energy Dissipation
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Seismic Isolation Modeling
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're delving into seismic isolation modeling using SDOF systems. These models help us understand how base-isolated structures operate during earthquakes. Can anyone tell me what a two-mass SDOF system consists of?

I think it includes the superstructure and the isolator!

Exactly! The superstructure is the part we typically think of as the building, and the isolator allows for movement during seismic events. Why do you think increasing the effective period is beneficial?

Because it reduces the acceleration response, right?

Correct! A longer effective period means the structure experiences less force, which is crucial during an earthquake. Remember the acronym 'PEAR' for Performance Evaluation: Period, Effective response, Acceleration, and Risk. Let's summarize: A two-mass SDOF system helps in reducing forces on buildings via seismic isolation.
Energy Dissipation Devices
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, we will discuss how SDOF systems assist us in evaluating energy dissipating devices like viscous dampers. Who can explain what energy dissipation means?

Isn't it about reducing the energy transferred to the structure during shaking?

Exactly! By dissipating energy, these devices protect structures from significant damage. Why do you think we first test these devices on SDOF systems before using them in MDOF setups?

I guess it’s to ensure their effectiveness and see how they behave under simpler conditions first?

That's right! Testing on SDOF systems helps identify potential issues before applying them to complex structures. To help you remember, think of the phrase 'DAMPER SAVES' — Dampers Absorb Motion, Protecting Engineered Residences. This summarizes their role in protecting buildings!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section elaborates on the modeling of base-isolated structures as two-mass SDOF systems to enhance their performance during seismic events, highlighting how effective periods and energy dissipating devices are evaluated before being integrated into more complex structures.
Detailed
Use of SDOF Systems in Seismic Isolation and Energy Dissipation
In this section, we explore the vital role that Single Degree of Freedom (SDOF) systems play in modern seismic design, particularly in seismic isolation and energy dissipation.
Seismic Isolation Modeling
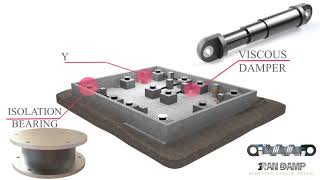
Base-isolated structures are commonly modeled using a two-mass SDOF system, which consists of the superstructure and the isolator. By employing this approach, designers increase the effective period of the system, which in turn reduces the acceleration response of the structure during seismic events. This configuration allows for a clearer understanding of the dynamics involved and enhances the overall performance of buildings in protecting against earthquakes.
Dampers and Energy Dissipating Devices
SDOF models are frequently employed to assess the effectiveness of various energy dissipation devices such as viscous dampers, yielding braces, and tuned mass dampers. Before being incorporated into complex Multi-Degree of Freedom (MDOF) frameworks, these devices are tested on SDOF systems to evaluate their capacity to dissipate energy and manage dynamic responses. This testing phase is crucial for ensuring that the devices will perform as intended when applied in real structures.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Seismic Isolation Modeling
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Base-isolated structures are often modeled as two-mass SDOF systems: superstructure + isolator.
Effective period of the system increases → reduces acceleration response.
Detailed Explanation
Seismic isolation is a technique used to protect structures from the effects of seismic activity. This method involves separating the building (superstructure) from the ground to reduce ground motion during an earthquake. In this context, we use a two-mass Single Degree of Freedom (SDOF) system model to represent both the superstructure and the isolator. By increasing the effective period of the system through this model, we can reduce the acceleration forces acting on the structure. In simpler terms, if the building takes longer to shake back and forth (longer period), the shaking is less severe, leading to lower forces on the structure.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a pendulum. The longer the pendulum arm, the slower it moves back and forth. Similarly, a building designed with isolation methods can 'slow down' how it responds to an earthquake, reducing potential damage—just like a long pendulum swinging gently instead of a short one that swings violently.
Dampers and Energy Dissipating Devices
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
SDOF models are used to evaluate energy dissipation capacity.
Devices like viscous dampers, yielding braces, or tuned mass dampers are first tested on SDOF systems before integration into MDOF frameworks.
Detailed Explanation
Dampers and energy-dissipating devices are crucial in modern seismic design because they help absorb and dissipate energy during an earthquake. This reduces the overall forces transmitted to the structure. When designing such systems, engineers often use SDOF models to evaluate how effectively these devices can absorb seismic energy. They will conduct tests on SDOF systems first to verify how these dampers perform before applying them to more complex Multi-Degree of Freedom (MDOF) structures, which have multiple ways of moving and responding.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine holding a soft sponge in your hands. When you squeeze it, it absorbs some of the pressure rather than your hand feeling the full force. Similarly, damper devices act like sponges during an earthquake—they absorb the energy and reduce the 'pressure' felt by the building, preventing damage. Testing these devices in SDOF systems is like testing how well a sponge can soak up water before using it in a larger, messier situation.
Key Concepts
-
Seismic isolation modeling: A method to reduce seismic forces by using isolation systems.
-
Two-mass SDOF system: A representation involving a superstructure and an isolator.
-
Energy dissipating devices: Mechanisms like dampers that reduce energy impact during seismic events.
Examples & Applications
A building designed with a base isolator where the isolator absorbs seismic energy and allows the structure to sway safely.
Use of viscous dampers in a tall building to control oscillations and minimize structural damage during an earthquake.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In a quake, let the base sway, with isolators making safety play.
Stories
Imagine a house on springs, dancing gracefully during earth’s shakings to protect its heart.
Memory Tools
Remember the key points with 'SIES' - Seismic Isolation Enhances Safety.
Acronyms
For dampers, think of 'DAMP' - Devices Absorbing Motion Protection.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- SDOF System
A Single Degree of Freedom system represents the simplest dynamic model, characterized by motion defined by a single coordinate.
- Seismic Isolation
A technique used to reduce structural response to seismic activity by isolating the building from ground motion.
- Energy Dissipation
The process of reducing the energy transmitted to the structure during seismic events through devices designed to absorb or dissipate energy.
- BaseIsolated Structure
A building designed with a flexible isolator that allows for movement during earthquakes, thereby minimizing stress on the structure.
- Damping Device
A tool used to absorb vibration energy and reduce the amplitude of oscillations in structures.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
