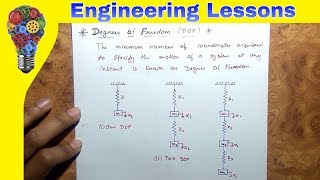
Dynamic Degrees of Freedom
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Definition of Dynamic Degrees of Freedom
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're discussing dynamic degrees of freedom, or DOFs. Can anyone tell me what we mean by 'dynamic' in this context?

Does it mean how the structure moves when forces like earthquakes act on it?

Exactly, great observation! Dynamic DOFs are the coordinates that describe how a structure moves under time-varying loads. Now, can you think of what types of loads we are concerned with?

Seismic loads, right? Like ground shaking?

Correct! By understanding dynamic DOFs, we can model how buildings behave during earthquakes. This is critical for safety in design. Let's remember the acronym DOF as 'Degrees of Freedom.'
Determination of Dynamic DOFs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let's discuss how to actually determine the number of dynamic DOFs a structure has. Who can start us off?

We look at the geometry of the structure, right?

Yes! Evaluating the geometry is essential. Once we examine the shape, we identify independent displacement points. What do you think those are?

I guess they are the points where the structure can move independently without affecting the rest?

Precisely! Lastly, we need to consider any constraints and supports on the structure. Can anyone provide an example of how supports might affect DOFs?

An example would be fixed supports that restrict movement at that point.

Exactly! Those fixed supports limit the DOFs available at that support point.
Examples of Dynamic DOFs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's look at a couple of examples. Can anyone name a structure that might only have one dynamic DOF?

A cantilever beam! It can only sway laterally at its top.

Great example! Now, what about a structure that has multiple dynamic DOFs?

A multi-story frame would have multiple lateral DOFs because each floor can move.

Exactly! Multi-story frames often behave as multi-degree-of-freedom systems. Remember, complexity increases with the number of floors and connections.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section defines dynamic degrees of freedom (DOF), outlining how they are determined through examining the structural geometry and evaluating independent displacement points, crucial for understanding the motion of structures subjected to dynamic loads, especially in earthquake engineering.
Detailed
Dynamic Degrees of Freedom
Dynamic degrees of freedom (DOF) are critical in structural engineering, particularly in the context of analyzing responses to seismic events. They refer to the coordinates required to describe a structure's motion due to dynamic loads like ground motion during an earthquake. To determine the number of dynamic DOFs in a structure, engineers must examine its geometry, identify independent displacement points, and apply the relevant constraints and supports. Examples include a cantilever beam with one DOF for lateral displacement and multi-story frames where each floor contributes lateral DOFs, resulting in a more complex multi-degree-of-freedom system. Understanding dynamic DOFs is foundational for effective structural analysis under seismic influences.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Dynamic Degrees of Freedom
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Dynamic degrees of freedom are those coordinates which define the motion of a structure due to dynamic (time-varying) loads such as seismic ground motion.
Detailed Explanation
Dynamic degrees of freedom (DOFs) refer to the specific parameters that describe how a structure can move when subjected to changing forces over time, such as the forces acting on a building during an earthquake. Each dynamic DOF corresponds to a direction of possible movement (for example, side to side or up and down) in response to these forces.
Examples & Analogies
Think of dynamic degrees of freedom like the way a dancer moves. A dancer can sway, jump, and spin in various ways depending on the music's rhythm. Similarly, a structure has various ways to respond dynamically based on the seismic forces acting on it.
Determining Dynamic Degrees of Freedom
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
To identify the number of dynamic DOFs:
- Examine the geometry of the structure.
- Identify possible independent displacement points.
- Apply constraints and supports.
Detailed Explanation
To establish how many dynamic degrees of freedom a structure has, engineers analyze the structural design (geometry) to see how it may move. First, they look for points where the structure could sway or buckle independently without affecting the entire system. This involves understanding where the structure is fixed (like at the ground) and where it is free to move.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a playground swing. The seat can move back and forth independently from where it is attached. An engineer would determine the swing's dynamic freedom by examining its hinge point and identifying how many directions the swing can move freely.
Examples of Dynamic Degrees of Freedom
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Cantilever Beam: A vertical cantilever with a mass at the top may have one dynamic DOF—lateral displacement at the top.
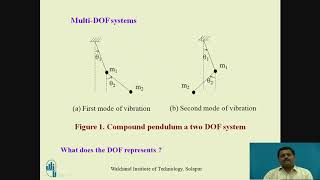
- Multi-story Frames: Each floor may have lateral DOFs, resulting in a multi-degree-of-freedom system.
Detailed Explanation
Dynamic degrees of freedom can be illustrated with specific structural examples. For instance, a cantilever beam that is fixed at one end and projects outwards has a single dynamic degree of freedom; it can sway sideways. In contrast, a multi-story frame building, where each floor can move individually, has multiple dynamic degrees of freedom due to the various ways each floor can respond to seismic activity.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a traditional one-story swing versus a three-floored bouncy castle. The swing can only move back and forth in one way, representing one degree of freedom. The bouncy castle's multiple levels can sway and bounce in various directions, reflecting multiple degrees of freedom.
Key Concepts
-
Dynamic Degrees of Freedom: Coordinates that define structural motion under dynamic loads.
-
Independent Displacement Points: Places where movement occurs independently in a structure.
-
Cantilever Beam: Structural element that only sways at one end.
-
Multi-Story Frames: Structures that have multiple floors resulting in complex dynamic behaviors.
Examples & Applications
A cantilever beam may only have one dynamic degree of freedom, lateral displacement at the top.
In a multi-story frame, each floor generally contributes to the lateral degrees of freedom, making it a multi-degree-of-freedom system.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
For every swaying beam that we see, one DOF is the key to ensure stability.
Stories
Imagine a tall building during an earthquake. Each floor, like a dancer, sways to a rhythm, contributing its own moves – these unique moves are its dynamic degrees of freedom.
Memory Tools
D.O.F. – Dynamic Occupies Floor: Remember that each floor in a multi-story frame has a unique degree of freedom.
Acronyms
D.D.F. – Dynamic Degrees of Freedom
The primary notion we identify when analyzing motion in structures.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Dynamic Degrees of Freedom
Coordinates that define the motion of a structure due to dynamic loads like seismic ground motion.
- Independent Displacement Points
Specific locations on a structure where motion can occur without affecting other parts.
- Cantilever Beam
A beam supported at one end that can experience lateral movement.
- MultiStory Frames
Structural systems with multiple floors that can exhibit complex dynamic behavior.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
