Earthquake Recording Networks
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Earthquake Recording Networks
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll be discussing earthquake recording networks. These systems are essential for monitoring seismic activity around the world. Can anyone tell me why monitoring earthquakes is important?

I think it's to help keep people safe during earthquakes.

Exactly! By monitoring seismic activity, we can better understand earthquakes and improve safety measures. The Global Seismographic Network, or GSN, is the main system for monitoring seismic events globally.

What exactly does the GSN do?

Great question! The GSN collects data on earthquakes to help scientists analyze them. It plays a vital role in global earthquake research. Remember the acronym GSN – Global Seismographic Network helps us 'Get Seismic News.'

So, does that mean we have similar networks in India?

Yes! That's where the Indian National Seismological Network, or INSN, comes into play. It's operated by the Indian Meteorological Department and focuses on collecting seismic data specific to India.

What do we use this data for?

The data is crucial not only for research but also for earthquake early warning systems. Monitoring networks like the INSN help us prepare better for earthquakes. Can anyone think of any benefits we gain from early warning systems?

They could save lives by alerting people before an earthquake hits!

Absolutely! Early warnings provide valuable seconds to minutes to alert the public, halt trains, or shut down utilities. To summarize today’s discussion, GSN and INSN are indispensable networks that enhance our understanding of earthquakes and improve safety measures.
Global Seismographic Network (GSN)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s discuss the Global Seismographic Network in more detail. The GSN enables scientists to monitor seismic activity in real-time. What do you think are its advantages?

It sounds like it would help us learn about earthquakes faster.

Exactly! The GSN provides valuable insights into seismic patterns and risks worldwide. This is critical for understanding tectonic processes – remember, GSN helps us 'Gather Seismic Proof.' What might be the challenges faced by GSN?

Maybe maintaining the equipment in different countries?

Spot on! Operational challenges and data sharing between countries can be complex. This leads us to our next discussion on the Indian National Seismological Network. Any thoughts on how INSN could complement GSN?

It must focus more on regional data and local earthquakes.

Yes! The INSN provides localized seismic data which is crucial for understanding the specific seismic risks in India. Together with the GSN, these networks allow for a comprehensive understanding of seismic activity globally and locally.

So both networks work together for better earthquake preparedness?

Exactly! They collaborate to enhance understanding and develop effective response strategies. Now, can anyone recap what we covered about GSN and its role?

GSN helps monitor global seismic activity, which aids research and helps us prepare for earthquakes!

Great summary! Keep in mind that the GSN is crucial for global seismic monitoring.
Indian National Seismological Network (INSN)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Moving on to the Indian National Seismological Network – INSN. The INSN is operated by the IMD and collects seismic data specifically for India. What kind of data do you think it gathers?

It probably records local earthquakes and their magnitudes.

Absolutely! It gathers information about the size, depth, and impact of local seismic events. How might this data be beneficial for residents in earthquake-prone areas?

It can help warn us when an earthquake is coming, so we can be prepared.

Precisely! The INSN plays a key role in developing earthquake early warning systems, which can provide alerts ahead of destructive waves arriving. Let’s remember, INSN stands for 'Information for National Safety in India.' What other aspects could INSN support in terms of research?

It could help in studying the risk of future earthquakes in those areas.

Exactly! By analyzing past seismic activity, we can estimate future risks and inform urban planning and infrastructure development. Can anyone summarize what we've learned about the INSN?

The INSN monitors local earthquakes and helps with early warnings and research in India.

Fantastic recap! The INSN is crucial for the safety of communities in earthquake-prone regions.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses two principal earthquake recording networks: the Global Seismographic Network (GSN) and the Indian National Seismological Network (INSN). Both networks play significant roles in monitoring seismic activity, with the INSN supporting research and earthquake early warning systems in India.
Detailed
Earthquake Recording Networks
Earthquake recording networks are essential infrastructures that monitor and record seismic activity, ensuring both scientific inquiry and practical responses to earthquakes. There are two primary networks discussed in this section:
Global Seismographic Network (GSN)
The GSN functions as a worldwide network dedicated to the continuous monitoring of seismic activity. It supports global earthquake research and contributes to understanding tectonic movements and seismic hazards.
Indian National Seismological Network (INSN)
Operated by the Indian Meteorological Department (IMD), the INSN focuses on collecting seismic data across India. This network is vital for research purposes as well as the development of earthquake early warning systems, enhancing the nation’s ability to respond effectively to seismic threats.
Significance
Together, these networks provide critical data for scientists to analyze seismic events and develop responsive measures to mitigate the impacts of earthquakes on communities.
Youtube Videos




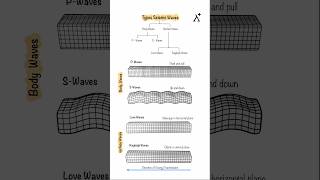



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Global Seismographic Network (GSN)
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Worldwide network for monitoring seismic activity.
Detailed Explanation
The Global Seismographic Network (GSN) is a coordinated system of seismometers distributed around the globe. Its primary purpose is to monitor and collect data on seismic activity, which includes earthquakes. This network helps scientists and engineers understand the frequency, magnitude, and location of earthquakes, enabling them to develop better predictions and risk assessments. This global framework also allows for the sharing of information across borders, enhancing collective knowledge about seismic phenomena.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a large, intricate web connecting various points across the globe, each point listening for the 'sound' of the Earth moving. Just like a network of security cameras that can detect any unusual activity in a city, the GSN continuously monitors the planet for seismic 'events'—helping to keep communities informed and safe.
Indian National Seismological Network (INSN)
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Operated by IMD (India Meteorological Department).
• Collects data for research and earthquake early warning systems.
Detailed Explanation
The Indian National Seismological Network (INSN) is managed by the India Meteorological Department (IMD). This network comprises a series of seismological stations across India, which gather data on seismic activity. The collected data serves dual purposes: it aids in conducting research related to earthquakes and supports the development of early warning systems. These early warning systems leverage real-time data to predict potential earthquakes, allowing residents to take precautionary measures, such as evacuating buildings or halting trains.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the INSN as a local weather station, but instead of predicting rain or sunshine, it predicts earthquakes. Just as the weather station uses meteorological data to issue warnings about storms, the INSN uses seismic data to warn people about potential earthquakes. This timely information can save lives, much like how knowing a storm is coming allows you to prepare.
Key Concepts
-
Global Seismographic Network (GSN): A global network monitoring seismic activities.
-
Indian National Seismological Network (INSN): A national network that focuses on earthquake data collection in India.
-
Earthquake Early Warning Systems: Systems designed to provide advance warning of upcoming earthquakes.
Examples & Applications
The GSN utilizes numerous seismometers located around the world to detect seismic waves from earthquakes.
The INSN helps provide early warnings in major Indian cities to mitigate the chances of casualties.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the world there’s a network, it’s GSN, it helps us understand when the earth will shake again.
Stories
Imagine a scientist sitting in a lab, studying earthquakes. One day, she gets data from a network that spans the globe, helping her predict where and when they might occur.
Memory Tools
Remember GSN for global data, INSN provides local news, together they keep us safe and informed.
Acronyms
GSN
Global Seismographic Network - 'Get Seismic News!'
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Global Seismographic Network (GSN)
A worldwide network for monitoring seismic activities and collecting earthquake data.
- Indian National Seismological Network (INSN)
A network operated by the Indian Meteorological Department that gathers seismic data specific to India.
- Seismic Activity
The occurrence of earthquakes and other ground vibrations.
- Seismic Data
Information collected from seismic activities, including magnitude, depth, and impact.
- Earthquake Early Warning Systems
Systems designed to provide messages of warning seconds to minutes before an earthquake hits.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
