Seismotectonics
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Seismotectonics
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we will dive into seismotectonics, which studies earthquakes in relation to tectonic movements. Can anyone explain why this relationship is important?

It helps us understand where earthquakes might happen and why.

Exactly! Knowing how tectonic movements relate to seismic activity allows us to improve building designs in earthquake-prone areas. What do you think active tectonics means?

It refers to tectonic plates that are still moving and creating stress which can lead to earthquakes.

Great explanation! Active tectonics are critical for assessing seismic hazards. Remember, think of tectonics like a constantly moving puzzle—any shift can change the whole picture. Let's summarize: seismotectonics links earthquakes with current tectonic activities.
Fault Mapping
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Fault mapping is essential in seismotectonics. Why do students think we need detailed fault maps?

To know where the faults are and how they move, which might help predict earthquakes.

Yeah, and it helps in microzonation, right?

Exactly! By identifying active faults and their movement history, we can allocate resources and designs to mitigate earthquake risks effectively. Can anyone recall what microzonation is?

It's about dividing an area into zones based on different seismic hazards!

Perfect! In summary, fault mapping is critical for understanding the potential risks and plan better urban infrastructures. Remember, active faults are like highway intersections where stress can build up.
Regional Seismotectonics in India
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s discuss specific regions in India affected by seismotectonics. Can anyone name a seismically active area in India?

The Himalayan region!

Exactly! The collision of the Indo-Australian and Eurasian plates creates significant seismic activity in the Himalayas. What other regions should we be aware of?

The Indo-Burmese Arc! It has unique tectonic interactions.

Don’t forget the Kachchh rift zone. I read it had a major earthquake in the past.

Correct! Each of these areas contributes to India's seismic landscape. The Peninsular Shield is also essential; despite being stable, it can still experience intraplate earthquakes. Who can summarize why we study these regions?

To prepare better for possible earthquakes and understand how the tectonics affect us!

Absolutely! It’s all about assessing risks and improving safety measures. Remember these regions and their significance—it's like connecting the dots on a seismic map.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section explores the field of seismotectonics, which examines how earthquakes are influenced by active tectonic movements and geological structures. Key components include fault mapping to understand earthquake history and regional seismotectonics specifically for different zones in India, such as the Himalayan collision zone and the Indo-Burmese arc.
Detailed
Seismotectonics
Seismotectonics is a vital area of study that focuses on the complex relationship between earthquakes, active tectonic behavior, and geological formations. By integrating geological, geophysical, and seismological data, scientists can better comprehend how different tectonic settings contribute to seismic activity.
Key Components of Seismotectonics
19.14.1 Definition and Scope
- Definition: Seismotectonics is the study of how tectonic movements lead to earthquakes, affecting geological structures in the process. It combines data across various scientific fields to analyze the interactions at play between tectonic activity and seismic events.
19.14.2 Fault Mapping
- Importance: This process involves identifying active faults and assessing their historical movements, which is crucial for seismic microzonation. Analyzing fault movements can help predict potential seismic hazards in certain areas.
19.14.3 Regional Seismotectonics in India
- Notable Zones: The section highlights several significant tectonic regions in India:
- Himalayan Collision Zone: Highly active due to the ongoing collision between the Indian and Eurasian plates.
- Indo-Burmese Arc: Another significant seismic region that demonstrates the complex tectonic activity resulting from plate interactions.
- Kachchh Rift Zone: A notable rift zone that has experienced significant seismic activity historically.
- Peninsular Shield: This area is relatively stable but can still experience intraplate earthquakes, contributing to the understanding of regional seismicity.
By studying these components, engineers and geoscientists can contribute to the design of earthquake-resistant infrastructures and improve seismic hazard assessments.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition and Scope
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Study of the relationship between earthquakes, active tectonics, and geological structures.
Combines geological, geophysical, and seismological data.
Detailed Explanation
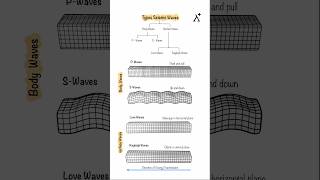
Seismotectonics is an interdisciplinary field that looks at how earthquakes are related to the movement of tectonic plates and the geological structures present in the Earth. It incorporates information from various disciplines, including geology (the study of Earth's materials), geophysics (the study of physical processes and properties of the Earth), and seismology (the study of earthquakes and seismic waves). By analyzing these interactions, scientists can better understand earthquake processes and predict where and when they might occur.
Examples & Analogies
Think of seismotectonics like a puzzle where each piece represents either a geological feature, a tectonic plate, or an earthquake. Just as each puzzle piece must fit together to reveal a picture, the various data from geology, geophysics, and seismology must be combined to understand the broader context of earthquakes.
Fault Mapping
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Identifies active faults and their movement history.
Important for seismic microzonation.
Detailed Explanation
Fault mapping is the process of locating and describing faults, which are fractures in the Earth's crust where movement has occurred. By studying these faults and their historical movements, scientists can understand how they behave during seismic events. This information is critical for seismic microzonation, a practice that assesses areas at risk of severe shaking during earthquakes based on local geological and seismic conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine mapping out a city's road network to identify where traffic jams frequently occur. Just like understanding traffic patterns helps in urban planning, fault mapping helps scientists identify earthquake-prone areas to improve the safety of buildings and infrastructure.
Regional Seismotectonics in India
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Himalayan collision zone.
Indo-Burmese arc.
Kachchh rift zone.
Peninsular shield (intraplate earthquakes).
Detailed Explanation
The regional seismotectonics of India focuses on specific areas where tectonic activities are prominent. The Himalayan collision zone is characterized by the collision of the Indo-Australian and Eurasian plates, which leads to frequent seismic activity. The Indo-Burmese arc is another significant area, while the Kachchh rift zone features tectonic processes that can generate earthquakes. Intraplate earthquakes occur in the Peninsular shield, showcasing seismic phenomena away from the plate boundaries.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a big puzzle where each corner represents different regions of India. Each corner has its unique characteristics that contribute to the overall shape of the puzzle. Similarly, the different seismic zones in India are like these corners, each playing a crucial role in the country's earthquake dynamics.
Key Concepts
-
Seismotectonics: Studying the interplay between earthquakes and tectonics.
-
Fault Mapping: Identifying faults to assess seismic hazards.
-
Microzonation: Segmenting regions by varying seismic characteristics.
-
Regional Seismotectonics: Understanding specific active tectonic zones in a region.
Examples & Applications
The Himalayas' active seismic zone due to the convergence of two major tectonic plates.
The Kachchh region, which experienced a significant earthquake in 2001, informs engineering practices in seismic design.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Faults can be mapped, seismic risks untangled, study tectonics, and safety's angled.
Stories
In a land where tectonic plates collided, a wise geologist mapped the faults. By understanding these movements, the townsfolk built with care, preventing disasters before they could dare.
Memory Tools
FIRE: Faults, Impacts, Regions, Energy - key areas for seismotectonics.
Acronyms
SMART
Study Maps And Regional Tectonics.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Seismotectonics
The study of the relationship between earthquakes, active tectonics, and geological structures.
- Fault Mapping
The process of identifying active faults and analyzing their movement history.
- Microzonation
The subdivision of a region into zones with similar seismic hazard characteristics.
- Himalayan Collision Zone
A tectonically active region in India formed by the convergence of the Indian and Eurasian plates.
- IndoBurmese Arc
A tectonically active zone in India due to the complex interactions of several plates.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
