Seismic Microzonation
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Seismic Microzonation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are discussing seismic microzonation. Can anyone tell me what they think it means?

Isn't it about dividing areas into different seismic risk levels?

That's correct! Seismic microzonation involves breaking down a region into smaller zones that share comparable seismic hazard characteristics, right down to finer details. This is crucial for urban planning.

What makes it different from regular seismic zoning?

Excellent question! While seismic zoning gives a broad overview, microzonation considers localized factors like soil type, topography, and groundwater level. These elements can change how buildings respond to earthquakes.

So, are cities in India using this?

Yes! Cities like Delhi, Guwahati, Bengaluru, and Chennai have implemented microzonation to enhance infrastructure safety against seismic events.

In summary, seismic microzonation is about localizing seismic risks to make urban planning more effective.
Parameters of Seismic Microzonation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's discuss the parameters that are critical for seismic microzonation. What are some factors we should consider?

Geology seems important. Different rocks must react differently to earthquakes.

Exactly! The geological composition greatly influences seismic wave behavior. What else?

Soil profile might change how firm the ground is, right?

Absolutely! The type of soil significantly affects ground motion during an earthquake. What about physical conditions like groundwater?

If the ground is saturated, it could change how stable it is!

Well said! Groundwater levels can lead to phenomena like liquefaction, impacting structures in an earthquake. Remember these factors—geology, soil type, topography, groundwater, and fault proximity—as they play a crucial role in microzonation assessments.

In summary of our session, the key parameters for seismic microzonation are geology, soil profile, topography, groundwater levels, and fault proximity.
Applications in Urban Planning
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

We've talked about seismic microzonation and its parameters. Now, how is this useful in urban planning?

Could it help decide where to build structures in a city?

Yes! By understanding the seismic risks associated with different zones, city planners can make more informed decisions. For instance, in areas identified as being at a higher risk, stricter building regulations might be enforced.

What about cities in India? Are they doing this?

Yes, cities like Delhi, Guwahati, Bengaluru, and Chennai have implemented seismic microzonation to enhance the resilience of their infrastructure to earthquakes. It helps prioritize areas for investment in seismic upgrades.

So, it's crucial for safety measures?

Exactly! Microzonation plays a vital role in preserving lives and properties during seismic events. Let's recap: we discussed how urban planning utilizes seismic microzonation to determine safe construction practices based on localized seismic data.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section outlines the concept of seismic microzonation, focusing on its parameters, applications, and significance in urban planning. It emphasizes how microzonation is distinct from broader seismic zoning by considering localized geological and hydrological factors.
Detailed
Seismic Microzonation
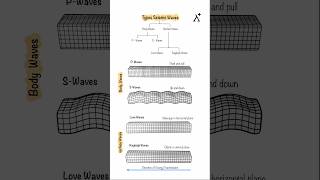
Seismic microzonation is a process that divides a region into smaller zones that share similar characteristics in terms of seismic hazards. Unlike general seismic zoning maps, which provide a broad overview based primarily on historical seismicity, microzonation investigates finer details such as geology, soil types, ground water levels, and proximity to faults. These aspects can significantly influence the amplification of ground motion during an earthquake.
Parameters Considered in Microzonation
Key parameters include:
- Geology: The composition and structure of the soil and rock can affect how seismic waves propagate.
- Soil Profile: Different soil types respond differently to seismic waves; for instance, soft soils may amplify shaking.
- Topography: The landscape can also influence local ground motion characteristics.
- Groundwater Level: The saturation level of soil impacts its ability to withstand seismic forces.
- Fault Proximity: Areas closer to active faults may face greater risk.
- Historical Seismicity: Past earthquake data helps in understanding the potential risks in the region.
Applications
Seismic microzonation finds applications chiefly in urban planning, where cities such as Delhi, Guwahati, Bengaluru, and Chennai have adopted specialized microzonation practices to enhance the resilience of urban infrastructure against earthquakes.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Concept of Seismic Microzonation
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Subdividing a region into zones with similar seismic hazard characteristics.
• Done at a much finer scale than seismic zoning maps.
Detailed Explanation
Seismic microzonation is the process of dividing a larger geographic area into smaller zones that share similar seismic hazard characteristics. This process is more detailed compared to general seismic zoning maps, which classify broader regions. The goal is to account for variations in geology, soil types, and other factors that can influence how earthquakes impact specific locations.
Examples & Analogies
Think of seismic microzonation like mapping different neighborhoods in a city. Just like some neighborhoods may be more prone to flooding due to lower elevation or poor drainage, certain areas may experience different earthquake effects based on their ground conditions.
Parameters Considered in Microzonation
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Geology, soil profile, topography, groundwater level, fault proximity.
• Historical seismicity and ground motion amplification.
Detailed Explanation
Several key parameters are taken into account for seismic microzonation. These include geological composition (the type of rocks and soils in an area), soil layers (which can amplify shaking), the layout of the land (topography), the level of groundwater, and the distance to nearby faults. Historical data on past earthquakes and how they affected regions also inform this process, ensuring that planners consider potential ground motion amplification, which can magnify the shaking.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are building a house. You wouldn't just choose any plot of land without checking what lies beneath it—like whether it's solid earth or a swampy area. Similarly, engineers must analyze the ground's characteristics where structures will be built in seismic zones.
Application of Seismic Microzonation
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Urban planning and infrastructure siting.
• Delhi, Guwahati, Bengaluru, Chennai are already microzoned.
Detailed Explanation
Seismic microzonation plays a crucial role in urban planning and the placement of critical infrastructure. By understanding which areas may face greater seismic risk, city planners can make informed decisions about where to build hospitals, schools, bridges, and other essential services. This tailored approach helps mitigate risks and enhances safety in densely populated urban areas. Cities like Delhi, Guwahati, Bengaluru, and Chennai have already implemented microzonation to better prepare for potential seismic events.
Examples & Analogies
Think about how city neighborhoods are designed based on their needs. For instance, if one area is known for tech startups, it might feature co-working spaces and high-speed internet connections. Similarly, in earthquake-prone regions, planners ensure that schools and hospitals take into account the specific risks from nearby geological features.
Key Concepts
-
Seismic Microzonation: The subdivision of regions into zones with similar seismic hazard characteristics.
-
Parameters: Specific factors that influence seismic response, including geology, soil type, and groundwater levels.
-
Urban Planning: The application of microzonation data to enhance infrastructure safety and resilience.
Examples & Applications
In cities like Delhi, microzonation has helped identify high-risk areas for building new infrastructure.
Guwahati's seismic microzonation utilizes local geological features to inform construction practices.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Microzonation is what we do, to keep buildings safe for me and you. With soil and rock in our sights, we build for safety in quake-filled nights.
Stories
Once upon a time in a city called Guwahati, the buildings trembled during an earthquake. The wise engineers decided to create zones based on the ground's story—soft and hard areas. They built safely, and the city thrived without fear.
Memory Tools
Remember the acronym 'GTSGF' for microzonation factors: Geology, Topography, Soil, Groundwater, Fault.
Acronyms
SLOOP - Soil, Location, Orientation, Overlapping factors, Proximity to faults.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Seismic Microzonation
The process of subdividing a region into zones with similar seismic hazard characteristics.
- Geology
The study of the Earth, especially in terms of its physical structure and substance.
- Soil Profile
The vertical section of soil that shows layers and characteristics affecting seismic response.
- Groundwater Level
The depth at which soil is saturated with water, influencing soil stability during seismic events.
- Fault Proximity
The distance to active fault lines, which can impact the level of seismic risk in an area.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
