Role in Seismic Zoning and Urban Planning
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Seismic Zoning
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to talk about how epicentres are crucial in the context of seismic zoning and urban planning. Can anyone tell me what an epicentre is?

It's the point on the Earth's surface above where an earthquake originates.

Exactly! This knowledge helps urban planners determine where to build safely. Can someone explain why knowing the epicentre is important for a city?

Because it helps predict which areas might be most affected during an earthquake?

Correct! Predicting affected areas is critical for effective zoning. Remember the acronym PACE—Planning And Construction Excellence— when we think about building in seismic areas.

What does PACE stand for again?

Planning And Construction Excellence! It reminds us that careful planning is essential for earthquake resilience.

Let’s summarize: Understanding the epicentre helps urban planning by identifying vulnerable areas and guiding development to enhance safety.
Microzonation Techniques
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's dive deeper into microzonation techniques. Can anyone tell me what microzonation entails?

It means breaking down regional hazard maps into smaller units that give a more detailed view of risk.

Exactly! Microzonation involves identifying clusters of epicentres. Why do you think this is useful?

It helps planners create specific regulations for small areas rather than using a one-size-fits-all approach.

Great insight! By tailoring our approach, we can better prepare communities. This is essential in urban planning, especially in earthquake-prone regions. Remember to consider local geology and historical data to inform these microzonation maps!

So, in summary, microzonation allows for more effective risk management by using epicentral data to focus on specific urban areas.
Integration into BIS Codes
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In this session, we will discuss how epicentral data is integrated into building codes. Can anyone provide an example of a code that uses this data?

I think BIS 1893 incorporates epicentral data for seismic design?

That’s right! BIS 1893 is crucial for setting standards for seismic resistance in buildings. Why do you think it's important to update these codes regularly?

Because seismic activity can change over time, and we need to ensure buildings are still safe?

Exactly! By regularly integrating historical epicentre data into these standards, the construction community can ensure safety and resilience. This is why adherence to building codes is vital in urban planning. What key term comes to your mind regarding this topic?

Seismic coefficients!

Exactly! Seismic coefficients derived from updated data help builders design structures that can withstand earthquakes. In summary, integrating epicentral data into building codes is essential for enhancing urban safety against seismic risks.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section outlines the significance of epicentres in seismic zoning through microzonation techniques, integration into national building codes, and updating regional seismic coefficients. These practices enhance urban planning and safety measures for communities at risk of earthquakes.
Detailed
Role in Seismic Zoning and Urban Planning
This section emphasizes the pivotal role epicentres play in seismic zoning and urban planning. It highlights two main applications:
24.9.1 Microzonation Techniques
Microzonation involves identifying local clusters of epicentres that can inform detailed hazard assessments for specific towns or districts. This process refines regional hazard maps into smaller, more precise microzonation units, which are vital for targeted urban planning and infrastructure development in earthquake-prone areas.
24.9.2 Integration into BIS Codes
The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) incorporates historical epicentral data, such as in BIS 1893, to continually update building codes and regulations. This ensures that the latest seismic activity data informs regional seismic coefficients, enhancing safety measures in construction and urban development efforts.
By applying these principles, urban planners and engineers can create structures and systems that mitigate earthquake impacts, aligning with national safety standards and promoting resilience in vulnerable communities.
Youtube Videos







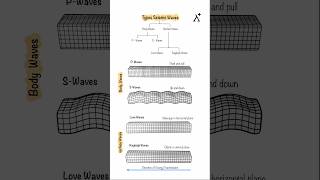

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Microzonation Techniques
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Identification of local epicentral clusters for specific towns or districts.
• Helps refine the regional hazard maps into microzonation units.
Detailed Explanation
Microzonation techniques involve identifying areas within regions that are likely to experience different levels of ground shaking during an earthquake. By studying local epicentral clusters, seismologists can determine which areas are more susceptible to damage. For instance, a town may be assessed for its unique geological characteristics and historical seismic activity, allowing planners to create detailed maps that show varying risk levels across different parts of the town, rather than applying a single risk level for the entire region.
Examples & Analogies
Think of this like assessing traffic patterns in a city. Just as some streets might see heavy traffic while others remain quiet depending on the layout and features of the area, microzonation allows for detailed insights into how different neighborhoods might respond in the event of an earthquake, refining the response and preparedness plans.
Integration into BIS Codes
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• BIS 1893 and other Indian standards use historical epicentral data for code updates.
• Regional seismic coefficients are derived from these data sets.
Detailed Explanation
The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) establishes building codes that are crucial for ensuring that structures can withstand earthquakes. These codes are continuously updated based on the analysis of historical epicentral data, which includes the locations and strengths of past earthquakes. By incorporating this data, the BIS can determine appropriate seismic coefficients that guide how buildings should be designed to handle seismic forces, making sure that they are resilient against future earthquakes.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine how sports teams use past performance data to improve their training and gameplay strategies. Similarly, building codes take into account the 'past performance' of areas during earthquakes to 'train' future buildings to be stronger and more resilient, minimizing damage and saving lives.
Key Concepts
-
Microzonation: A technique for breaking down hazard maps into smaller, manageable units for effective risk assessment.
-
BIS Codes: Standards set by India to enhance earthquake resistance in construction projects.
-
Seismic Coefficients: Values derived from statistical data that inform building designs in seismic zones.
Examples & Applications
In areas like California, microzonation has led to more tailored and resilient building practices due to thorough understanding of local seismic threats.
Following the 2001 Bhuj earthquake, updates to BIS codes incorporated lessons learned regarding local building vulnerabilities, improving safety standards in subsequent constructions.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To build with care, epicentres we know, helps planners see where the dangers flow.
Stories
Imagine a town preparing for an earthquake. They study the epicentres and their data guides their building codes, ensuring the structures are safe.
Memory Tools
P.A.C.E. - Planning And Construction Excellence!
Acronyms
S.E.A.S. - Seismic Evaluation and Assessment for Structures.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Epicentre
The point on the Earth's surface directly above the hypocentre where an earthquake originates.
- Microzonation
A technique that refines regional hazard maps into smaller, specific units based on local seismic risk.
- BIS Codes
Building codes set by the Bureau of Indian Standards that dictate construction practices to ensure safety in seismic areas.
- Seismic Coefficients
Values derived from seismic data that are used in building codes to design earthquake-resistant structures.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
