Seismic Wave Generation at the Hypocentre
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Seismic Waves
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to delve into seismic waves, specifically the primary waves, which we call P-waves. Can anyone tell me what they know about P-waves?

I think they are the first waves that we detect during an earthquake, right?

Exactly! P-waves are indeed the first to be detected. They travel the fastest, and they're key in understanding the earthquake's origin. Can anyone describe how P-waves move?

Aren't they compressional waves that move in the same direction as the particles?

Precisely, that's a perfect description! They create a push-pull motion as they travel through various media. Remember: P-waves are longitudinal waves. Let's keep that in mind as we move forward.

To help remember, think of 'P' as 'Primary' and 'Push'. Now, does anyone remember how fast these waves can travel?

I believe they can go between 5 to 13 kilometers per second, depending on the material.

Great job! P-waves vary in speed based on the medium they travel through. This understanding can help in locating the hypocentre.

In summary, we've learned that P-waves are the first waves detected during an earthquake, they move in a push-pull motion, and they travel at high speeds through different materials.
Locating the Hypocentre with P-Waves
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

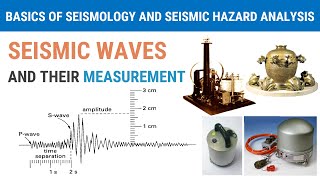
Now that we've established what P-waves are, let's look at their role in locating the hypocentre. Who can explain how seismologists use the difference in arrival times to locate the hypocentre?

They measure the time difference between the P-wave and the S-wave arrivals at various seismic stations.

Exactly right! By analyzing this time difference, they can calculate the distance from each station to the hypocentre. And when they use data from at least three different stations, they can triangulate the exact position, right?

Yes, I remember that from last class! They draw circles on a map where each circle represents an area where the hypocentre could be.

Exactly, well remembered! This method of triangulation is essential in pinpointing the hypocentre location. Why do you think it's important to identify the hypocentre?

It helps in understanding how strong the earthquake will be in that area.

Spot on! Knowing the hypocentre's location aids in seismic hazard assessments and disaster preparedness. So, to summarize, the arrival times of P-waves help us determine the hypocentre's distance and location, crucial in earthquake analysis.
Impact of P-Waves on Earthquake Analysis
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss the impact of P-waves in relation to earthquake analysis. Can someone summarize why they are significant?

They are the first waves detected and help us identify how far the earthquake's hypocentre is from the recording station.

Correct! This early detection allows emergency services to respond quickly. Can anyone explain how P-waves can offer some insights into safety preparations?

Since they arrive first, we can alert people about the earthquake before the more damaging S-waves arrive.

Exactly! The faster we can detect the waves, the better we can prepare for the shaking. How does this knowledge influence building designs in earthquake-prone areas?

Structures can be designed with the knowledge of likely P-wave impact, using materials that can absorb some of the energy.

Exactly! Buildings can be engineered to withstand the forces of earthquakes based on insights gained from P-wave data. So we have highlighted how P-waves are crucial for quick detection and influencing engineering practices.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section explores the generation of seismic waves at the hypocentre, focusing on primary waves (P-waves) and their characteristics. It highlights the role of P-waves in determining the hypocentre location and discusses their impact on earthquake detection.
Detailed
Seismic Wave Generation at the Hypocentre
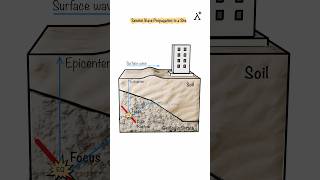
This section discusses the seismic wave generation at the hypocentre, the exact point within the Earth’s crust where an earthquake rupture initiates. The hypocentre is fundamental in seismic studies, as all types of seismic waves originate from this point, particularly the primary (P) waves and secondary (S) waves.
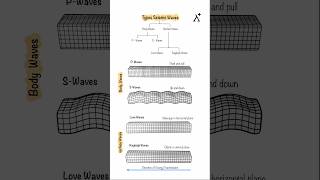
Primary Waves (P-Waves)
P-waves are distinguished as the fastest seismic waves, traveling at speeds ranging from 5 to 13 km/s, depending on the material they encounter. They are longitudinal or compressional waves, meaning they move in the same direction as the particle vibrations, creating a push-pull motion. Importantly, P-waves can traverse through solids, liquids, and gases.
Role of P-Waves in Hypocentre Location
One critical aspect covered is the role of P-waves in earthquake detection. They are the first seismic waves that are recorded on a seismograph, providing the initial indication of an earthquake's occurrence at seismic stations. Seismologists analyze the time difference between the arrival of P-waves and secondary (S-wave) arrivals to calculate the distance to the hypocentre from each station. Utilizing data from at least three stations allows for precise triangulation of the hypocentre's location, demonstrating the importance of these primary waves in understanding and analyzing seismic activities.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Seismic Waves
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The hypocentre is the origin of all types of seismic waves, but most notably the primary (P) waves and secondary (S) waves.
Detailed Explanation
The hypocentre, also known as the focus, is the starting point of an earthquake within the Earth’s crust. When an earthquake occurs, it generates different types of seismic waves, including primary (P) waves and secondary (S) waves. P-waves are the first to be detected by instruments, while S-waves follow. This distinction is crucial because it helps seismologists understand where the earthquake originated and the nature of the seismic event.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine throwing a stone into a pond. The point where the stone hits the water is like the hypocentre. The ripples that spread outwards from that point represent the seismic waves generated by the earthquake.
Primary Waves (P-Waves)
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Nature: Longitudinal/compressional waves.
• Speed: Fastest seismic waves (~5–13 km/s depending on material).
• Direction: Move in the same direction as the particle vibration (push-pull motion).
• Medium: Travel through solids, liquids, and gases.
• Detection: First to be recorded on a seismograph, useful in determining hypocentre location.
Detailed Explanation
P-waves are a type of seismic wave characterized as longitudinal or compressional. This means they move by compressing and expanding the material they travel through, such as rocks or water. P-waves are the fastest seismic waves, traveling at speeds between 5 to 13 kilometers per second, depending on the type of material they move through. They can traverse solids, liquids, and gases, making them versatile. When an earthquake occurs, P-waves are the first to arrive at a seismic station, allowing scientists to quickly determine the hypocentre's location using the time they take to travel from the hypocentre to the station.
Examples & Analogies
Think of P-waves as the first sound waves you hear when someone claps their hands. Just like that sound travels through the air quickly to reach your ears, P-waves travel swiftly through different materials, alerting us to the earthquake before the more destructive waves arrive.
Role of P-Waves in Hypocentre Location
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
P-waves provide the first indication of an earthquake at seismic stations. By analyzing the time difference between P- and S-wave arrivals, seismologists can determine the distance to the hypocentre from each station. With data from at least three stations, the exact position can be triangulated.
Detailed Explanation
When an earthquake occurs, P-waves are detected first, and their arrival time is recorded at various seismic stations. By comparing the arrival times of both P-waves and S-waves, seismologists can calculate how far away each station is from the hypocentre. Using data from at least three different stations, they can triangulate the exact location of the hypocentre. This is crucial for understanding the earthquake's impact and for emergency response efforts.
Examples & Analogies
This process is similar to using a GPS app to find your location. If you only know the distance from one signal, you won't know exactly where you are. However, if you triangulate your position using three or more signals from different towers, you can pinpoint your exact location accurately.
Key Concepts
-
Hypocentre: The starting point of earthquake ruptures, critical to understanding seismic waves.
-
P-Waves: The first and fastest seismic waves responsible for initial earthquake detection.
-
Triangulation: Method used by seismologists to locate the hypocentre based on wave arrival times.
Examples & Applications
The use of data from P-waves helps determine the precise location of the hypocentre in real-time during seismic events.
The analysis of P-wave arrival times can lead to early warning alerts in earthquake-prone regions.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
P-waves rush in, fast as a flash, find the hypocentre without any crash.
Stories
Imagine a race among seismic waves. The P-wave, the fastest runner, reaches the finish line before its slower competitors, providing early alerts to all.
Memory Tools
Remember 'P' for 'Primary and 'P' for 'Push' to connect wave movement with their nature.
Acronyms
P-WAVE
Primary Wave
Arrival Very Early.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Hypocentre
The exact point within the Earth where an earthquake rupture initiates.
- Seismic Waves
Waves of energy that travel through the Earth, generated by earthquakes.
- Primary Waves (PWaves)
The fastest seismic waves that move as longitudinal or compressional waves.
- Triangulation
A method used to determine the location of the hypocentre by measuring the time difference of seismic wave arrivals.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
