Instrumentation and Data Collection
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Seismometers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to discuss seismometers, which are essential instruments in monitoring earthquakes. Can anyone tell me what they think a seismometer does?

Is it used to measure earthquakes?

Correct! A seismometer measures ground displacement and records the seismic waveforms produced during an earthquake. It helps us understand how the ground shakes during these events.

How does it actually work?

Great question! Seismometers work by detecting the movement of the ground. They have sensitive components that respond to vibrations, allowing them to record the amplitude and frequency of seismic waves.

Can they tell us where the earthquake started?

Yes! By analyzing the data from multiple seismometers, scientists can triangulate the earthquake's epicenter. Remember, 'Measure to know' can be a good mnemonic for understanding the importance of measuring seismic waves.

So they are like detectives for earthquakes?

Exactly! They help us investigate the mysteries of how earthquakes happen. Let’s summarize: seismometers measure ground movement and help locate the epicenter of earthquakes.
Understanding Accelerographs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's look at accelerographs. Who can tell me what they do?

Do they measure how fast the ground shakes?

Exactly! Accelerographs record the acceleration of ground motion during earthquakes, which is crucial for structural analysis. What do you think we can learn from this data?

I guess we can see how buildings might react during shaking.

Right again! This information helps engineers design buildings that can withstand earthquake forces. A helpful mnemonic is 'Acceleration for Action' to remember that accelerographs give data necessary for action in design.

Are they used together with seismometers?

Yes, they complement each other. Seismometers track the waves, while accelerographs assess the impact of those waves on structures. So, we learn both what happens in the ground and how it affects buildings.

Got it! So they work together like a team.

Exactly! Let's recap: accelerographs measure acceleration, helping us understand how ground motion impacts structures.
Applications in Earthquake Analysis
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we know what seismometers and accelerographs do, how do you think engineers use this data?

They probably use it to make buildings safer!

Absolutely! They analyze the data to estimate parameters like epicentral distance, which helps in determining how strong the shaking will be at a specific location.

So they can figure out where buildings should be built?

Exactly! By understanding site response, engineers can decide where to place buildings to minimize risk. Remember: 'Safe Sites Save Lives' is a great mnemonic for this idea.

What about after an earthquake? How do they use the instruments then?

Good question! Data from these instruments is crucial in post-event assessments to evaluate damage and guide recovery efforts. It's a continuous cycle of learning and improving safety.

So, we are always learning from each earthquake?

Exactly! Each event teaches us valuable lessons to inform future designs. Let's summarize: seismometers and accelerographs are vital in analyzing and improving earthquake resilience in our built environment.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section provides insights into two key instruments used in earthquake monitoring: seismometers, which measure ground displacement, and accelerographs, which record acceleration crucial for understanding the ground's response during seismic events. It highlights their roles in estimating epicentral distance, ground motion parameters, and site response.
Detailed
Instrumentation and Data Collection
In the context of earthquake engineering, precise measurements are critical for understanding seismic events and their implications for structural safety. This section focuses on two main instruments:
Seismometers
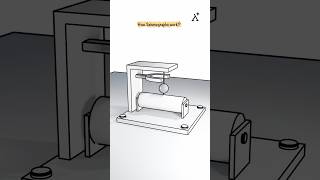
Seismometers are devices designed to measure ground displacement. They effectively record the waveforms generated during seismic occurrences, enabling scientists and engineers to analyze the behavior of seismic waves. Through these recordings, crucial data related to the earthquake's magnitude, location, and timing can be derived.
Accelerographs
Accelerographs serve a complementary role to seismometers by recording the acceleration of ground motion, providing essential data necessary for structural engineering analysis. The readings obtained from accelerographs help assess how structures respond to shaking, which in turn informs design practices aimed at enhancing earthquake resistance.
Key Applications
Both instruments play a pivotal role in:
- Estimating epicentral distances, which contributes to locating the earthquake's origin.
- Determining ground motion parameters, crucial for designing and retrofitting buildings in seismically active regions.
- Analyzing site response to ground shaking, which varies due to local geological conditions, further informing engineering practices.
In summary, seismometers and accelerographs are indispensable tools in earthquake research and engineering, providing data that directly influence safety measures and construction practices.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Seismometers and Accelerographs
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Seismometer: Measures ground displacement and records waveforms.
• Accelerograph: Records acceleration, essential for structural engineering analysis.
Detailed Explanation
Seismometers and accelerographs are essential instruments used to understand how earthquakes affect the Earth. A seismometer measures the ground's movement, or displacement, during an earthquake. It captures the changes in position and records the seismic waves, which are the energy released by the earthquake. On the other hand, an accelerograph measures the acceleration of the ground during seismic activity, which provides crucial data for constructing earthquake-resistant buildings and understanding how structures will respond to ground shaking.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a seismometer like a very sensitive microphone that picks up vibrations, just like how a regular microphone captures sounds. An accelerograph is like a speedometer in a car that measures how quickly the car accelerates when you press the gas pedal. Together, these instruments help scientists and engineers understand how strong an earthquake was and how buildings might behave during one.
Purpose of Seismometers and Accelerographs
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Both help estimate:
– Epicentral distance
– Ground motion parameters
– Site response
Detailed Explanation
The data collected from seismometers and accelerographs serve several important purposes. First, they help determine the epicentral distance, which is the distance from the earthquake's origin to the point on the surface. Knowing this distance is vital for assessing the impact of the earthquake at particular locations. Additionally, these devices provide ground motion parameters such as the intensity and duration of shaking, which are crucial for understanding the earthquake's effects. Finally, they help analyze site response, which refers to how different types of ground materials (like soil or rock) react to seismic waves.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are at a concert. The microphones (seismometers) pick up the sound waves from the music and help the sound engineer determine how far the singer is from the speakers. The sound engineer (accelerograph) measures how loud the music gets in different parts of the venue. By combining this information, they can figure out if certain areas are better or worse for hearing the concert, similar to how engineers use data to ensure buildings can withstand earthquakes.
Key Concepts
-
Seismometer: Measures ground displacement and records seismic activities.
-
Accelerograph: Records acceleration during seismic events, essential for structural analysis.
-
Epicentral Distance: Distance from a measuring station to the earthquake's epicenter.
-
Ground Motion Parameters: Measurements that quantify the shaking effects of an earthquake.
-
Site Response: How local geological conditions affect ground shaking intensity.
Examples & Applications
An example of a seismometer recording would be a graph showing the seismic waves from a major earthquake, indicating amplitude and frequency.
An accelerograph might show rapid spikes in acceleration during an earthquake, demonstrating how quickly the ground shakes.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Seismometer's to measure the ground's sway, 'Acc' helps to gauge in a shaking display.
Stories
Once, there were two friends, Seismometer and Accel, who worked together to document an earthquake event to tell how buildings should be built as well as harden.
Memory Tools
SA - Seismometer's Amplitude, A - Accelerograph's Acceleration.
Acronyms
SAGE - Seismometers Analyze Ground Events, helping to remember their roles.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Seismometer
An instrument that measures ground displacement and records seismic waveforms during an earthquake.
- Accelerograph
An instrument that records the acceleration of ground motion, crucial for analyzing how structures respond to seismic activity.
- Epicentral Distance
The distance from a seismic recording station to the epicenter of an earthquake.
- Ground Motion Parameters
Quantitative measures of the effects of seismic waves at a specific location, including acceleration, velocity, and displacement.
- Site Response
The behavior of ground shaking at a particular location influenced by local geological conditions.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
