Seismic Retrofitting to Improve Ductility
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Seismic Retrofitting
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Good morning, everyone! Today, we're going to talk about seismic retrofitting. Can anyone tell me why retrofitting is important for older buildings?

It's important because many older buildings weren't designed for earthquakes.

Exactly! Buildings designed before modern codes often lack ductility. Retrofitting helps enhance their ability to withstand seismic forces.

What are some techniques we can use to retrofit these buildings?

Great question! Techniques include jacketing of columns and beams, adding shear walls, and using FRP wrapping. Are you all familiar with FRP?

Not really. What does FRP do?

FRP stands for Fiber-Reinforced Polymer. It's used to wrap columns to provide confinement, enhancing their strength. Remember FRP - think of it as a 'seatbelt' for columns!

So, like a protective layer?

Exactly! At the end of our session today, I want you to remember these key techniques and their purpose.
Retrofitting Techniques
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive deeper into retrofitting methods. Can anyone describe what jacketing involves?

Is it when we add more concrete around the existing columns and beams?

Yes! Jacketing not only increases their strength but also enhances ductility. Can you think of another method?

Adding shear walls helps, right?

Correct! Shear walls provide additional lateral support, crucial during seismic events. Now, what about base isolation—why do we use it?

It helps the building move separately from the ground motion?

Exactly! Base isolation allows for more independent motion, reducing the force transferred to the structure. Remember the acronym 'J-S-F-B' for Jacketing, Shear Walls, FRP Wrapping, and Base Isolation!
Objectives of Retrofitting
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's talk about the objectives of seismic retrofitting. Why do you think we want to improve ductility?

To prevent buildings from collapsing during an earthquake?

Absolutely! Increasing ductility ensures that the structure can endure deformation without failure. What else can retrofitting improve?

It should help with load paths, right?

Correct! Effective load paths ensure that forces can be transmitted efficiently through the structure. Lastly, why do we need to comply with standards like IS 13935?

To follow best practices and make sure the buildings are safe?

Exactly! Compliance ensures that we're applying the best methods for seismic strength and performance. Remember this phrase: 'Ductility for Safety' as we wrap up today's lesson!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses various retrofitting techniques that improve the structural ductility and strength of existing buildings not originally designed for seismic events. Focus is placed on methods such as column and beam jacketing, shear wall addition, and FRP wrapping, emphasizing compliance with IS 13935.
Detailed
Seismic Retrofitting to Improve Ductility
In the context of earthquake engineering, retrofitting refers to modifying existing structures to improve their performance during seismic events. Many buildings constructed before modern seismic codes lack the ductility required to withstand dynamic forces during earthquakes. This section outlines essential retrofitting techniques that contribute to enhancing the ductility of these structures.
Key Techniques:
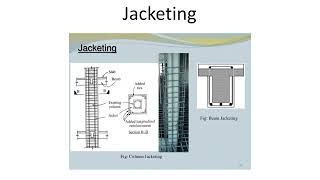
- Jacketing: Enhancing columns and beams with reinforced concrete (RC) or steel, providing increased strength and stiffness.
- Addition of Shear Walls or Braces: Implementing shear walls or braces to provide additional lateral support, improving the structure's stability under seismic loads.
- FRP Wrapping: Using Fiber-Reinforced Polymer (FRP) to wrap columns, increasing their confinement and strength.
- Base Isolation or Damping Systems: Installing base isolators or damping systems to mitigate seismic forces by allowing the building to move independently from ground movements.
Objective of Retrofitting:
The primary goals of retrofitting include:
- Increase Ductility: Enhancing the ability of buildings to undergo deformations without experiencing failure.
- Improve Load Paths: Ensuring that loads can be transmitted through the structure effectively.
- Energy Dissipation: Improving the building's ability to absorb and dissipate energy generated by seismic activities.
- Compliance with Standards: Following guidelines outlined in IS 13935, which addresses seismic evaluation and strengthening of existing structures.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Seismic Retrofitting
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Many existing buildings are not designed for ductility. Retrofitting is essential to improve performance under future earthquakes.
Detailed Explanation
Many older buildings were constructed without considering the need for ductility, which is vital for handling the stresses and strains of seismic activity. As buildings age or as new seismic information becomes available, it's crucial to update them. Retrofitting involves modifying these structures to improve their ability to withstand seismic events. This process ensures they can perform better in future earthquakes, reducing the risk of collapse and enhancing safety.
Examples & Analogies
Think of retrofitting like upgrading an old car with new safety features. Just as you would want your car to handle emergencies better, buildings also need updates to ensure they can withstand the forces of an earthquake.
Retrofitting Techniques
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Retrofitting Techniques:
- Jacketing of columns and beams (RC or steel)
- Addition of shear walls or braces
- FRP Wrapping for confinement
- Base isolation or damping systems
Detailed Explanation
There are several techniques used to retrofit buildings for improved ductility. These include:
1. Jacketing: This technique involves encasing existing columns and beams with additional concrete or steel to increase their strength and ductility.
2. Shear Walls and Braces: Adding these components helps distribute seismic forces more evenly throughout the structure.
3. FRP (Fiber Reinforced Polymer) Wrapping: This method provides strong confinement around concrete elements, aiding in their strength.
4. Base Isolation/Damping Systems: These reduce the amount of seismic energy that reaches the building, minimizing movement and potential damage during an earthquake.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine wrapping a fragile gift in padding to protect it from bumps during transport. Similarly, retrofitting techniques enhance a building’s ability to handle shocks from an earthquake.
Objectives of Retrofitting
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Objective:
- Increase ductility and strength.
- Improve load paths and energy dissipation.
- Comply with IS 13935 (for seismic evaluation and strengthening).
Detailed Explanation
The objectives of retrofitting focus on several key areas:
1. Increasing Ductility and Strength: The primary aim is to allow buildings to deform without failing during seismic events, effectively 'stretching' rather than breaking.
2. Improving Load Paths and Energy Dissipation: Retrofits are designed to create more efficient pathways for forces to travel through a structure, allowing energy from seismic forces to be absorbed and managed effectively.
3. Compliance with Standards: Retrofitting not only enhances safety but also ensures buildings meet modern codes and regulations like IS 13935, which guides seismic evaluation and strengthening methods.
Examples & Analogies
Consider retrofitting a bridge to add support beams. Just as these beams allow the bridge to better manage traffic loads, retrofitting buildings helps them better handle the forces of an earthquake.
Key Concepts
-
Seismic Retrofitting: Modifying existing structures to enhance seismic performance.
-
Ductility: Crucial for preventing sudden failure during seismic events.
-
Jacketing: A method to strengthen structural elements.
-
Base Isolation: A technique that allows independent movement during earthquakes.
Examples & Applications
Implementing FRP wrapping on columns of a pre-1970s building to enhance ductility.
Adding shear walls to an existing structure to resist lateral forces during an earthquake.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Retrofitting is the fix, for buildings that can’t do tricks!
Stories
Imagine an old building that loves to dance but is afraid of earthquakes. With retrofitting, it gets a special dance floor that helps it groove without falling!
Memory Tools
Remember J-S-F-B: Jacketing, Shear walls, FRP, Base Isolation for retrofitting techniques.
Acronyms
D.E.C.A.
Ductility
Energy dissipation
Compliance
and Augmentation are what retrofitting aims for.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Ductility
The ability of a structure to undergo large deformations without losing strength.
- Retrofitting
The process of modifying an existing structure to improve its performance in seismic events.
- Jacketing
The application of additional layers of material to columns and beams to increase strength and ductility.
- FRP (FiberReinforced Polymer)
A composite material used to wrap structural elements for added strength and confinement.
- Base Isolation
A technique that allows a building to move independently from ground motions during an earthquake.
- Shear Wall
A structural element that resists lateral forces acting on a building.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
