Limitations and Assumptions
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Assumptions of Linear SDOF Systems
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, let's start by discussing the assumption that structures behave like linear single-degree-of-freedom systems. Why do you think this assumption is made, and what does it imply?

I think it makes calculations simpler and more manageable. But is it realistic for all buildings?

Good point! While it simplifies the analysis, many real-world scenarios involve complex structural behavior. Structures often have multiple degrees of freedom, especially in irregular shapes or those with varying stiffness.

And what are the risks if we rely too heavily on this assumption?

If we incorrectly assume linearity, we may underestimate the response of the structure under actual earthquake conditions, leading to potential structural failures.

A tip to remember is: Linear assumptions simplify analysis but may not capture real-world phenomena, so always be cautious!

So, does this mean we need to use more complex models for certain buildings?

Exactly! Using multi-degree-of-freedom models is key for those structures.

In summary, understanding that response spectra assume linear SDOF behavior helps us gauge when to apply simpler approaches and when to adopt more complex analyses.
Neglect of Phase Information
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's talk about another limitation: the neglect of phase information in ground motion. What does that mean for our analyses?

Does it mean we might miss how the timing of the motions affects the structure?

Exactly! Ground motion consists of various frequencies and timing patterns. Not including this phase information can result in inaccurate predictions of how a structure may respond during an earthquake.

So, it's kind of like listening to music without paying attention to when the notes are played?

Great analogy! Understanding the timing and interaction between different frequencies is crucial for an accurate response prediction.

To summarize this point, neglecting phase information can lead us into oversimplifications that impact the safety and effectiveness of our designs.
Limitations in Nonlinear Evaluations
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let’s address the limitations concerning nonlinear evaluation. Why are response and design spectra not suitable for detailed nonlinear analyses?

Because they are based on linear assumptions, right? Nonlinear behavior during an earthquake might not fit those assumptions?

Spot on! Nonlinear analyses require detailed input on material behavior and deformation, which spectra cannot provide accurately.

So for critical structures, we definitely need to conduct time history analyses!

Exactly! It's crucial to account for inelastic behavior, especially in essential structures. Using spectra for these assessments would be inadequate.

In conclusion, while response spectra offer a quick method for preliminary design, they have limitations in capturing nonlinearity, making them less valid for detailed evaluations.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we discuss the key limitations and assumptions made when applying response and design spectra in earthquake engineering. It highlights the reliance on linear behavior of structures, the exclusion of phase information in ground motion, and the inapplicability for detailed nonlinear evaluations.
Detailed
Limitations and Assumptions
This section emphasizes the critical limitations and assumptions that come into play when using response and design spectra in seismic analysis and design.
- Assumptions of Linear Single-Degree-of-Freedom Systems:
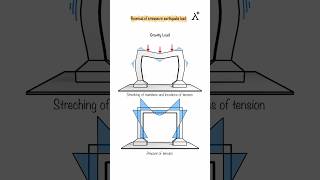
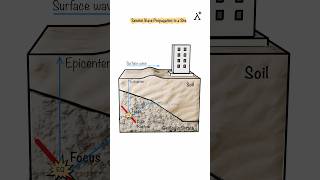
- The assessment of structures typically assumes they behave as linear single-degree-of-freedom (SDOF) systems under seismic loads. This is a simplifying assumption that may not hold true in all cases, especially for complex structures where multi-degree-of-freedom (MDOF) behaviors are evident.
- Neglect of Phase Information:
- The spectra do not account for the phase information inherent in actual ground motion data. This can lead to discrepancies in the predicted response of structures, particularly in complex seismic scenarios where the timing of ground motions can influence structural behavior.
- Limitations in Nonlinear Evaluation:
- The use of spectra is limited when it comes to detailed non-linear time-history analyses, which are critical for evaluating the performance of structures experiencing significant inelastic behavior during extreme seismic events.
Understanding these limitations is crucial for engineers and designers to use response and design spectra effectively and responsibly.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Linear SDOF Systems Assumption
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Assumes response is governed by linear SDOF systems.
Detailed Explanation
This part states that the response spectrum assumes that structures behave like linear Single-Degree-of-Freedom (SDOF) systems during seismic activity. In essence, it simplifies complex structural responses to a single mass, spring, and damper system. This assumption is critical because it simplifies the mathematical modeling involved in predicting how a structure will respond to earthquakes.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a simple swing set. When you push a swing (our SDOF system), it moves back and forth in a predictable, linear motion. If you were to exert too much force, the swing might start moving chaotically, similar to how a real building's response becomes unpredictable beyond linear behavior.
Phase Information Ignored
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Ignores phase information in ground motion.
Detailed Explanation
In seismic analysis using response spectra, the phase information of ground motion—the timing and order of the seismic waves—is not taken into account. This means that while we can estimate the maximum response (like height or acceleration), we miss detailed dynamics that could affect how different parts of a structure respond at different times. This can lead to inaccuracies in predicting structural behavior during actual seismic events.
Examples & Analogies
Think about listening to a band playing music. If you only pay attention to the loudest notes (the response) but ignore how they play together over time (the phase), you might miss the nuances that affect the overall harmony of the performance. Similarly, the ignored phase information can lead to an incomplete picture of how structures will behave during an earthquake.
Limitations for Non-linear Evaluations
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Cannot be used for detailed non-linear time history evaluation.
Detailed Explanation
The response spectrum method is not suitable for structures that exhibit non-linear behavior under loading, such as those experiencing plastic deformations. Non-linear time history evaluation considers the actual material properties and response of the structure throughout the loading process, allowing for a more nuanced understanding of how buildings will perform in real-world scenarios. The limitations of the response spectrum mean it may not accurately capture severe damage effects.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a car braking hard on a slippery road. The initial response might not directly correspond to how the vehicle will slide—its stopping distance could vary significantly based on tire conditions and road texture (non-linear behavior). Similarly, response spectra might fall short in predicting how impactful these variances will be on a building’s structure during extreme events.
Key Concepts
-
Linear SDOF Assumption: An assumption that structures can be simplified to single-degree-of-freedom models for dynamic analysis.
-
Phase Neglect: The omission of phase information can lead to inaccurate assessments of structural responses.
-
Nonlinear Analysis Limitations: Response spectra are not suitable for evaluating structures undergoing nonlinear behavior.
Examples & Applications
For a small residential building, assuming a linear SDOF behavior may be appropriate; however, for larger buildings like skyscrapers, a multi-degree-of-freedom analysis could yield more accurate results.
In a seismic analysis, if the timing of the ground motion leads to resonance effects that aren't captured in linear spectral analysis, a structure could experience different forces than predicted.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Sway the way, remember the phase, neglect it not, or face a dismay.
Stories
Imagine an architect designing a bridge. They rely on simple models for speed but forget that the wind's timing can sway it dramatically, leading to expensive fixes after the fact.
Memory Tools
Remember S.D.O.F. - Single Degree Of Failure if assumptions go awry!
Acronyms
LNP - Linear, Neglect Phase - a reminder to consider linear assumptions and phase in analysis!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- SingleDegreeofFreedom (SDOF) Systems
A simplified model that represents a structure's dynamic behavior by considering only one degree of freedom.
- Phase Information
Details about the timing of different components of ground motion that can influence the structural response.
- Nonlinear Analysis
A method to evaluate a structure's behavior considering materials' nonlinear properties and responses to dynamic loading.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
