Spectral Matching Techniques
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Spectral Matching Techniques
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are discussing spectral matching techniques, which modify ground motion time histories to align them with target design spectra. Why do you think this is important?

I think it helps ensure structures can withstand earthquakes better.

Exactly! Accurate matching can lead to more precise assessments of how buildings will perform during seismic events.

Right, it’s all about improving safety and performance. Remember, these techniques are crucial, especially in nonlinear time history analysis.
Frequency Domain Spectral Matching
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s dive deeper into one method: frequency domain spectral matching. What do you think this involves?

Maybe adjusting the frequencies in the ground motion data?

Exactly! By using techniques like wavelet-based analysis, engineers can modify frequency components so the modified ground motion matches the target spectrum. This allows for a better fit to the expected site response.

So it's about making sure the structure responds how we expect it to during an earthquake?

Indeed! It's about ensuring that seismic assessments reflect reliable representations of potential ground shaking.
Time Domain Adjustments
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's talk about time domain adjustments. Who can explain what this method involves?

Does it mean changing the actual time history instead of just the frequency components?

Correct! This method modifies the time history itself to ensure it meets the desired spectral characteristics. What do you think could be the challenge here?

Maybe keeping the overall characteristics of the ground motion while altering its spectrum?

Exactly! It’s a balancing act between accuracy and maintaining the integrity of the time history.
Significance of Spectral Matching Techniques
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To wrap up our discussion, how would you summarize the significance of spectral matching techniques?

They help improve the accuracy of seismic analysis, leading to better building designs.

And they ensure we understand the response of structures better during actual earthquakes.

Exactly! Using these techniques can lead to more resilient buildings and safer communities. Remember, safety is always the top priority.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
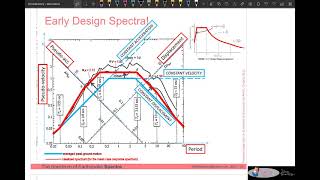
This section discusses spectral matching techniques that adjust ground motion time histories to closely match a target design spectrum. These techniques, crucial in nonlinear time history analysis, include frequency domain spectral matching and time domain adjustments.
Detailed
Spectral Matching Techniques
Spectral matching techniques are essential in earthquake engineering as they allow engineers to modify ground motion time history to ensure its spectrum closely matches a target design spectrum. This is particularly important when using nonlinear time history analysis, where accurate representation of seismic demands on structures is crucial for safety and performance. The main approaches include:
- Frequency Domain Spectral Matching: This technique employs methods such as wavelet-based analysis to adjust the frequency components of the ground motion, ensuring that the modified seismic input closely corresponds to the target spectral properties.
- Time Domain Adjustment: This method directly modifies the time history of the ground motion to achieve the desired spectral characteristics. Such adjustments can help in refining the ground motion representation to better meet engineering objectives.
Understanding these techniques can significantly enhance the accuracy of seismic assessments and ultimately lead to improved structural resilience against seismic events.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Spectral Matching Techniques
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Modify ground motion time history so that its spectrum closely matches the target design spectrum.
Detailed Explanation
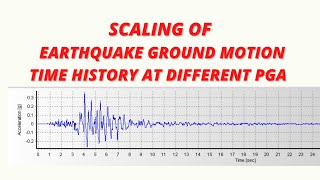
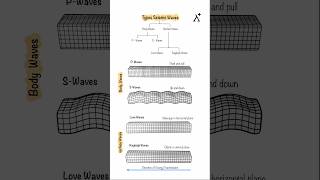
Spectral matching techniques involve adjusting the recorded or simulated ground motion time histories so that their frequency response matches a specified design spectrum. This is important in earthquake engineering because it helps ensure that the input used in structural analyses is representative of the expected seismic demands for a specific site. By modifying the ground motion to fit the design spectrum, engineers can achieve more accurate predictions of how structures will perform during an earthquake.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like tuning a musical instrument. If you want a guitar to sound perfect for a certain song, you might need to adjust its strings to reach the right notes. Similarly, in spectral matching, you adjust the 'notes' of the ground motion (i.e., its frequency content) to match the 'musical score' (the design spectrum). This way, the 'performance' (how a building responds in an earthquake) will be just right.
Applications of Spectral Matching in Nonlinear Time History Analysis
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Used in nonlinear time history analysis.
Detailed Explanation
Nonlinear time history analysis accounts for the complex behavior of materials and structures that do not respond in a purely elastic manner during an earthquake. The goal is to evaluate how the structure behaves, including any permanent deformations or failures. By applying spectral matching techniques in this analysis, engineers can better simulate real-world earthquake conditions and evaluate the ultimate performance of structures, ensuring they are designed to withstand severe ground motions without collapsing.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a rubber band. If you stretch it gently, it returns to its original shape (elastic behavior). But if you pull it too far, it stays stretched out (nonlinear behavior). In an earthquake, buildings can behave like that rubber band, and nonlinear time history analysis helps us predict those 'stretched' responses when the ground shakes. Spectral matching helps us ensure that the 'shakes' we're using in our analysis reflect realistic scenarios.
Methods of Spectral Matching
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Techniques:
- Frequency domain spectral matching (e.g., wavelet-based)
- Time domain adjustment.
Detailed Explanation
There are various methods for performing spectral matching, which can be broadly categorized into frequency domain and time domain techniques. Frequency domain spectral matching typically involves transforming the time history data into the frequency domain, adjusting the spectrum to align with the target, and transforming it back. Wavelet-based techniques are one common approach within this category. Time domain adjustments, on the other hand, involve directly manipulating the original time history by scaling or modifying certain time segments to ensure that the resultant spectrum aligns with the design spectrum.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the process of editing a video. In a frequency domain approach, you might first convert the video into a storyboard that highlights key actions (like changing the spectrum). Once you know what needs to be adjusted, you can edit specific clips to fit the overall theme. In time domain adjustments, you're like a director who directly tweaks scenes in real-time to ensure the final movie (the adjusted ground motion) fits the desired vision (the target design spectrum).
Key Concepts
-
Spectral Matching: A modification process of ground motion to fit a target spectrum.
-
Frequency Domain Techniques: Methods that adjust frequency components of ground motion.
-
Time Domain Techniques: Methods that alter the time history to achieve the desired spectral response.
Examples & Applications
An engineer adjusts a recorded earthquake ground motion's frequency spectrum using wavelet transforms to better align with the target design spectrum.
A seismic analysis software modifies the time history of a seismic event so that the output closely resembles a target response spectrum.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To match the spectrum, don't just take a guess, adjust the wave, and aim for success.
Stories
Imagine an engineer at a desk, taking signals from the earthquakes that emerge on the I-desks. With numbers in hand, they adjust and refine, making sure structures withstand the seismic design.
Memory Tools
FAT stands for Frequency adjustments, Accurate time modifications, and Targeted spectral alignment.
Acronyms
MARS
Modify
Align
Refine Spectral response.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Spectral Matching
A technique used to modify ground motion time histories to ensure their spectrum aligns with a target design spectrum.
- Frequency Domain
A method of representing functions or signals based on frequencies rather than time.
- Time Domain
The analysis of signals or functions as they vary over time.
- Nonlinear Time History Analysis
An analysis method that accounts for material non-linearities in structural response due to dynamic loads.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
