BJT as an Amplifier
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to BJT Amplification
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we will discuss how BJTs are used as amplifiers. Who can briefly explain what an amplifier does?

An amplifier increases the strength of a signal.

Exactly! In a BJT, we use a small base current to control a much larger collector current. This is significant for signal amplification. Can anyone think of a simple example where this might be used?

Audio amplifiers, like in speakers?

Yes, audio amplifiers are a great example! So remember, the key idea is that a small input can lead to a much larger output. This property is often described by the current gain, represented by beta (β).
Current Control Mechanism
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive deeper into how the base current actually controls the collector current. What phenomenon allows this to happen?

I think it's because the base is very thin, so the electrons can cross over to the collector easily!

Correct! The thin base ensures that most of the injected electrons from the emitter diffuse into the collector. Can someone explain why this is important?

It allows for amplification — a small change in base current can create a large change in collector current.

Exactly! That’s why BJTs are widely used in applications such as RF amplifiers and sensor conditioning.
Applications of BJT Amplifiers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's explore practical applications. In what circuits do you think BJTs as amplifiers are used?

They can be used in radio frequency amplifiers!

I also think they might be used in microphone preamps.

Great suggestions! BJTs play a key role in audio and RF amplification as well as in sensor signal conditioning, where small signals need amplification before processing.
Summary and Recap
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To wrap up, what key points should we remember about BJTs as amplifiers?

A small base current can control a larger collector current!

And they are used in applications like audio and RF amplifiers.

Perfect! Remember the significance of the current gain and how important it is in applying BJTs in various circuits.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The BJT acts as an amplifier when it operates in its active region, where a small base current is able to control a much larger collector current, allowing for effective signal amplification. Common applications include audio amplifiers, RF amplifiers, and sensor signal conditioning.
Detailed
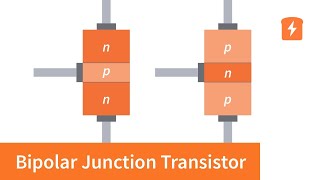
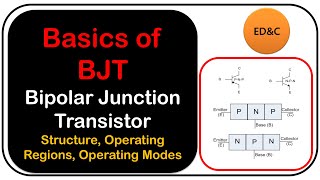
BJT as an Amplifier
In this section, we explore the function of the Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) as an amplifier. The BJT operates predominantly in the active region, where it is exceptionally effective in amplifying signals due to its unique current-controlling nature. A small base current can control a significant collector current, which is critical for enhancing signals in various applications such as audio amplifiers, RF amplifiers, and sensor signal conditioning.
Key Points:
- The BJT allows a small input current (base current) to induce a larger output current (collector current).
- This relationship makes BJTs ideal for applications requiring signal amplification, including consumer electronics and communication devices.
- Understanding this principle is crucial for various electronic circuit designs, emphasizing the importance of BJTs in both analog and digital electronics.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Operating in the Active Region
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Operates in Active Region.
Detailed Explanation
In a BJT amplifier, the transistor operates in the active region, which is a specific mode where it can amplify signals. This mode allows the transistor to control a large output current based on a smaller input current. This property is crucial for amplification as it means a small change in the input can lead to a significant change in the output.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the BJT as a water faucet. The small movement of the faucet handle (small base current) can allow a large flow of water (large collector current) to come out. Just as a slight turn can change the water flow dramatically, a small input current can modify a larger output current.
Control of Collector Current
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The small base current controls a large collector current, making it suitable for signal amplification in:
Detailed Explanation
The BJT uses a small current at the base terminal to regulate a much larger current at the collector terminal. This relationship is fundamental for signal amplification. For instance, if there’s a tiny current at the base, it can lead to a substantial current flowing from collector to emitter. This ability to control a larger current with a smaller one makes BJTs valuable in applications where boosting signal strength is necessary.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a dimmer switch for your room lights. A small adjustment on the switch (base current) controls how bright the lights become (collector current). Just as you can create a brighter or dimmer light with a small adjustment, BJTs amplify input signals with a small base current controlling the larger collector current.
Applications of BJT Amplification
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Suitable for signal amplification in: ● Audio amplifiers ● RF amplifiers ● Sensor signal conditioning
Detailed Explanation
BJTs are widely used in different types of circuits for signal amplification. Audio amplifiers take weak audio signals and amplify them so they can drive speakers. RF (Radio Frequency) amplifiers work with radio signals to enhance communication. Additionally, sensor signal conditioning involves improving and preparing signals from sensors for further processing, which can also be achieved using BJTs for amplifying weak signals. Each of these applications highlights the versatile nature of BJTs in amplifying various types of signals.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a concert where the musicians are playing quietly but the audience needs to hear them clearly. An audio amplifier works like a large speaker system that takes the quiet sounds and makes them loud enough for everyone to hear. Similarly, BJTs take weak signals from sensors and make them strong enough for further action or evaluation.
Key Concepts
-
Active Region: The state at which the BJT amplifies signals.
-
Current Gain (β): Reflects the amplification factor of the BJT.
-
Signal Amplification: The process of increasing the power or amplitude of a signal.
Examples & Applications
An audio amplifier circuit where a BJT is used to boost the signal from a microphone.
RF amplifiers in communication systems utilize BJTs to enhance weak signals for transmission.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When base is small, collector stands tall — amp up the signal, that's the call!
Stories
Imagine a tiny gatekeeper (base current) controlling a huge crowd (collector current) at a concert. The gatekeeper lets a small number in, but this small action allows massive enjoyment to grow!
Memory Tools
For remembering BJT functions: 'Base In, Collect Power' — (BICP) signifies the base current's role in amplifying collector power.
Acronyms
A simple acronym for BJT functions
'A-C-B' (Amplifier-Collector-Base) illustrates the flow of functions inBJT operation.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)
A semiconductor device that uses both electrons and holes as charge carriers for amplification and switching.
- Active Region
The operational region of a BJT where it can amplify signals.
- Current Gain (β)
The ratio of collector current to base current in a BJT, indicating its amplification ability.
- Amplification
The process of increasing the strength of a signal.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
