Database Design Principles
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Normalization
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll discuss normalization. Can anyone tell me what normalization means?

Isn't it about organizing data to avoid redundancy?

Exactly! Normalization aims to reduce data redundancy and ensure dependencies are logical. It has several forms, starting with the First Normal Form or 1NF. Can anyone explain what 1NF requires?

It eliminates duplicate columns and makes sure each column has atomic values, right?

That's right! Let's remember that using the acronym 'AD' for 'Atomic and Distinct' can help you recall what 1NF requires. Now, what about the Second Normal Form?

2NF ensures non-key attributes depend fully on the primary key, I think?

Right again! To summarize, normalization helps maintain data integrity and makes updating data easier. Remember: 'Normalization helps eliminate headaches!'
Denormalization
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's shift gears and talk about denormalization. Can anyone tell me what that means?

I remember that it's the opposite of normalization. It combines tables to speed up read access.

Exactly! Denormalization is often used in databases that are predominantly read-heavy. Why do you think this is a trade-off?

It can lead to more storage use and potentially slower write operations.

Spot on! Denormalization can optimize your database for specific workloads. Remember that: 'More data stored means slower writes!'
Entity-Relationship Diagrams (ERDs)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let’s discuss Entity-Relationship Diagrams, or ERDs. Who can explain their purpose?

They visually represent the relationships between different entities in a database.

Absolutely! ERDs are instrumental in database design. Can you name the main components of an ERD?

Entities, relationships, and attributes!

Correct! Think of it as a blueprint for your database structure. Remember, 'ERDs are the roadmap to relational systems!'
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
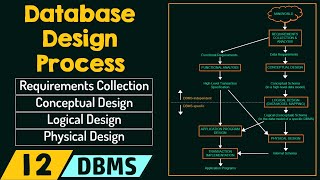
Effective database design is crucial for scalability and efficiency in applications. Key principles include normalization to eliminate data redundancy, denormalization for improved performance in specific use cases, and the creation of Entity-Relationship Diagrams (ERDs) to visualize database relationships.
Detailed
Database Design Principles
Good database design is key to maintaining efficient and scalable systems. This section highlights foundational principles:
1. Normalization
Normalization is the process of organizing data to reduce redundancy and dependencies in a database. The main objectives are to avoid duplicate data and ensure logical data storage. The various forms of normalization include:
- 1st Normal Form (1NF): Eliminates duplicate columns and ensures each column contains atomic values.
- 2nd Normal Form (2NF): Ensures all non-key attributes are fully dependent on the primary key.
- 3rd Normal Form (3NF): Eliminates transitive dependencies among non-key attributes.
2. Denormalization
Denormalization involves merging tables to optimize read performance, typically at the cost of increased storage or slower write operations. This is used in scenarios where the application experiences read-heavy workloads.
3. Entity-Relationship Diagrams (ERDs)
ERDs are visual representations of the relationships between entities (tables) in a database. They are essential in designing clear and maintainable databases. Understanding these diagrams helps to create an organized online resource for database interactions.
In summary, mastering these principles of database design ensures that developers can create efficient, scalable, and easy-to-maintain database systems crucial for robust applications.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Normalization
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Normalization is the process of organizing data to reduce redundancy and dependency. The primary goal is to ensure that data is stored logically and can be easily updated.
- 1st Normal Form (1NF): Eliminate duplicate columns and ensure each column contains atomic values.
- 2nd Normal Form (2NF): Ensure that each non-key attribute is fully dependent on the primary key.
- 3rd Normal Form (3NF): Eliminate transitive dependencies, i.e., ensure no non-key attribute depends on another non-key attribute.
Detailed Explanation
Normalization involves structuring your database to minimize duplication of data, which improves efficiency and makes it easier to maintain. The first step, 1NF, requires that every column in a database table must hold unique and indivisible values. Next, 2NF mandates that every non-key column must be directly linked to the primary key, fostering a stronger relationship between the key and the dependent attributes. Finally, 3NF seeks to remove any indirect relationships between non-key attributes, ensuring that they do not reference or depend on each other, effectively streamlining the dataset.
Examples & Analogies
Think of normalization like organizing a library. In 1NF, each book represents an individual entity without duplicates on the shelf. In 2NF, all books by the same author are grouped together, assuring each author has their own section. In 3NF, unrelated books are kept in separate sections to avoid confusion, just like ensuring that different genres don’t intermingle unnecessarily.
Denormalization
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Denormalization is the opposite of normalization. It involves merging tables to optimize read performance, often at the cost of increased storage or slower writes. This is typically used in systems with read-heavy workloads.
Detailed Explanation
Denormalization is the process of intentionally increasing data redundancy by combining tables for faster data retrieval. While normalization improves data integrity, denormalization can enhance performance by minimizing the number of tables accessed during a read operation. This is especially beneficial in scenarios where an application frequently reads data but seldom updates it. However, this optimization can lead to data anomalies and requires careful management to prevent issues during writes.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a restaurant that has all its menu items on a single long list, rather than separating them into appetizers, mains, and desserts. This denormalized list allows customers to quickly see their options without flipping through multiple menus, which enhances the dining experience even though it makes the restaurant’s inventory management a bit more complex.
Entity-Relationship Diagrams (ERDs)
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
ERDs are used to visually represent the relationships between entities (tables) in a database. Understanding these diagrams is critical for designing clear and maintainable databases.
Detailed Explanation
Entity-Relationship Diagrams (ERDs) serve as a blueprint for database design, showcasing how data entities interact and relate to one another. In these diagrams, entities are typically represented by rectangles, and relationships are illustrated with lines connecting these entities. Attributes, or specific data points about each entity, are indicated in ovals. By clearly mapping these relationships, developers can ensure that their database design is logical and meets application needs.
Examples & Analogies
Think of an ERD as a family tree diagram. Each family member represents an entity, and the lines connecting them indicate relationships (like parent, child, or sibling). This visual representation helps us understand how everyone in the family connects and who depends on whom, just like how an ERD clarifies how data entities are linked in a database.
Key Concepts
-
Normalization: A method of organizing data to minimize redundancy.
-
Denormalization: The process of reducing the number of tables to improve read performance.
-
Entity-Relationship Diagrams: Visual tools used to depict database relationships.
Examples & Applications
An example of normalization is converting a list of employee records with duplicate addresses into a separate 'Addresses' table.
Using denormalization might include merging 'Orders' and 'Customers' tables to speed up retrieval for reports.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In a normalized room, data won't bloom; keep it neat, avoid the mess, without excess, you'll feel blessed!
Stories
Imagine you're designing a library, one without duplicates where each book gets a unique home. As you build the collection, you ensure every detail is in its right place, reducing chaos and enhancing user experience. That’s normalization helping you run a better library!
Memory Tools
For Normalization, remember: 'AD-FD-ND' (Atomic, Dependence Fully, No Dependencies) for 1NF, 2NF, 3NF.
Acronyms
NDE
Normalize for Data Efficiency helps remind us to keep our data structured.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Normalization
The process of organizing data to reduce redundancy and dependency.
- Denormalization
The process of merging tables to optimize read performance.
- EntityRelationship Diagrams (ERDs)
Visual representations of the relationships between entities in a database.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
