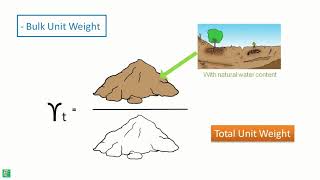
Bulk Unit Weight
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Volume Relations
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll discuss volume relations in soil. First, can anyone tell me what the void ratio is?

Is it how much space is empty in the soil?

Exactly! The void ratio is the ratio of the volume of voids to the volume of soil solids. We express it as a decimal. So, what's the formula for void ratio?

It’s V_v to V_s, right?

Correct! Now, how does this relate to porosity?

Porosity is the volume of voids compared to the total volume.

That's right! And porosity is expressed as a percentage. Remember the relationship: if we know one, we can calculate the other. S=V_v / (V_v + V_s) can help us understand this better.

So if we have high void ratio, we might have low porosity?

Typically yes! Let’s close this session by noting that a well-understood void ratio and porosity can lead to better predictions of soil behavior.
Introducing Weight Relations
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's transition to weight relations. Who can explain what density measures?

It measures how much mass is in a volume?

Yes! And unit weight is similar but expressed in weight per volume. Can anyone provide the units we use for density?

It can be kg/m³ or g/cm³.

That’s correct! Moving on, there’s also the concept of specific gravity, G_s. What is it?

It’s the mass of solid particles in proportion to the unit weight of water.

Exactly right! A specific gravity between 2.60 and 2.80 is common in inorganic soils. Now, can anyone explain the difference between bulk unit weight and dry unit weight?

Bulk unit weight includes water, while dry unit weight only considers solids.

Perfectly said! Understanding these weights is crucial for effective soil design and engineering.
Exploring Saturated and Buoyant Unit Weight
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In this session, we will look deeper into saturated and buoyant unit weights. What does saturated unit weight refer to?

It’s the weight when all voids are filled with water?

Correct! And can someone tell me the significance of buoyant unit weight?

Isn't that when the soil is under water, and it accounts for buoyancy?

Yes! Buoyant unit weight is essential for calculating effective stress in geotechnical engineering. Why do we care about effective stress?

Because it helps us understand how soil behaves under load, right?

Exactly! When doing construction, knowing how soil reacts when submerged is crucial for safety. Can anyone summarize what we've learned about weights?

We learned how density, unit weight, and specific gravity play essential roles in understanding soil behavior!

Great summary! Remember, grasping these concepts helps in effective soil management.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section elaborates on the relationships of void ratio, porosity, degree of saturation, and various weight measures including dry and bulk unit weight. It highlights the significance of these definitions in understanding soil behavior and properties.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of Bulk Unit Weight:
This section discusses two primary categories: volume relations and weight relations, which are essential for understanding the physical properties of soils.
Volume Relations:
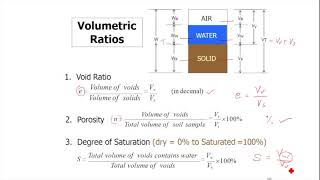
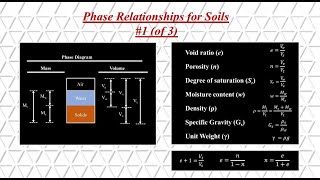
- Void Ratio (e): This is the ratio of the volume of voids (V_v) to the volume of soil solids (V_s), represented as a decimal. It indicates the space within the soil that is not occupied by solid particles.
- Porosity (n): Defined as the ratio of the volume of voids to the total volume of soil (V_t), expressed as a percentage. It gives insight into how much of the soil is comprised of air and water.
- Degree of Saturation (S): This term expresses the volume of water (V_w) as a percentage of the volume of voids. A dry soil has an S of 0%, while a fully saturated soil has an S of 100%.
- Air Content (a): The ratio of the volume of air (V_a) to the volume of voids, indicating the air-filled spaces within the soil.
- Percentage Air Voids (n_a): The ratio of the volume of air to the total volume.
Weight Relations:
- Water Content (w): This is the ratio of the mass of water to the mass of solid particles, with values ranging from 0% for dry soils and exceeding 100% for wet soils.
- Specific Gravity (G_s): This indicates the mass of solid particles per unit volume, usually between 2.60 and 2.80 for inorganic soils.
- Dry Unit Weight: Represents the weight of solids per unit volume, a critical measure in various engineering calculations.
- Bulk Unit Weight: The weight of solids plus water per unit volume, vital for understanding soil behavior under different conditions.
- Saturated Unit Weight: Equivalent to bulk density when all voids are filled with water.
- Buoyant Unit Weight: Represents the effective mass of soil when submerged under water, accounting for the buoyancy effect.
Youtube Videos



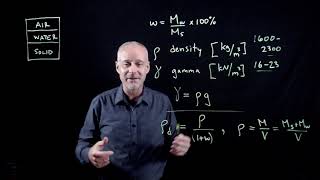


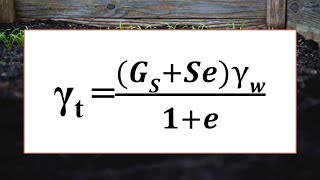
Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Bulk Unit Weight
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Bulk unit weight is a measure of the amount of solid particles plus water per unit volume.
Detailed Explanation
Bulk unit weight refers to the combined weight of solid particles in the soil along with the water that fills the voids within the soil. It's measured as weight per unit volume, and is significant in engineering applications because it helps determine the load a soil can bear. Essentially, it takes both the weight of the soil particles and the water into account, which can influence how the soil behaves under different loads.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a sponge. When it's dry, it’s light because it contains only the weight of the sponge material. Once you soak it in water, it becomes heavier, because now, in addition to the sponge, you also have the weight of the water inside it. Similarly, bulk unit weight of soil denotes how much weight is present in a given volume when both soil and water are included.
Importance of Bulk Unit Weight
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Saturated unit weight is equal to the bulk density when the total voids is filled up with water.
Detailed Explanation
Saturated unit weight is a specific case of bulk unit weight that occurs when all void spaces in the soil are completely occupied by water. This concept is crucial in geotechnical engineering, as understanding how much weight the soil can support when it is saturated helps in designing stable foundations for buildings. During wet conditions, knowing the saturated unit weight allows engineers to assess the potential risks, such as settlement or failure.
Examples & Analogies
Think about a sponge again, but this time consider it as a dry sponge lying on the kitchen counter, which starts absorbing water. When it’s fully soaked, it can no longer hold any more water, reflecting that every void in the sponge is filled. In terms of soil, when it is saturated, it reflects the maximum weight that can be supported by that soil, as all available space is now taken by water.
Buoyant Unit Weight
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Buoyant unit weight or submerged unit weight is the effective mass per unit volume when the soil is submerged below standing water or below the ground water table.
Detailed Explanation
Buoyant unit weight refers to the weight of the soil when it is submerged underwater. Under these conditions, the water exerts an upward buoyant force, effectively reducing the weight of the soil when calculating how much load it bears. This is crucial for evaluating the behavior of soil and the stability of structures like bridges or basements, where groundwater interaction is a factor.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a beach ball that you push underwater. As it tries to rise back up due to its buoyancy, it feels lighter when submerged than when it's out of the water. Similarly, when soil is submerged, the upward force from the water makes the soil 'feel' lighter, which is what we refer to as buoyant unit weight. This concept is essential in construction zones near water bodies, ensuring proper foundation design.
Key Concepts
-
Void Ratio: The ratio of voids to solids indicating soil compaction.
-
Porosity: Indicates the capacity of soil to hold water and air.
-
Degree of Saturation: Shows the extent of water content in the soil.
-
Bulk Unit Weight: Affects soil stability and drainage characteristics.
-
Buoyant Unit Weight: Important for understanding submerged soil properties.
Examples & Applications
If a soil sample has a void ratio of 0.5 and a total volume of 1 m³, the volume of voids is 0.5 m³ and the volume of solids is 0.5 m³.
A soil with a porosity of 30% means 30% of the soil volume consists of voids, which can inform water retention capacity.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In soil below, voids may flow, keep solids high, to help them grow.
Stories
Once upon a time, a soil grain named Sandy learned it was important to fill its voids with water. The happier Sandy was with less void, the stronger Sandy's foundation became.
Memory Tools
Peds See Layers - Remember Porosity, Specific Gravity, and Density are key!
Acronyms
VBSP - Volume, Bulk, Saturated, Porous - all related to soil weight!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Void Ratio (e)
The ratio of the volume of voids to the volume of soil solids.
- Porosity (n)
The ratio of the volume of voids to the total volume of soil, expressed as a percentage.
- Degree of Saturation (S)
The volume of water in the soil expressed as a percentage of the volume of voids.
- Water Content (w)
The ratio of the mass of water present to the mass of solid particles.
- Specific Gravity (G_s)
The mass of solid particles as compared to the weight of an equivalent volume of water.
- Dry Unit Weight
The weight of solid particles per unit volume.
- Bulk Unit Weight
The weight of solid particles plus water per unit volume.
- Saturated Unit Weight
The bulk density when soil voids are completely filled with water.
- Buoyant Unit Weight
The effective mass per unit volume of soil when submerged in water.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
