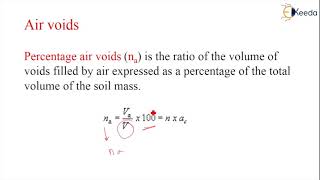
Percentage Air Voids (n)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Void Ratio
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's start by understanding the term 'void ratio', denoted as 'e'. It represents the volume of voids to the volume of soil solids. Can anyone tell me why this is a key concept in soil mechanics?

Is it because it helps us understand how much space is not occupied by solids?

Exactly! A higher void ratio indicates more space for air and water. Now, if we know the void ratio, what can we calculate next?

We can calculate porosity, right? The relationship between the two is important.

That's correct! To remember, think of the acronym *PAV*—Porosity as a Volume. Let’s move on to discuss porosity itself.
Defining Porosity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Porosity, typically denoted as 'n', is the ratio of the volume of voids to the total volume of the soil. Why do you think this is significant?

It shows us how much of the soil's volume is made up of voids, which affects how water and air can move through it.

Exactly! Let’s calculate it for a given volume of soil and discuss its implications on drainage and stability.

Wait, how do we find the percentage of air voids from porosity?

Great question! The percentage air voids is linked to both void ratio and porosity. We’ll get to that soon!
Understanding Percentage Air Voids
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's focus on percentage air voids, denoted as 'na'. It’s calculated as the volume of air divided by the total soil volume. Can someone explain how this can be useful?

It tells us about the air content in soil, which can affect its strength and compression!

Yes! An important aspect to consider in construction and agricultural practices. Let's do an example calculation together.

Can we also connect it to the degree of saturation if we know the water content?

Absolutely! The degree of saturation will give us insight into how filled those voids are with water versus air.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore the definition and significance of percentage air voids in soil mechanics. It describes how percentage air voids relate to void ratio and porosity and highlights the importance of understanding the interactions between air, water, and soil solids within a given volume.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
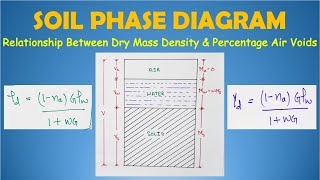
The concept of percentage air voids (na) is an important aspect in soil mechanics, representing the ratio of the volume of air present in the voids of soil to the total volume of the soil system. This section covers various volumetric relationships that are foundational to understanding soil behavior, including:
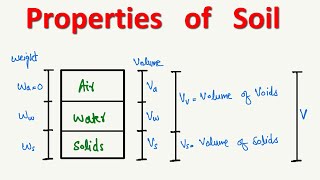
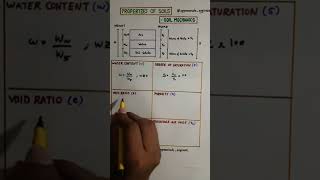
- Void Ratio (e): Defined as the ratio of the volume of voids (Vv) to the volume of soil solids (Vs).
- Porosity (n): The ratio of the volume of voids (Vv) to the total volume of soil (Vt), expressed as a percentage.
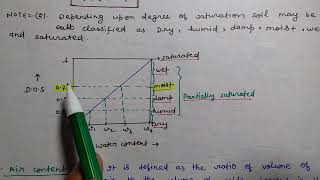
- Degree of Saturation (S): Indicates soil moisture content, with a range from 0% for dry soil to 100% for fully saturated soil.
- Air Content (ca): The ratio of the volume of air (Va) to the volume of voids (Vv).
- Percentage Air Voids (na): The ratio of the volume of air (Va) to the total volume (Vt) expressed as a percentage.
Understanding these relationships is crucial for predicting how soil behaves under different loading and environmental conditions.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Percentage Air Voids
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Percentage air voids (n_a) is the ratio of the volume of air (V_a) to the total volume.
Detailed Explanation
Percentage air voids (n_a) is a measurement that indicates how much air is present in the soil compared to the total volume of the soil. It is calculated by dividing the volume of air in the soil (V_a) by the total volume of the soil, which includes the volume of solids, water, and voids (the spaces between particles). This ratio helps to quantify the air space within the soil structure.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a sponge. When a sponge is dry, it contains a lot of air spaces that can absorb water. When you soak the sponge, those air spaces fill up with water. The percentage of air voids is like measuring how much air is in that sponge compared to how much total space (air plus water) it can hold. If you squeeze it out, the air voids increase again.
Importance of Air Voids in Soil
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Air voids are important because they affect soil properties such as drainage, aeration, and the ability of plants to grow.
Detailed Explanation
Air voids in soil play a crucial role in influencing various soil characteristics. They contribute to how well water drains through the soil and how much air is available for roots to breathe. High levels of air voids can lead to better aeration, which is essential for healthy plant growth, while too many voids may indicate poor soil stability.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a garden. Good soil should have a balance of air and moisture. If the soil has too many air voids, like dry, loose sand, plants might struggle to get the water they need. Conversely, if the soil is too compacted with very few air spaces, like clay during a drought, the plants may drown due to poor drainage. A healthy garden requires the right mixture of air and moisture.
Key Concepts
-
Void Ratio: Ratio of the volume of voids to the volume of solids.
-
Porosity: Reflects the amount of void space in soil as a percentage.
-
Percentage Air Voids: Indicates how much of the soil’s total volume is air.
Examples & Applications
A soil sample has 30% voids. If its total volume is 100 m³, then the volume of voids is 30 m³, and figuring the air from this gives insights into drainage capabilities.
In a saturated soil, all voids are filled with water (S=100%), while in a completely dry state (S=0%), voids consist only of air.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In soil where the air does hide, voids and solids must abide.
Stories
Imagine a sponge full of water; when you squeeze it, air bubbles rise. This dynamic illustrates how in soil, depending upon water content, air voids change too!
Memory Tools
PAV: Percentage Air Voids — Porosity And Volume always correlates.
Acronyms
VAPS
Voids
Air
Porosity
Saturation. Remember these key concepts together!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Void Ratio (e)
The ratio of the volume of voids to the volume of soil solids.
- Porosity (n)
The ratio of the volume of voids to the total volume of soil expressed as a percentage.
- Degree of Saturation (S)
The percentage of voids filled with water, ranging from 0% to 100%.
- Air Content (ca)
The ratio of the volume of air to the volume of voids.
- Percentage Air Voids (na)
The ratio of the volume of air to the total volume of soil expressed as a percentage.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
