Buoyant Unit Weight
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Unit Weight
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will start by exploring unit weight. Can anyone tell me how unit weight differs from density?

Isn't density just the mass per unit volume?

Exactly! Density is mass per volume, while unit weight incorporates gravity, giving you a weight value instead. Unit weight is important to know, especially in soil mechanics.

Can you explain what unit weight means in relation to soil?

Certainly! In soil, unit weight helps identify how much weight a specific volume of soil can exert, which is crucial for foundation stability.

Let’s remember it with the acronym WDS: Weight per Density in Soil.

That helps! But what about 'buoyant unit weight'?

Great question! Buoyant unit weight comes into play when the soil is submerged. Let's move on to that topic next.
Understanding Buoyant Unit Weight
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Buoyant unit weight is defined as the effective mass per unit volume when the soil is submerged. This is calculated using the formula γ_b = γ_s - γ_w. Can anyone interpret this?

So, we're subtracting the unit weight of water from the soil's unit weight?

Correct! This subtraction accounts for the upward force of water, which reduces the effective weight of the soil.

What happens in different saturation levels?

Excellent question! Buoyant unit weight varies with saturation. For fully saturated soil, the buoyant weight is at its maximum because all voids are filled with water.

To remember, use the mnemonic: `Saturate Good = Buoyancy High!`

That’s a catchy way to recall it!
Applications of Buoyant Unit Weight
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Beyond definition, let’s talk about the real-world applications of buoyant unit weight. Why might engineers need this information?

Maybe for designing foundations?

Exactly! Knowing buoyant unit weight helps in evaluating how deep foundations must go and how they will behave when water levels rise.

What about retaining walls?

Great point! Retaining walls also need calculations of buoyancy forces to ensure they resist not only soil load but also water pressure.

Remember, 'An Engineer's See Buoyancy Impacts!' helps highlight how the right knowledge impacts designs.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The discussion on buoyant unit weight covers its definition as the effective mass per unit volume of soil when submerged. It is contextualized alongside volume and weight relations crucial for understanding soil behavior in various environments.
Detailed
Buoyant Unit Weight
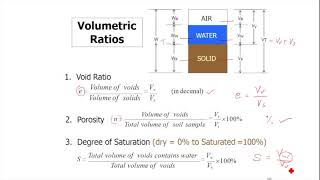
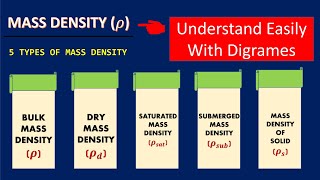
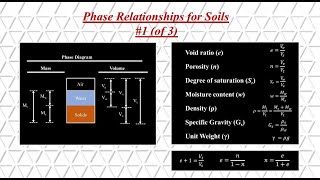
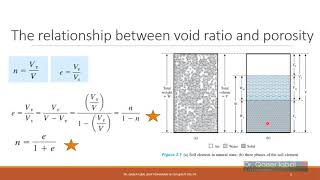
In soil mechanics, the concept of buoyant unit weight refers to the effective mass per unit volume of soil when submerged in water or under groundwater conditions. This section lays the groundwork for understanding various volume and weight relations critical to soil mechanics. It highlights the void ratio, porosity, degree of saturation, air content, and the relationship between these parameters with buoyant weight. It emphasizes that the buoyant unit weight is essential for applications such as foundation design and understanding soil behavior under saturated conditions.
Youtube Videos

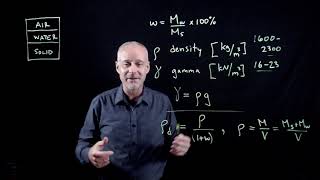



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Buoyant Unit Weight
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Buoyant unit weight or submerged unit weight is the effective mass per unit volume when the soil is submerged below standing water or below the ground water table.
Detailed Explanation
Buoyant unit weight refers to the weight of a material when it is under water or in a saturated condition. When soil is submerged, the weight that we measure is not the full weight due to the buoyancy effect of water. This allows us to find out how much 'lighter' the soil becomes when it is underwater. Essentially, it's the weight of the solid particles minus the weight of the water they displace.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a beach ball that you push underwater. It feels lighter because the water provides an upward force that counters the weight of the ball. Similarly, when soil is underwater, the weight measured includes this upward force, making the soil's buoyant unit weight lower than its dry weight.
Importance of Buoyant Unit Weight
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Understanding buoyant unit weight is crucial for various engineering applications, especially those involving foundations, earth dams, and pipelines.
Detailed Explanation
Buoyant unit weight plays a significant role in civil engineering projects. For instance, when constructing foundations, knowing how much weight the soil can effectively support when saturated informs decisions about design and safety. Similarly, for earth dam constructions and pipelines submerged in water, understanding how the weight is affected by buoyancy is necessary to avoid failures or accidents.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a bridge that needs to be built over a river. Engineers must account for how much weight the sediment under the river can support when it gets saturated. If they ignore buoyant unit weight, they risk building a bridge that could sink or collapse due to the soil’s actual carrying capacity when it's wet.
Key Concepts
-
Buoyant Unit Weight: Effective mass per unit volume of soil when submerged.
-
Density: Mass per volume, crucial in defining unit weight.
-
Unit Weight: Specific weight designated to materials based on gravity.
-
Degree of Saturation: Indicates how much of soil's void space is filled with water.
Examples & Applications
Example 1: A soil sample weighing 1200 kg/m³ submerged in water would have a buoyant unit weight calculated by subtracting the unit weight of water (approximately 9.8 kN/m³).
Example 2: A fully saturated soil would exhibit a buoyant unit weight closer to the unit weight of the dry soil.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When soil's in a flood, its weight goes to thud!
Stories
Imagine a castle built on sandy shores; when waves rise, buoyancy opens doors for balance.
Memory Tools
Remember 'Swim Soils'. S for Saturation, W for Weight, and S for Soils, emphasizing the interrelation.
Acronyms
B.U.W
Buoyant Unit Weight.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Buoyant Unit Weight
The effective mass per unit volume of soil when submerged in water.
- Density
Mass per unit volume of a material.
- Unit Weight
The weight of a unit volume of a material.
- Degree of Saturation
The ratio of water volume to soil voids, expressed as a percentage.
- Void Ratio
The ratio of the volume of voids to the volume of soil solids.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
