Common temperature scales
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Temperature Scales
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're starting with an essential concept—temperature. Does anyone know how we define temperature?

Isn't it related to how hot or cold something is?

Great observation! Temperature actually measures the average kinetic energy of particles. Now, what units do we use to measure temperature?

I think Celsius and Fahrenheit!

Exactly! Celsius and Fahrenheit are two of the main scales we use. What about the Kelvin scale?

Isn't Kelvin used more in science?

Yes! Kelvin is the SI unit and is primarily used in scientific contexts. Remember, Kelvin starts at absolute zero. That makes it essential for scientific calculations.

How do we convert between these scales?

Good question! We have established formulas for conversions. For instance, Celsius to Fahrenheit is F = (9/5)C + 32. Can anyone remember the Celsius to Kelvin conversion?

K = C + 273, right?

Correct! Let's summarize: Temperature measures kinetic energy, and three major scales are Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin, with specific conversion formulas between them.
Applications of Temperature Scales
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we know about the common temperature scales, let's discuss where we encounter these in our daily lives. Can someone give me an example?

I see the Celsius scale used in weather reports!

Absolutely! And in the U.S., how often do we use Fahrenheit?

All the time, especially for temperature settings in thermometers!

Yes! Furthermore, scientists often prefer Kelvin for absolute temperatures. Can you think of why?

Because it starts at absolute zero, no negative temperatures?

Exactly! This absolute baseline is vital in many scientific calculations. Let’s wrap up this session by stating the importance of accurate temperature measurements in science and daily applications.
Conversion Practice
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's apply what we've learned about temperature conversions. If the temperature is 25°C, how would we convert it to Fahrenheit?

I’d use the formula F = (9/5)C + 32. So, F = (9/5 * 25) + 32.

Correct! Can you calculate that for us?

That would be F = 45 + 32, which equals 77°F.

Well done! Now, what if we started with 0°F, how would we find Celsius?

I think we rearrange the formula: C = (F - 32) * 5/9.

Great! Now calculate it.

That gives me C = (0 - 32) * 5/9, which approximates to -17.8°C.

Excellent! Let’s summarize: conversion formulas are crucial in both scientific and everyday contexts.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
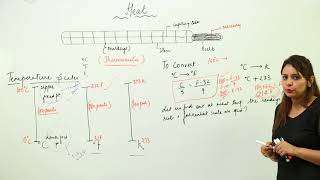
The section delves into the definition of temperature and how it relates to kinetic energy, presenting three common temperature scales—Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin. It provides formulas for converting between these scales and highlights their relevance in scientific and everyday contexts.
Detailed
Common Temperature Scales
In this section, we explore the concept of temperature, defining it as a measurement of the average kinetic energy of particles within a substance. The SI Unit of Temperature is the Kelvin (K), but we commonly encounter Celsius (°C) and Fahrenheit (°F) in various contexts.
Common Temperature Scales:
- Celsius (°C): Widely used around the world, especially in scientific contexts.
- Fahrenheit (°F): Predominantly utilized in the United States.
- Kelvin (K): Essential for scientific measurements and experiments.
Conversions:
- Celsius to Fahrenheit: F = (9/5)C + 32
- Celsius to Kelvin: K = C + 273
Understanding these scales is crucial for interpreting temperature-related data correctly and for applications across scientific fields.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Common Temperature Scales
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Common temperature scales:
○ Celsius (°C): The most common scale.
○ Fahrenheit (°F): Primarily used in the United States.
○ Kelvin (K): Used in scientific experiments.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk introduces three main temperature scales: Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin. Celsius is the most widely used scale globally, where water freezes at 0°C and boils at 100°C. Fahrenheit is mainly utilized in the United States; in this scale, water freezes at 32°F and boils at 212°F. Kelvin is the scale used in the scientific community and does not use negative numbers; absolute zero is 0 K, which is equivalent to -273.15°C.
Examples & Analogies
Think of temperature scales like different languages for expressing the same concept of heat. Just like how ‘hello’ might be ‘hola’ in Spanish, temperature can be communicated in several ways, making understanding dependent on the context and location.
Celsius Scale
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
○ Celsius (°C): The most common scale.
Detailed Explanation
The Celsius scale is the temperature scale commonly used around the world for everyday measurements. It is based on the freezing point (0°C) and boiling point (100°C) of water at standard atmospheric pressure. It provides a straightforward framework for understanding temperature changes relative to these common reference points.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a recipe that calls for cooking something at 180°C. This temperature tells you exactly how the dish will turn out, similar to how a specific score in a game gives you a clear idea of performance.
Fahrenheit Scale
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
○ Fahrenheit (°F): Primarily used in the United States.
Detailed Explanation
The Fahrenheit scale is mainly used in the USA, where temperatures are recorded in degrees Fahrenheit. In this scale, water freezes at 32°F and boils at 212°F. It uses a different numerical system compared to Celsius and can lead to confusion when converting temperatures, especially for those accustomed to Celsius.
Examples & Analogies
Think of Fahrenheit as a unique dialect. Just like some phrases can be misunderstood when translated from one dialect to another, temperature readings in Fahrenheit can be confusing for those accustomed to Celsius. For instance, a hot day at 90°F might seem different without knowing the freezing point of water isn't part of its scale.
Kelvin Scale
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
○ Kelvin (K): Used in scientific experiments.
Detailed Explanation
The Kelvin scale is the standard unit of temperature used in scientific experiments. It starts at absolute zero, which is 0 K, the point where molecular movement stops. This scale is essential for scientists because it provides a direct reference that helps avoid negative temperatures, maintaining a clear understanding of thermal energy.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine Kelvin as a way to measure temperature in a 'scientific universe' where every number represents a state of energy. For example, 300 K is a comfortable room temperature that scientists can easily relate back to energy levels in their experiments, just like how the speed of light is a universal constant in physics.
Conversion Between Temperature Scales
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Conversion between temperature scales:
● Celsius to Fahrenheit: F = (9/5)C + 32
● Celsius to Kelvin: K = C + 273
Detailed Explanation
This chunk discusses the formulas for converting between different temperature scales. To convert Celsius to Fahrenheit, you multiply the Celsius temperature by 9/5 and then add 32. To switch Celsius to Kelvin, simply add 273 to the Celsius temperature. These conversions are critical for understanding temperature in various contexts or when using different scales.
Examples & Analogies
Think of conversion like translating a book into different languages. To ensure that every reader understands the story, we need to convert (translate) the words into their familiar language. Similarly, we convert temperatures to allow everyone, regardless of the system they’re used to, to understand the same thermal conditions.
Key Concepts
-
Temperature: A measure of the average kinetic energy of particles in a substance.
-
Celsius: A common temperature scale, starting at 0°C for freezing water.
-
Fahrenheit: A scale mainly used in the United States, beginning at 32°F for the freezing point of water.
-
Kelvin: The absolute temperature scale used in science, starting at absolute zero.
Examples & Applications
The boiling point of water is 100°C, which equals 212°F and 373.15 K.
Body temperature is generally around 37°C, approximately 98.6°F or 310.15 K.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When the Celsius hits a hundred, boiling water's what you'll get, Fahrenheit will show the same, it's two hundred twelve, you bet!
Stories
Once there was a scientist who decided to make a sustainable soup using temperature. At 0°C and 32°F, water boiled just right for great flavor at 100°C or 212°F!
Memory Tools
To remember the Kelvin conversion: 'Konnor's Celsius Conversion: Add269.' Konnor= K (Kelvin), Celsius= C.
Acronyms
Use the acronym C.F.K to remember Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Celsius (°C)
A temperature scale used globally, primarily in most scientific applications.
- Fahrenheit (°F)
A temperature scale commonly used in the United States for everyday temperature measurement.
- Kelvin (K)
The SI unit of temperature, used primarily in scientific measurements.
- Conversion
The process of changing temperature values from one scale to another.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
