Second Law of Thermodynamics
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to the Second Law
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we will discuss the Second Law of Thermodynamics, which states that heat energy flows naturally from a hotter body to a cooler one. Can someone tell me what that means in practical terms?

It means that if I put ice in warm water, the heat flows from the water to the ice until they reach the same temperature.

So, heat doesn't flow from the ice to the water, right?

Exactly! This natural direction of heat flow helps us understand why certain processes occur and introduces us to entropy. Remember the acronym **DHE** for Direction of Heat Energy, which is critical in this law.
Understanding Entropy
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's talk about entropy. Can anyone define it?

Is it like a measure of disorder?

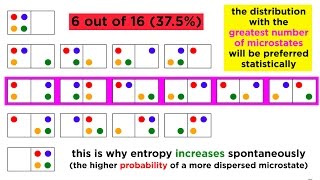
Correct! Entropy is indeed a measure of disorder. Systems naturally progress towards higher entropy states. Can anyone think of an example?

When I mix cream into coffee, the mixture becomes more disordered.

Great example! We can use the mnemonic **SOD**, which stands for 'System Order Decrease,' to remember that entropy measures how order decreases. Does everyone understand how entropy relates to the second law?
Examples and Applications
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s apply what we’ve learned. How does the Second Law affect the efficiency of heat engines?

The efficiency is limited because some heat is always lost to lower temperatures.

So not all energy can be converted into work?

Exactly! That’s why heat engines can’t be 100% efficient. Remember the phrase **Heat Loss Limits Power** as a key takeaway. How does this affect real-world applications?

It means we have to find ways to maximize efficiency to save energy.
Reviewing Key Concepts
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Before we end, let’s summarize. What are the main points we've discussed regarding the Second Law of Thermodynamics?

Heat flows from hot to cold.

Entropy measures disorder and tends to increase.

Efficiency of heat engines is limited due to this law.

Excellent summary! Make sure to remember the implications of these concepts. They are foundational for understanding thermodynamics.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section delves into the Second Law of Thermodynamics, explaining that it dictates the direction of heat transfer between systems and introduces the concept of entropy as a measure of disorder. Understanding this law is crucial for grasping fundamental thermodynamic processes and the efficiency of heat engines.
Detailed
Second Law of Thermodynamics
The Second Law of Thermodynamics states that heat energy naturally flows from a body at a higher temperature to one at a lower temperature. This principle underpins many natural processes and is critical in various applications, including heat engines, refrigerators, and understanding entropy.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of the Second Law
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Second Law of Thermodynamics: Heat energy flows naturally from a body at a higher temperature to one at a lower temperature.
Detailed Explanation
The Second Law of Thermodynamics states that heat naturally moves from hot objects to cold ones, meaning that if you have a hot cup of coffee in a cold room, the heat from the coffee will flow into the cooler air until they reach a balance in temperature. This natural direction of heat flow is essential in understanding thermal processes in nature.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like a crowded room. If you have a group of people clustered together (hot object), and someone tries to spread out to the edges of the room (cold object), they will naturally begin to move toward the exits until everyone finds a comfortable distance from one another.
Concept of Entropy
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
○ This law also introduces the concept of entropy (a measure of disorder).
Detailed Explanation
Entropy is a measure of the disorder or randomness in a system. In simple terms, as energy is transferred or transformed, the overall disorder in a closed system tends to increase. This means that energy becomes less useful over time because it spreads out and becomes more random rather than being concentrated. The Second Law suggests that natural processes tend to move toward a state of higher entropy.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you have a box of colored marbles that are neatly sorted. If you shake the box, the marbles will become mixed up, representing a move towards a higher state of disorder. Just like in nature, where systems tend to move toward more disordered states, the effort to keep things organized (low entropy) requires energy.
Key Concepts
-
Second Law of Thermodynamics: Describes the natural direction of heat flow from hot to cold.
-
Entropy: Indicates the level of disorder in a system, tends to increase over time.
Examples & Applications
Ice melting in warm water demonstrates heat flow from hot to cold.
Mixing of cream into coffee exemplifies the increase in entropy.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Heat flows down, never up, that's how we warm and cool, that's the Thermodynamics rule!
Stories
Imagine a party where everyone starts organized, but as the night goes on, people mix and mingle, making things chaotic - that's how entropy increases!
Memory Tools
DHE = Direction of Heat Energy.
Acronyms
SOD = System Order Decrease.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Entropy
A measure of disorder or randomness in a system, associated with the distribution of energy.
- Heat Engine
A device that converts heat energy into mechanical work.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
