Conclusion
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Overview of Developmental Biology
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll recap key concepts from developmental biology, focusing on how organisms grow and develop.

Can you remind us why developmental biology is important?

Absolutely! Developmental biology helps us understand congenital diseases and advancements in regenerative medicine. Remember, growth and differentiation are at its core. Think of it as G.D. – for Growth and Differentiation.

What are the key processes involved?

Great question! Key processes include cell division, differentiation, morphogenesis, and growth. Each plays a crucial role in how cells become specialized.

How do these processes link to biotechnology?

By understanding these processes, scientists can develop better therapies, especially regenerative medicine that utilizes stem cells.

So, all this knowledge is applied to create innovations in healthcare?

Exactly! That's the essence of the link between developmental biology and biotechnology.

In summary, developmental biology not only provides foundational insights but also empowers medical advancements.
Overview of Immunology
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's shift our focus to immunology. What role does it play in maintaining health?

It helps protect us from diseases, right?

Exactly! The immune system is like our body's defense army. It recognizes and eliminates pathogens, such as viruses and bacteria.

What happens if the immune system doesn't work properly?

Good point! If it fails, we can develop autoimmune disorders or immunodeficiencies. Consider this: I.M.P. – Immunity Maintains Protection.

How do immunology and developmental biology intersect?

Both fields contribute to biotechnology advancements, especially for therapies using immune responses for disease treatment.

So, understanding both fields can lead to innovative health solutions?

Exactly! Their synergy opens the door for impactful treatment strategies.

In closing, the interplay of developmental biology and immunology is crucial for modern healthcare advancements.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The conclusion emphasizes the interconnectedness of developmental biology and immunology, detailing how insights from these fields advance therapeutic methods like regenerative medicine and immune-based treatments.
Detailed
Conclusion
This section synthesizes the overarching themes from the chapter on Developmental Biology and Immunology. Developmental biology investigates critical processes of growth, differentiation, and morphogenesis that occur in organisms, outlining the essential mechanisms by which cells, tissues, and organs form. Concurrently, immunology delves into how the immune system effectively protects the body against diseases, showcasing various components and responses critical for immune defense.
Both fields play a pivotal role not only in enhancing our understanding of biological systems but also in advancing technologies in biotechnology. This knowledge is crucial for pushing boundaries in therapeutic techniques, including regenerative medicine, stem cell therapies, and immune-based treatments. Such advancements have far-reaching implications for treating congenital diseases and improving healthcare outcomes.
Youtube Videos




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Summary of Key Points in Developmental Biology
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
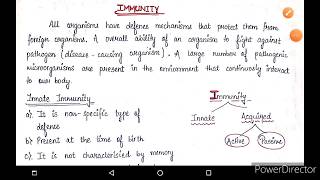
Developmental biology explores the processes of growth, differentiation, and morphogenesis in organisms.
Detailed Explanation
Developmental biology is a field that studies how living organisms grow and develop from a single cell into complex structures. Key processes include growth, which is how organisms increase in size, differentiation, which is how cells become specialized (for example, muscle cells versus nerve cells), and morphogenesis, which explains how an organism takes shape and forms its structure, like how limbs are formed on animals.
Examples & Analogies
Think of developmental biology like a recipe for baking a cake. The ingredients (cells) need to grow (rise) and be mixed in a specific way (differentiation) to create the final product (the cake) with the right shape and structure.
Summary of Key Points in Immunology
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
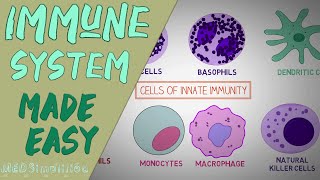
Immunology studies the mechanisms by which the immune system protects the body from diseases.
Detailed Explanation
Immunology is the study of the immune system, which is the body's defense against infections and diseases. This field looks at how the immune system recognizes and neutralizes pathogens such as bacteria and viruses, and how it distinguishes these harmful invaders from the body's own cells. Understanding immunology is crucial for developing vaccines and treatments for various diseases.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the immune system as the security team of a building. It constantly monitors for intruders (pathogens) and has training to recognize who belongs inside (the body’s cells) and who doesn’t. When an intruder is found, the security team acts swiftly to remove the threat.
The Importance of Developmental Biology and Immunology in Biotechnology
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Knowledge in these fields is essential for advancing therapeutic techniques, including regenerative medicine, stem cell therapy, and immune-based treatments.
Detailed Explanation
Both developmental biology and immunology provide critical knowledge that leads to advances in biotechnology. For instance, regenerative medicine uses insights from developmental biology to create therapies that help repair or replace damaged tissues and organs. Similarly, understanding immunology helps in developing treatments that can harness the immune system to fight diseases, such as cancer. These advances are critical for creating new medical therapies.
Examples & Analogies
Think of biotechnology as a toolbox for health. Developmental biology gives us the tools to repair and rebuild (like using a hammer and nails), while immunology provides ways to defend and protect (like a shield). Together, they enhance our ability to tackle health challenges effectively.
Key Concepts
-
Developmental Biology: The exploration of organism growth, differentiation, and morphogenesis.
-
Immunology: Understanding the immune system's role in protecting against pathogens.
-
Congenital Diseases: The implications of developmental biology in healthcare outcomes.
-
Therapeutic Techniques: The application of developmental biology and immunology for medicinal advancements.
Examples & Applications
Example of Developmental Biology: Studying how a zygote develops into a fully formed organism through various stages.
Example of Immunology: Understanding how vaccines work by training the immune system to recognize and combat specific pathogens.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In growth we trace, the cells embrace, the paths of life we all must face.
Stories
Once upon a time, there was a tiny zygote that grew into a fabulous creature through the power of development, overcoming every challenge thanks to the immune system's knights.
Memory Tools
G.D. for Growth and Differentiation - Remember the core of developmental biology!
Acronyms
I.M.P. for Immunity Maintains Protection - A reminder of how the immune system works.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Developmental Biology
The study of the processes by which organisms grow, develop, and mature.
- Immunology
The study of the immune system and its responses to pathogens.
- Congenital diseases
Disorders present at birth, often due to genetic or environmental factors.
- Regenerative Medicine
A branch of medicine that aims to repair or replace damaged cells, tissues, or organs.
- Therapeutic Techniques
Methods used to treat diseases and improve health outcomes.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
