Innate Immunity
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Innate Immunity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll explore innate immunity. Can anyone tell me what innate immunity refers to?

Is it the body's first line of defense against pathogens?

Exactly! Innate immunity is the immediate, non-specific response our body utilizes to protect itself from infections. It includes physical barriers like our skin.

What types of cells are involved in innate immunity?

Good question! Key players include phagocytes, such as macrophages and neutrophils, as well as natural killer cells. Can someone explain how phagocytes work?

Phagocytes engulf and digest pathogens, right?

That's correct! They literally eat up the pathogens to keep us safe! Remember, innate immunity acts quickly and without prior exposure, making it a crucial first response.
Physical Barriers in Innate Immunity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's delve deeper into the physical barriers of innate immunity. What do you think are examples of these barriers?

I think skin is a primary barrier!

Yes, the skin is vital! It acts as a protective shield against pathogens. What about other barriers?

Mucosal membranes?

Exactly! Mucosal membranes in places like the respiratory and digestive tracts trap pathogens and can flush them out. So, what role do these barriers play in our immune system?

They prevent pathogens from entering our body!

Absolutely! Hence, maintaining the integrity of these barriers is crucial for our health.
Role of Natural Killer Cells
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Natural killer (NK) cells are vital components of innate immunity. Can someone explain what they do?

Don't they target and destroy infected or cancerous cells?

Correct! NK cells do just that. They recognize abnormal cells without prior exposure. How do you think they accomplish this?

Do they use some kind of receptor?

Exactly! They use activating and inhibitory receptors to identify stressed or infected cells. This capacity is vital in controlling infections and preventing cancer spread.

So, they’re like our body's patrol officers!

Great analogy! They patrol and initiate responses without needing prior exposure, adding another layer of defense effectively.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The innate immune system is the body's natural defense mechanism that provides immediate response to invaders through physical barriers, phagocytic cells, and natural killer cells. It operates non-specifically and is crucial for initial protection against pathogens.
Detailed
Innate Immunity
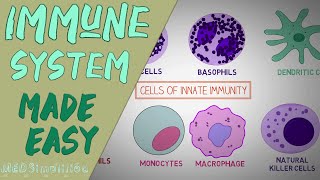
Innate immunity represents the body’s primary, non-specific defense mechanism against pathogens. This system is always present and ready to respond, providing immediate protection against infections. The components of innate immunity include physical barriers such as the skin and mucosal membranes, as well as various cells like phagocytes (including macrophages and neutrophils) and natural killer (NK) cells.
Key Features of Innate Immunity:
- Immediate Response: Unlike adaptive immunity, which takes time to develop, innate immunity responds instantly to harmful invaders.
- Non-Specific: It targets all pathogens indiscriminately rather than specific antigens or pathogens.
- Physical Barriers: The skin serves as a physical barrier, while mucosal membranes trap pathogens to prevent them from entering the body.
- Phagocytic Cells: Cells such as macrophages and neutrophils engulf and digest pathogens and debris.
- Natural Killer (NK) Cells: These cells identify and destroy infected or cancerous cells without prior exposure to them.
Understanding innate immunity is crucial as it not only prevents infections but also sets the stage for the adaptive immune system to take over once a specific pathogen is identified.
Youtube Videos




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Innate Immunity
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The natural defense mechanisms that provide immediate protection against pathogens. It is non-specific and involves barriers, phagocytic cells, and natural killer (NK) cells.
Detailed Explanation
Innate immunity is the body's first line of defense against pathogens, which includes bacteria, viruses, and fungi. This type of immunity is not specific to any particular pathogen; rather, it provides broad-spectrum protection right after an encounter with a virus or bacterium. The innate immune system comprises physical barriers like skin and mucosal membranes that prevent pathogens from entering the body. If these barriers are breached, various immune cells such as phagocytes (including macrophages and neutrophils) respond by engulfing and destroying the invading pathogens. Additionally, natural killer (NK) cells play a crucial role in identifying and killing infected cells, thus preventing the spread of infections.
Examples & Analogies
Think of innate immunity like the security guards at a building. Their role is to monitor everyone who tries to enter and to stop any intruder immediately. Just like these guards don't need to know every detail about a specific intruder but react quickly to any unauthorized person trying to break in, the innate immune system doesn’t need to recognize specific pathogens before it acts.
Components of Innate Immunity
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
It is non-specific and involves barriers, phagocytic cells, and natural killer (NK) cells.
Detailed Explanation
The innate immune system includes several key components: physical barriers such as the skin, which acts like a first layer of armor that protects internal organs and systems; mucosal membranes, which line various body cavities and provide additional defense against pathogens. If pathogens bypass these barriers, phagocytic cells, such as macrophages and neutrophils, come into action. They can engulf and digest microbial invaders. Additionally, natural killer (NK) cells are unique immune cells responsible for detecting and destroying infected or cancerous cells almost immediately, helping to prevent the spread of the infection.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a castle that is well-protected with thick walls and a moat. The walls represent physical barriers that keep enemies out, just like skin does for our bodies. If an enemy somehow gets past the walls, guards (phagocytes) rush in to capture and deal with the threat swiftly. If the enemy is hiding inside the castle (inside our cells), then special forces (NK cells) are called in to root out and eliminate the hidden threat.
Key Concepts
-
Innate Immunity: The body's first and immediate response to pathogens.
-
Phagocytes: Cells that engulf and absorb bacteria and other small cells or particles.
-
Natural Killer (NK) Cells: A type of white blood cell that destroys virus-infected cells and tumor cells.
-
Physical Barriers: Natural defenses such as skin and mucosal membranes that block pathogen entry.
Examples & Applications
The skin acts as a barrier that prevents bacteria and viruses from entering the body.
Phagocytes, such as macrophages, engulf pathogens like bacteria to eliminate threats.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the body, barriers stand tall, against pathogens, they block and pall.
Stories
Imagine a castle (the body) protected by walls (skin) and guards (phagocytes) that fight off invaders (pathogens) at all times.
Memory Tools
Remember 'SPIN' for innate immunity: Skin, Phagocytes, Immediate response, Non-specific.
Acronyms
PHAGOCYTIC
Protecting Health Against Germs
Offering Cellular Yields Thoroughly In Combat.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Innate Immunity
The natural defense mechanisms that provide immediate and non-specific protection against pathogens.
- Phagocytes
Cells that engulf and digest pathogens and debris.
- Natural Killer (NK) Cells
A type of lymphocyte that identifies and destroys infected or cancerous cells.
- Physical Barriers
Structural defenses like skin and mucosal membranes that prevent pathogen entry.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
